继续上一篇的介绍
1、上一篇分析到createAopProxy方法,创建Aop代理对象
protected final synchronized AopProxy createAopProxy() {
if (!this.active) {
activate();
}
return getAopProxyFactory().createAopProxy(this);
}
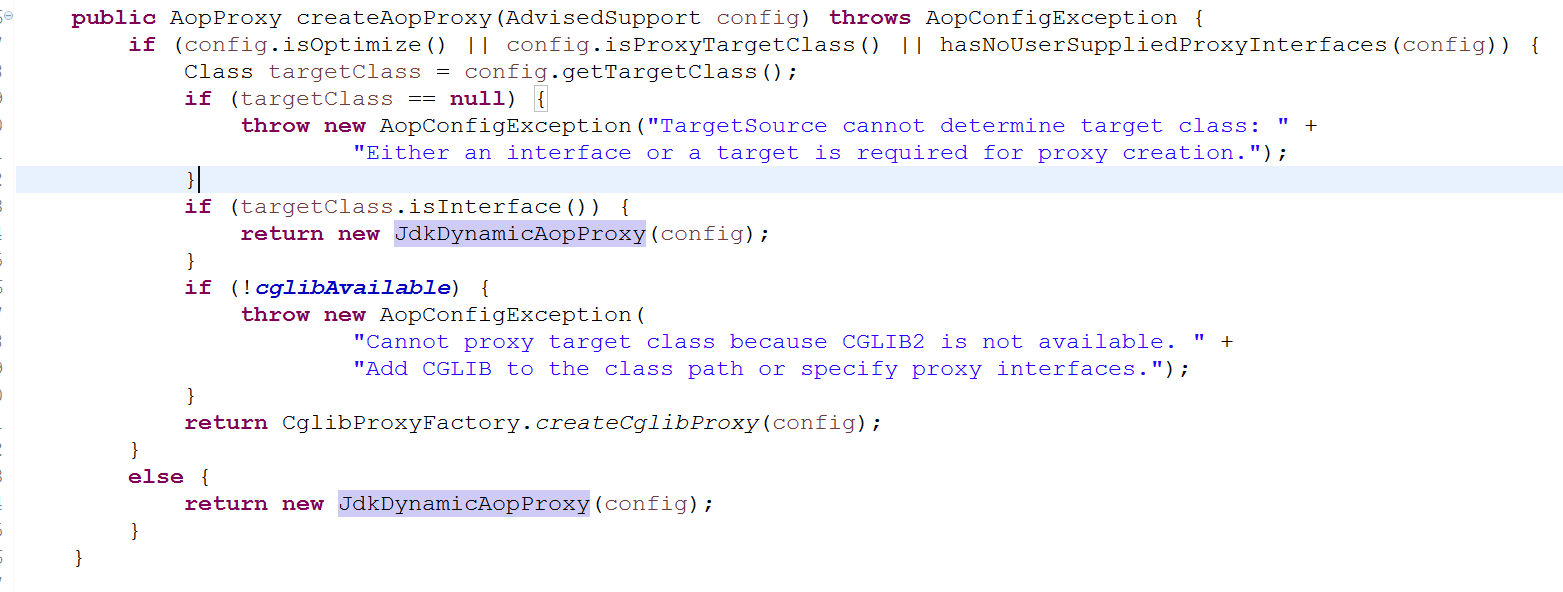
2、进入DefaultAopProxyFactory类的createAopProxy方法
3、创建代理对象后,进入getProxy方法
this.singletonInstance = getProxy(createAopProxy());
protected Object getProxy(AopProxy aopProxy) {
return aopProxy.getProxy(this.proxyClassLoader);
}
分别进入对应的JdkDynamicAopProxy与CglibAopProxy的getProxy方法
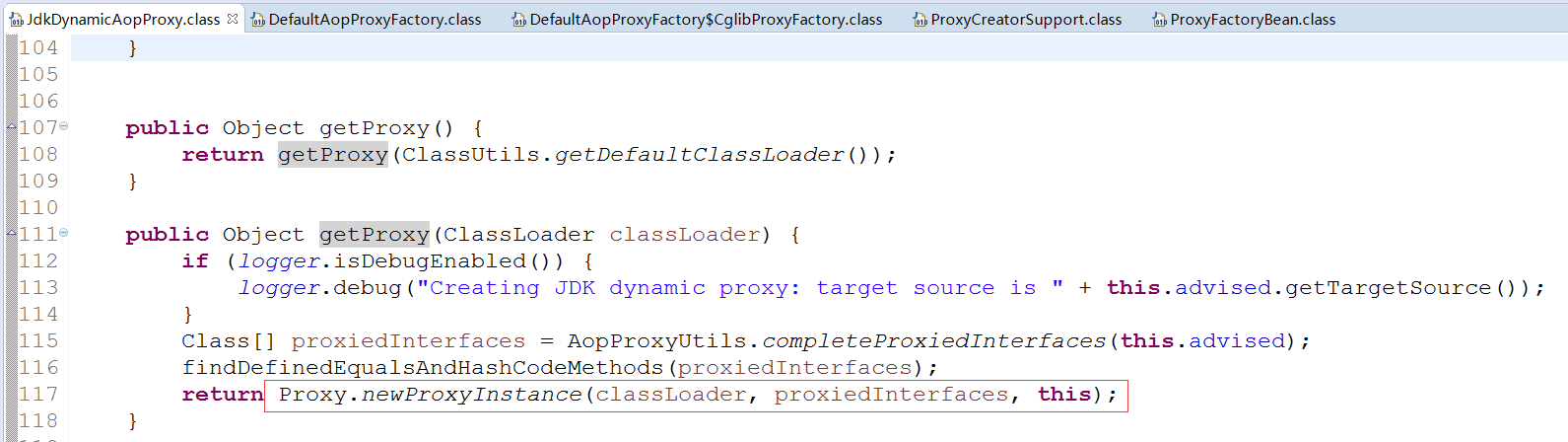
JdkDynamicAopProxy类对应的getProxy方法如下图:
JdkDynamicAopProxy中的invoke方法
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
MethodInvocation invocation;
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource;
Class targetClass = null;
Object target = null;
try {
if (!this.equalsDefined && AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) {
// The target does not implement the equals(Object) method itself.
return equals(args[0]);
}
if (!this.hashCodeDefined && AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) {
// The target does not implement the hashCode() method itself.
return hashCode();
}
if (!this.advised.opaque && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface() &&
method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) {
// Service invocations on ProxyConfig with the proxy config...
return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.advised, method, args);
}
Object retVal;
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
// Make invocation available if necessary.
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
// May be null. Get as late as possible to minimize the time we "own" the target,
// in case it comes from a pool.
target = targetSource.getTarget();
if (target != null) {
targetClass = target.getClass();
}
// Get the interception chain for this method.
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
// Check whether we have any advice. If we don't, we can fallback on direct
// reflective invocation of the target, and avoid creating a MethodInvocation.
if (chain.isEmpty()) {
// We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly
// Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor so we know it does
// nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot swapping or fancy proxying.
retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, args);
}
else {
// We need to create a method invocation...
invocation = new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain);
// Proceed to the joinpoint through the interceptor chain.
retVal = invocation.proceed();
}
// Massage return value if necessary.
if (retVal != null && retVal == target && method.getReturnType().isInstance(proxy) &&
!RawTargetAccess.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
// Special case: it returned "this" and the return type of the method
// is type-compatible. Note that we can't help if the target sets
// a reference to itself in another returned object.
retVal = proxy;
}
return retVal;
}
finally {
if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {
// Must have come from TargetSource.
targetSource.releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) {
// Restore old proxy.
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}
4、CglibAopProxy的getProxy方法
public Object getProxy(ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Creating CGLIB2 proxy: target source is " + this.advised.getTargetSource());
}
try {
Class rootClass = this.advised.getTargetClass();
Assert.state(rootClass != null, "Target class must be available for creating a CGLIB proxy");
Class proxySuperClass = rootClass;
if (ClassUtils.isCglibProxyClass(rootClass)) {
proxySuperClass = rootClass.getSuperclass();
Class[] additionalInterfaces = rootClass.getInterfaces();
for (Class additionalInterface : additionalInterfaces) {
this.advised.addInterface(additionalInterface);
}
}
// Validate the class, writing log messages as necessary.
validateClassIfNecessary(proxySuperClass);
// Configure CGLIB Enhancer...
Enhancer enhancer = createEnhancer();
if (classLoader != null) {
enhancer.setClassLoader(classLoader);
if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader &&
((SmartClassLoader) classLoader).isClassReloadable(proxySuperClass)) {
enhancer.setUseCache(false);
}
}
enhancer.setSuperclass(proxySuperClass);
enhancer.setStrategy(new UndeclaredThrowableStrategy(UndeclaredThrowableException.class));
enhancer.setInterfaces(AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised));
enhancer.setInterceptDuringConstruction(false);
Callback[] callbacks = getCallbacks(rootClass);
enhancer.setCallbacks(callbacks);
enhancer.setCallbackFilter(new ProxyCallbackFilter(
this.advised.getConfigurationOnlyCopy(), this.fixedInterceptorMap, this.fixedInterceptorOffset));
Class[] types = new Class[callbacks.length];
for (int x = 0; x < types.length; x++) {
types[x] = callbacks[x].getClass();
}
enhancer.setCallbackTypes(types);
// Generate the proxy class and create a proxy instance.
Object proxy;
if (this.constructorArgs != null) {
proxy = enhancer.create(this.constructorArgTypes, this.constructorArgs);
}
else {
proxy = enhancer.create();
}
return proxy;
}
catch (CodeGenerationException ex) {
throw new AopConfigException("Could not generate CGLIB subclass of class [" +
this.advised.getTargetClass() + "]: " +
"Common causes of this problem include using a final class or a non-visible class",
ex);
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new AopConfigException("Could not generate CGLIB subclass of class [" +
this.advised.getTargetClass() + "]: " +
"Common causes of this problem include using a final class or a non-visible class",
ex);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
// TargetSource.getTarget() failed
throw new AopConfigException("Unexpected AOP exception", ex);
}
}