| 运行级就是Linux操作系统当前正在运行的功能级别。存在七个运行级别,编号从0到6。系统可以引导到任何给定的运行级别。运行级别由数字标识。 |
每个运行级别指定不同的系统配置,并允许访问不同的进程组合。默认情况下,Linux会引导至运行级别3或运行级别5。启动时一次只执行一个运行级别。它不会一个接一个地执行。
系统的默认运行级别在SysVinit系统的/etc/inittab文件中指定。
但是systemd系统不读取此文件,它使用以下文件/etc/systemd/system/default.target来获取默认的运行级别信息。
我们可以使用以下五种方法检查Linux系统当前运行级别。runlevel命令:runlevel打印系统的上一个和当前运行级别。who命令:打印有关当前登录用户的信息。它将使用“-r”选项打印运行级别信息。systemctl命令:它控制systemd系统和服务管理器。
使用/etc/inittab文件:系统的默认运行级别在SysVinit System的/etc/inittab文件中指定。
使用/etc/systemd/system/default.target文件:系统的默认运行级别在systemd System的/etc/systemd/system/default.target文件中指定。
详细的运行级别信息在下表中描述。
系统将根据运行级别执行程序/服务。
运行级别0 - /etc/rc.d/rc0.d/ 运行级别1 - /etc/rc.d/rc1.d/ 运行级别2 - /etc/rc.d/rc2.d/ 运行级别3 - /etc/rc.d/rc3.d/ 运行级别4 - /etc/rc.d/rc4.d/ 运行级别5 - /etc/rc.d/rc5.d/ 运行级别6 - /etc/rc.d/rc6.d/
runlevel1.target – /etc/systemd/system/rescue.target runlevel2.target – /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants runlevel3.target – /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants runlevel4.target – /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants runlevel5.target – /etc/systemd/system/graphical.target.wants
runlevel打印系统的上一个和当前运行级别:
[linuxidc@localhost linuxidc.com]$ runlevel
N 5
1]、N:“N”表示自系统启动后运行级别尚未更改。
2]、5:“5”表示系统的当前运行级别。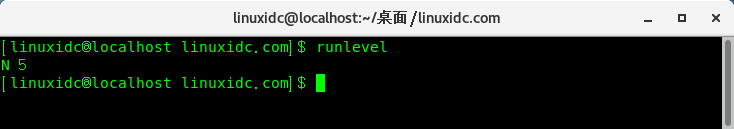
打印有关当前登录用户的信息,它将使用-r选项打印运行级别信息:
[linuxidc@localhost linuxidc.com]$ who -r
运行级别 5
systemctl命令systemctl用于控制systemd系统和服务管理器,systemd是Unix操作系统的系统和服务管理器。它可以作为sysvinit系统的直接替代品,systemd是内核启动并保持PID 1的第一个进程。systemd使用.service文件而不是bash脚本(SysVinit使用),systemd将所有守护进程排序到他们自己的Linux cgroup中,可以通过浏览/cgroup/systemd文件来查看系统层次结构:
[linuxidc@localhost linuxidc.com]$ systemctl get-default graphical.target
系统的默认运行级别在SysVinit System的/etc/inittab文件中指定,但systemd不读取文件,因此,它仅适用于SysVinit系统而不适用于systemd系统。
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/inittab # inittab is only used by upstart for the default runlevel. # ADDING OTHER CONFIGURATION HERE WILL HAVE NO EFFECT ON YOUR SYSTEM. # System initialization is started by /etc/init/rcS.conf # Individual runlevels are started by /etc/init/rc.conf # Ctrl-Alt-Delete is handled by /etc/init/control-alt-delete.conf # Terminal gettys are handled by /etc/init/tty.conf and /etc/init/serial.conf, # with configuration in /etc/sysconfig/init. # For information on how to write upstart event handlers, or how # upstart works, see init(5), init(8), and initctl(8). # Default runlevel. The runlevels used are: # 0 - halt (Do NOT set initdefault to this) # 1 - Single user mode # 2 - Multiuser, without NFS (The same as 3, if you do not have networking) # 3 - Full multiuser mode # 4 - unused # 5 - X11 # 6 - reboot (Do NOT set initdefault to this) id:5:initdefault:
[linuxidc@localhost linuxidc.com]$ vim /etc/inittab # inittab is no longer used when using systemd. # # ADDING CONFIGURATION HERE WILL HAVE NO EFFECT ON YOUR SYSTEM. # # Ctrl-Alt-Delete is handled by /usr/lib/systemd/system/ctrl-alt-del.target # # systemd uses 'targets' instead of runlevels. By default, there are two main targets: # # multi-user.target: analogous to runlevel 3 # graphical.target: analogous to runlevel 5 # # To view current default target, run: # systemctl get-default # # To set a default target, run: # systemctl set-default TARGET.target
可以看到,里面除了注释,什么也没有,并没有CentOS 6中设置默认运行级别的方式。
注释内容大意是说,
# multi-user.target类似于runlevel 3; # graphical.target类似于runlevel5
获得当前默认运行级别的方式为
systemctl get-default
设置默认运行级别的方式
systemctl set-default TARGET.target
设置运行级别命令格式:
systemctl [command] [unit.target]
需要命令 systemctl
设置默认的运行级别为 1 则命令为:systemctl set-default xxx
中对系统的级别对应是
init级别 systemctl target 0 shutdown.target 1 emergency.target 2 rescure.target 3 multi-user.target 4 无 5 graphical.target 6 无
备注:以上命令均需要超级管理员权限,如果需要临时切换 直接 init + 需要切换到的数字。
系统的默认运行级别在systemd System的/etc/systemd/system/default.target文件中指定,它不适用于SysVinit系统:
[linuxidc@localhost linuxidc.com]$ cat /etc/systemd/system/default.target