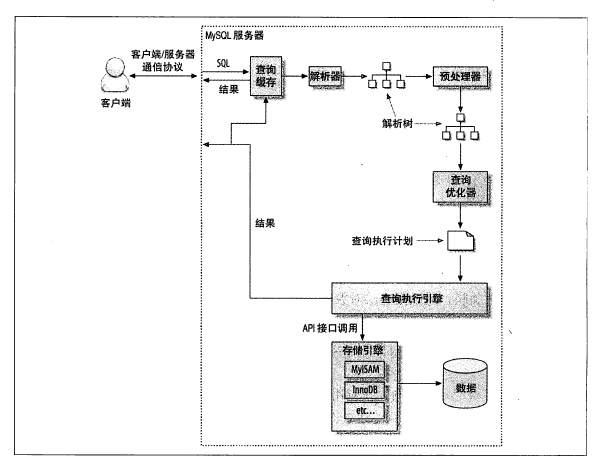
mariadb的查询流程图
select语句的从句分析顺序:from(过滤表)-->where(过滤行)-->group by(分组)-->having(分组过滤)-->order by(排序)--
>select(选取字段)-->limit(查询限制)-->最终结果
DISTINCT: 数据去重
SQL_CACHE: 显式指定存储查询结果于缓存之中
SQL_NO_CACHE: 显式查询结果不予缓存
show global variables like '%query%';
query_cache_type | ON 表示缓存开启
query_cache_size | 0 表示缓存空间大小,如果为0则不缓存
query_cache_type的值为'DEMAND'时,显式指定SQL_CACHE的SELECT语句才会缓存;其它均不予缓存
缓存并不会缓存所有查询结果,例如select now();就不会缓存
WHERE子句:指明过滤条件以实现“选择”的功能
算术操作符:+, -, *, /, %
比较操作符:=, !=, <>, <=>, >, >=, <, <=
BETWEEN min_num AND max_num
IN (element1, element2, ...)
IS NULL
IS NOT NULL
LIKE:
%: 任意长度的任意字符
_:任意单个字符
RLIKE
逻辑操作符: NOT,AND,OR
GROUP:根据指定的条件把查询结果进行“分组”以用于做“聚合”运算:avg(), max(), min(), count(), sum()
HAVING: 对分组聚合运算后的结果指定过滤条件
ORDER BY: 根据指定的字段对查询结果进行排序:升序ASC 降序:DESC
LIMIT [[offset,]row_count]:对查询的结果进行输出行数数量限制
例如:
select name,age from students where age/2=11;

select name,age from students where age+30>50;
select distinct gender from students;

select name as stuname from students;

select name,classid from students where classid is null;
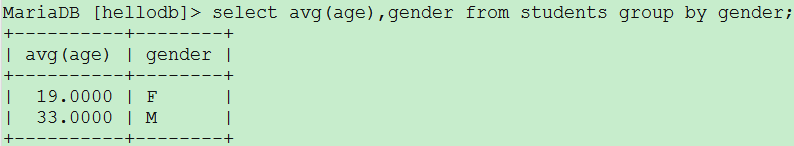
select avg(age),gender from students group by gender;
select avg(age) as ages,gender from students group by gender having ages>20;

select count(stuid) as NO,classid from students group by classid;

select count(stuid) as NO,classid from students group by classid having NO>2;
select name,age from students order by age limit 10,10; (第一个表示偏移10个,第二个表示取10个)
多表查询:
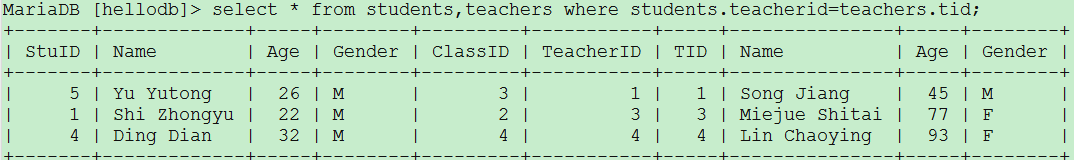
交叉连接:笛卡尔乘积(最消耗资源的一种查询) 例如:select * from students,teachers; 如果students有20行,teachers也有20行,则显示400行
内连接:
等值连接:让表之间的字段以“等值”建立连接关系;
不等值连接
自然连接
自连接
外连接:
左外连接 例如:FROM tb1 LEFT JOIN tb2 ON tb1.col=tb2.col
右外连接 例如:FROM tb1 RIGHT JOIN tb2 ON tb1.col=tb2.col
等值连接:
select s.name as studentname,t.name as teachername from students as s,teachers as t where s.teacherid=t.tid;(这个够复杂)

select s.name,c.class from students as s,classes as c where s.classid=c.classid;

左外连接:
select s.name,c.class from students as s left join classes as c on s.classid=c.classid;

以左表作为基准
select s.name,c.class from students as s right join classes as c on s.classid=c.classid;

以右表为基准
子查询:在查询语句嵌套着查询语句,基于某语句的查询结果再次进行的查询 (mariadb对子查询优化不够,建议一般情况不使用)
select name,age from students where age>(select avg(age) from students);
select name,age from students where age in (select age from teachers);
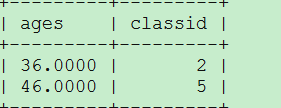
select s.ages,s.classid from (select avg(age) as ages,classid from students where classid is not null group by classid) as s where s.ages>30;
联合查询:UNION
select name,age from students union select name,age from teachers;