一、连表操作
1)为何需要连表操作
1、把所有数据都存放于一张表的弊端 1、表的组织结构复杂不清晰 2、浪费空间 3、扩展性极差
2)表设计,分析表与表之间的关系
寻找表与表之间的关系的套路 举例:emp表 dep表 步骤一: part1: 1、先站在左表emp的角度 2、去找左表emp的多条记录能否对应右表dep的一条记录 3、翻译2的意义: 左表emp的多条记录==》多个员工 右表dep的一条记录==》一个部门 最终翻译结果:多个员工是否可以属于一个部门? 如果是则需要进行part2的流程 part2: 1、站在右表dep的角度 2、去找右表dep的多条记录能否对应左表emp的一条记录 3、翻译2的意义: 右表dep的多条记录==》多个部门 左表emp的一条记录==》一个员工 最终翻译结果:多个部门是否可以包含同一个员工 如果不可以,则可以确定emp与dep的关系只一个单向的多对一 如何实现? 在emp表中新增一个dep_id字段,该字段指向dep表的id字段
3)表之间的关系多对一
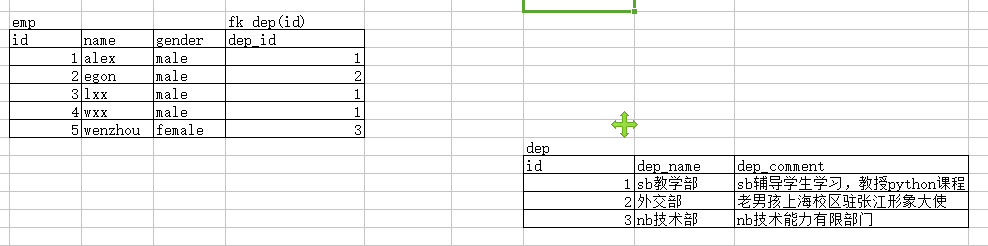
约束1:在创建表时,先建被关联的表dep,才能建关联表emp。
强调:生产环境不要加foreign key(dep_id),会强耦合在一起,以后无法扩展。应该从应用逻辑程序来限制

create table dep( id int primary key auto_increment, dep_name char(10), dep_comment char(60) ); create table emp( id int primary key auto_increment, name char(16), gender enum('male','female') not null default 'male', dep_id int, foreign key(dep_id) references dep(id) );
约束2:在插入记录时,必须先插被关联的表dep,才能插关联表emp

insert into dep(dep_name,dep_comment) values ('sb教学部','sb辅导学生学习,教授python课程'), ('外交部','老男孩上海校区驻张江形象大使'), ('nb技术部','nb技术能力有限部门'); insert into emp(name,gender,dep_id) values ('alex','male',1), ('egon','male',2), ('lxx','male',1), ('wxx','male',1), ('wenzhou','female',3);
约束3:更新与删除都需要考虑到关联与被关联的关系
解决方案: 1、先删除关联表emp,再删除被关联表dep,准备重建 mysql> drop table emp; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.11 sec) mysql> drop table dep; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec)
解决方法 :重建:新增功能,同步更新,同步删除

create table dep( id int primary key auto_increment, dep_name char(10), dep_comment char(60) ); create table emp( id int primary key auto_increment, name char(16), gender enum('male','female') not null default 'male', dep_id int, foreign key(dep_id) references dep(id) on update cascade on delete cascade ); insert into dep(dep_name,dep_comment) values ('sb教学部','sb辅导学生学习,教授python课程'), ('外交部','老男孩上海校区驻张江形象大使'), ('nb技术部','nb技术能力有限部门'); insert into emp(name,gender,dep_id) values ('alex','male',1), ('egon','male',2), ('lxx','male',1), ('wxx','male',1), ('wenzhou','female',3);
4)表与表之间多对多的关系
两张表之间是一个双向的多对一关系,称之为多对多
如何实现?
建立第三张表,该表中有一个字段fk左表的id,还有一个字段是fk右表的id
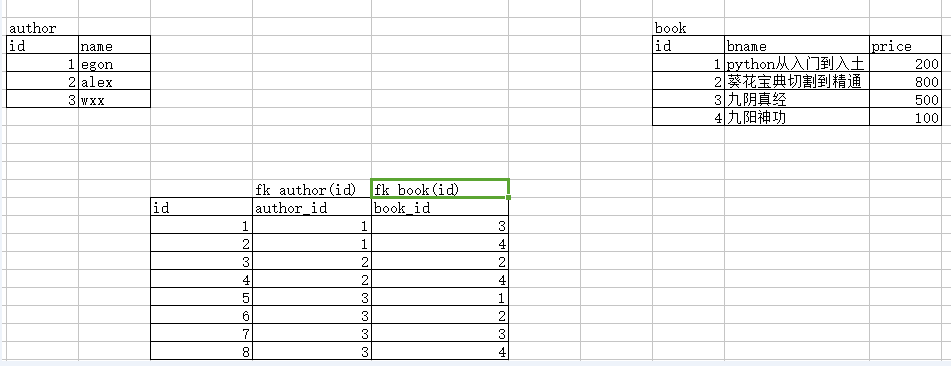
先建立2张没有关系的表

create table author( id int primary key auto_increment, name char(16) ); create table book( id int primary key auto_increment, bname char(16), price int ); insert into author(name) values ('egon'), ('alex'), ('wxx') ; insert into book(bname,price) values ('python从入门到入土',200), ('葵花宝典切割到精通',800), ('九阴真经',500), ('九阳神功',100) ;
再建立连接2张表的关系表

create table author2book( id int primary key auto_increment, author_id int, book_id int, foreign key(author_id) references author(id) on update cascade on delete cascade, foreign key(book_id) references book(id) on update cascade on delete cascade ); insert into author2book(author_id,book_id) values (1,3), (1,4), (2,2), (2,4), (3,1), (3,2), (3,3), (3,4);
没有foreign key,都是关联表,可对比查看

create table author2book( id int not null unique auto_increment, author_id int not null, book_id int not null, constraint fk_author foreign key(author_id) references author(id) on delete cascade on update cascade, constraint fk_book foreign key(book_id) references book(id) on delete cascade on update cascade, primary key(author_id,book_id) );
5)表之间的关系一对一的关系表
左表的一条记录唯一对应右表的一条记录,反之也一样


create table customer( id int primary key auto_increment, name char(20) not null, qq char(10) not null, phone char(16) not null ); create table student( id int primary key auto_increment, class_name char(20) not null, customer_id int unique, #该字段一定要是唯一的 foreign key(customer_id) references customer(id) #外键的字段一定要保证unique on delete cascade on update cascade ); insert into customer(name,qq,phone) values ('李飞机','31811231',13811341220), ('王大炮','123123123',15213146809), ('守榴弹','283818181',1867141331), ('吴坦克','283818181',1851143312), ('赢火箭','888818181',1861243314), ('战地雷','112312312',18811431230) ; #增加学生 insert into student(class_name,customer_id) values ('脱产3班',3), ('周末19期',4), ('周末19期',5) ;
二、单表操作
1)插入数据 insert

1. 插入完整数据(顺序插入) 语法一: INSERT INTO 表名(字段1,字段2,字段3…字段n) VALUES(值1,值2,值3…值n); 语法二: INSERT INTO 表名 VALUES (值1,值2,值3…值n); 2. 指定字段插入数据 语法: INSERT INTO 表名(字段1,字段2,字段3…) VALUES (值1,值2,值3…); 3. 插入多条记录 语法: INSERT INTO 表名 VALUES (值1,值2,值3…值n), (值1,值2,值3…值n), (值1,值2,值3…值n); 4. 插入查询结果 语法: INSERT INTO 表名(字段1,字段2,字段3…字段n) SELECT (字段1,字段2,字段3…字段n) FROM 表2 WHERE …;
2)更新数据 update

语法: UPDATE 表名 SET 字段1=值1, 字段2=值2, WHERE CONDITION; 示例: UPDATE mysql.user SET password=password(‘123’) where user=’root’ and host=’localhost’;
3)删除数据 delete。删除所有数据并非清空数据。truncate 清空表数据

语法: DELETE FROM 表名 WHERE CONITION; 示例: DELETE FROM mysql.user WHERE password=’’; 练习: 更新MySQL root用户密码为mysql123 删除除从本地登录的root用户以外的所有用户
三、重点。单表操作之单表查询
查询表语法结构
# distinct 去重
# 单表查询语法: select distinct 字段1,字段2,字段3,... from 表名 where 条件 group by 分组的字段 having 条件 order by 排序字段 limit 限制显示的条数
1)创建表,及先创建好环境

# 先创建表 create table employee( id int not null unique auto_increment, name varchar(20) not null, sex enum('male','female') not null default 'male', #大部分是男的 age int(3) unsigned not null default 28, hire_date date not null, post varchar(50), post_comment varchar(100), salary double(15,2), office int, #一个部门一个屋子 depart_id int ); #查看表结构 mysql> desc employee; +--------------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +--------------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment | | name | varchar(20) | NO | | NULL | | | sex | enum('male','female') | NO | | male | | | age | int(3) unsigned | NO | | 28 | | | hire_date | date | NO | | NULL | | | post | varchar(50) | YES | | NULL | | | post_comment | varchar(100) | YES | | NULL | | | salary | double(15,2) | YES | | NULL | | | office | int(11) | YES | | NULL | | | depart_id | int(11) | YES | | NULL | | +--------------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ #插入记录 #三个部门:教学,销售,运营 insert into employee(name,sex,age,hire_date,post,salary,office,depart_id) values ('egon','male',18,'20170301','老男孩驻沙河办事处外交大使',7300.33,401,1), #以下是教学部 ('alex','male',78,'20150302','teacher',1000000.31,401,1), ('wupeiqi','male',81,'20130305','teacher',8300,401,1), ('yuanhao','male',73,'20140701','teacher',3500,401,1), ('liwenzhou','male',28,'20121101','teacher',2100,401,1), ('jingliyang','female',18,'20110211','teacher',9000,401,1), ('jinxin','male',18,'19000301','teacher',30000,401,1), ('成龙','male',48,'20101111','teacher',10000,401,1), ('歪歪','female',48,'20150311','sale',3000.13,402,2),#以下是销售部门 ('丫丫','female',38,'20101101','sale',2000.35,402,2), ('丁丁','female',18,'20110312','sale',1000.37,402,2), ('星星','female',18,'20160513','sale',3000.29,402,2), ('格格','female',28,'20170127','sale',4000.33,402,2), ('张野','male',28,'20160311','operation',10000.13,403,3), #以下是运营部门 ('程咬金','male',18,'19970312','operation',20000,403,3), ('程咬银','female',18,'20130311','operation',19000,403,3), ('程咬铜','male',18,'20150411','operation',18000,403,3), ('程咬铁','female',18,'20140512','operation',17000,403,3) ; # 删除多余的字段 alter table employee drop office; alter table employee drop depart_id;
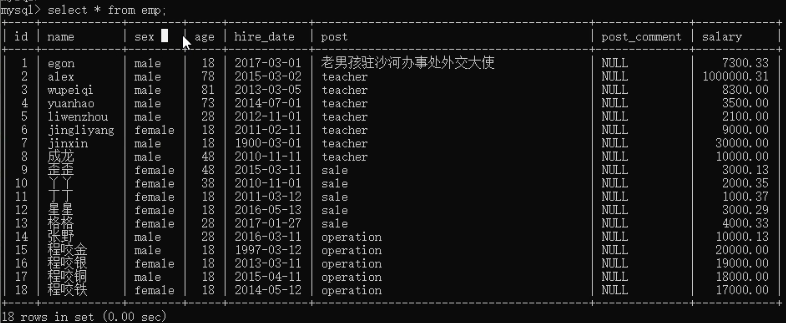
2)查看所有员工的姓名和薪资:select name,salary from employee;

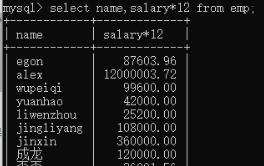
3)查询过程中的四则运算:select name,salary*12 from employee;
4)字段名起别名:select name,salary*12 annual_salary from employee;
5)查看有多少post职位。需要去重:select distinct post from employee;
6)查询显示结果 名字:egon 薪资:7300。select concat('名字: ',name,'sb'),concat('薪资: ','salary') from emp
7) 加上重命名字段:select concat('名字: ',name,'sb') as new_name,concat('薪资: ','salary') as new_sal from emp
也可实现将输入结果重定向与新表
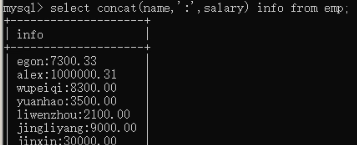
8)实现 名字:薪资。。select concat(name,':',salary) info from employee;
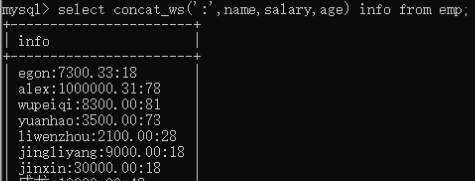
9)concat_ws,拼接多个字段,且是相同的分割符。select concat_ws(':',name,salary,age) info from employee;
10)查询语句的逻辑判断
select ( case when name = 'egon' then concat(name,'_nb') when name = 'alex' then concat(name,'_dsb') else column(name,'_sb') end ) as new_name from employee;

建议使用python来做逻辑应用判断
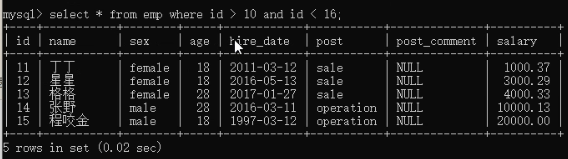
11)条件筛选 where 和 and使用。select * from employee where id > 10 and id < 16;
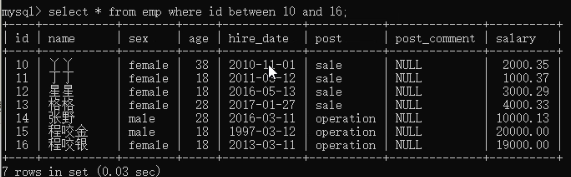
select * from employee where id between 10 and 16;
select * from employee where id = 3 or id = 5 or id =7;
上面也可以取反操作

12)like模糊匹配

12)group by 分组使用:select post,count(id) from employee group by post;
13)聚合函数。统计最高工资。select post,max(salary) from employee group by post;

select post,max(salary) from employee group by post; 最高工资 select post,min(salary) from employee group by post; 最低工资 select post,avg(salary) from employee group by post; 平均工资 select post,sum(salary) from employee group by post; 工资和
14)组和组成员:select post,group_concat(name) from employee group by post;
也可以 : select post,group_concat(name,'_SB') from employee group by post;
15)查出每个部门年龄在30岁以上的人员的平均工资
select post,avg(salary) from employee where age >= 30 group by post;
16)查出平均工资大于10000的部门
select post,avg(salary) from employee group by post having avg(salary) > 10000;

查出30岁以上员工的平均薪资在10000以上的部门
select post,avg(salary) from employe where age <= 30 group by post having avg(salary) > 10000;
17)排序,order by。 select * from employe by salary; 默认升序
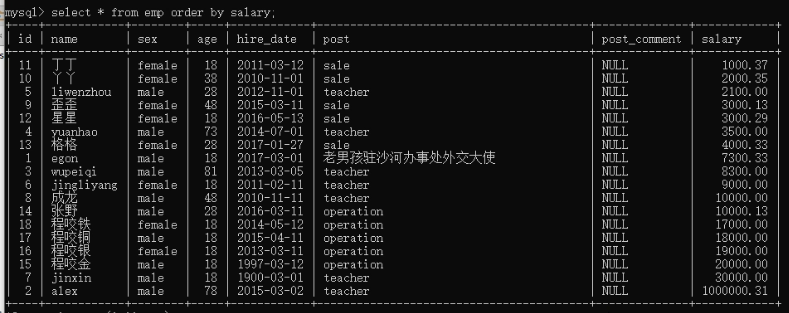
select * from employe by salary desc; 降序
select * from employe by age,asc,salary desc; 双重比较。先按照年龄升序排,再安装工资降序排
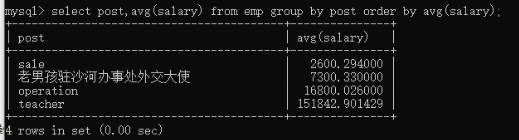
select post,avg(salary) from employee group by post order by avg(salary); 取出每个部门的平均工资进行排序
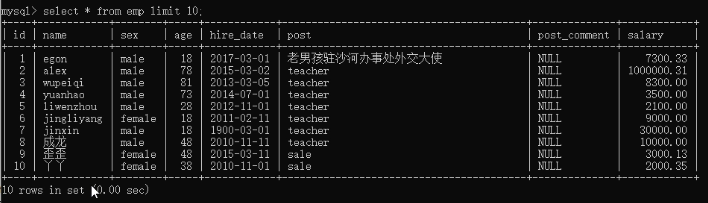
18)limit 取出前10行的信息:select * from employee limit 10;
select * from employee order by salary desc limit 1; 先安装倒序的工资排序,再取出第一个
select * from employee limit 0,5; 从0开始往后取5条
select * from employee limit 5,5; 从5开始往后取5条
select * from employee limit 10,5; 从10开始往后取5条
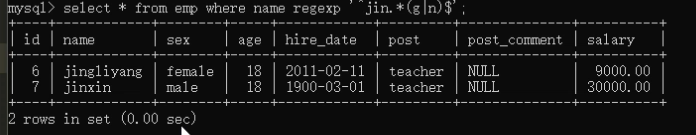
19)regexp 正则匹配 select * from employee where name regexp '^jin.*(g|n)$';
五、多表查询
1)准备工作,准备表

#建表 create table department( id int, name varchar(20) ); create table employee( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20), sex enum('male','female') not null default 'male', age int, dep_id int ); #插入数据 insert into department values (200,'技术'), (201,'人力资源'), (202,'销售'), (203,'运营'); insert into employee(name,sex,age,dep_id) values ('egon','male',18,200), ('alex','female',48,201), ('wupeiqi','male',38,201), ('yuanhao','female',28,202), ('liwenzhou','male',18,200), ('jingliyang','female',18,204) ; mysql> select * from department; +------+--------------+ | id | name | +------+--------------+ | 200 | 技术 | | 201 | 人力资源 | | 202 | 销售 | | 203 | 运营 | +------+--------------+ mysql> select * from employee; +----+------------+--------+------+--------+ | id | name | sex | age | dep_id | +----+------------+--------+------+--------+ | 1 | egon | male | 18 | 200 | | 2 | alex | female | 48 | 201 | | 3 | wupeiqi | male | 38 | 201 | | 4 | yuanhao | female | 28 | 202 | | 5 | liwenzhou | male | 18 | 200 | | 6 | jingliyang | female | 18 | 204 | +----+------------+--------+------+--------+ alter table employee rename emp; alter table department rename dmp;
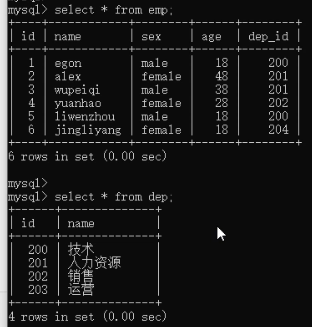
2)非专业连表查询方法where。select * from emp,dep where emp.dep_id = dep.id;
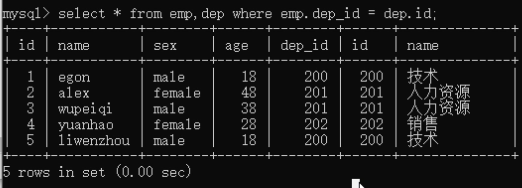
select * from emp,dep where emp.dep_id = dep.id and dep.name='技术'; # 可能出现相同的字段,所有需要指定 表名.字段
3)专业的连表查询方法,inner join 方法

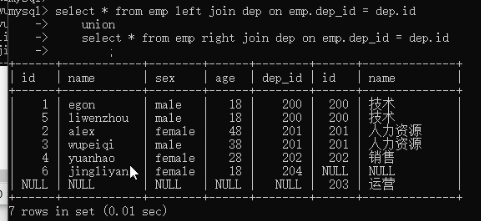
inner/left/right join:连接2张有关系的表 select * from emp inner join dep on emp.dep_id = dep.id; # 取有对应关系的部分 select * from emp inner join dep on emp.dep_id = dep.id where dep.name = '技术'; # 再取出技术部吗 select * from emp left join dep # 在jnner基础上,再保留左表部分,null填充 on emp.dep_id = dep.id; select * from emp right join dep # 在jnner基础上,再保留右表部分,null填充 on emp.dep_id = dep.id; select * from emp left join dep on emp.dep_id = dep.id union select * from emp right join dep on emp.dep_id = dep.id; # 分别优先保留2张表,再去重
4)组合条件查询。找到年龄大于25岁的员工以及员工所在的部门
select emp.name,dep.name from emp inner join dep on emp.dep_id = dep.id where age > 25;
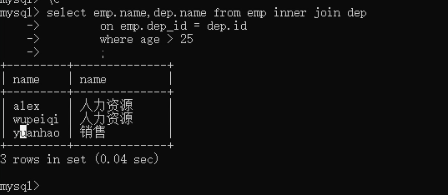
找到平均年龄>=20岁的部门
找到平均年龄>=20岁的部门 select dep.name,avg(age) from emp inner join dep on emp.dep_id = dep.id group by dep.name having avg(age) >= 20;
六、子查询。一个查询的结果,当做查询条件去使用
1)找到平均年龄>=20岁的部门
第一步:获取到部门id
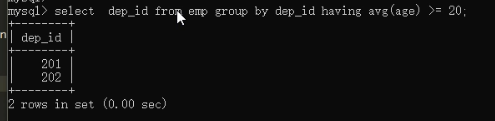
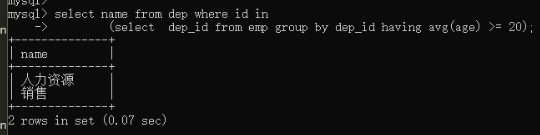
第二步:拿到查询结果做条件
select name from dep where id in (select dep_id from emp group by dep_id having avg(age) >= 20);
2)查看销售部的人员
第一步:select id from dep where name = '销售';
第二步:利用查询结果查询
where * from emp where dep_id = (select id from dep where name = '销售');

3)表自己连接自己。自己查询的结果再变成自己查询的条件
练习。原表查看内容。查询每个部门最新入职的那个员工

第一步:select post,max(hire_date) from emp group by post;
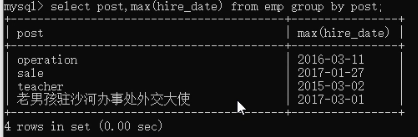
第二步:根据上面的结果,联合表操作
select t1.name,t1.hire_date,t1.post,t2.post,t2.max_date from emp as t1 inner join (select post,max(hire_date) as max_date from emp group by post) as t2; on t1.post = t2.post;

第三步:根据上面结果在进行条件查询
select t1.name,t1.hire_date,t1.post,t2.post,t2.max_date from emp as t1 inner join (select post,max(hire_date) as max_date from emp group by post) as t2; on t1.post = t2.post where t1.hire_date = t2.max_date;

