迷宫求解描述:
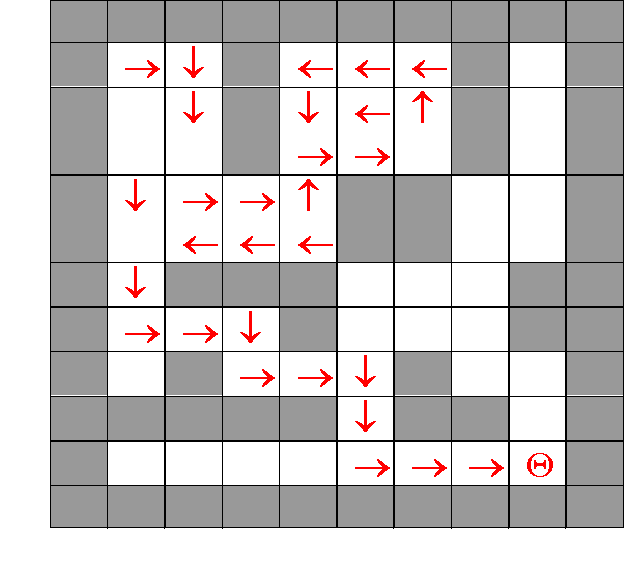
栈的方式——深度优先
算法:
- 初始化栈,出发点先入栈
- 当栈不空时,出栈顶元素,当前位置不是墙壁并且没走过,标记已走
- 把相邻的四个位置压入栈,依次等待搜索
- 不断循环2-3,如果已经到达终点,退出循环

#include "stdio.h" #define StackSize 100 typedef struct{ int i; int j; } ElemType; typedef struct { ElemType elem[StackSize]; int top; }SqStack; InitStack(SqStack *pS) { pS->top=0; /* top指向栈顶的上一个元素 */ } int Push(SqStack *pS,ElemType e) { if (pS->top==StackSize-1) /* 栈满 */ return 0; pS->elem[pS->top]=e; pS->top=pS->top+1; return 1; } int Pop(SqStack *pS,ElemType* pe) { if (pS->top==0) /* 栈空 */ return 0; pS->top = pS->top - 1; *pe = pS->elem[pS->top]; return 1; } main() { SqStack S; ElemType e; int maze[10][10]={ /* 离散迷宫矩阵,0表示墙壁,1表示可以走的道路 */ {0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0}, {0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0}, {0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0}, {0,1,1,1,1,0,0,1,1,0}, {0,1,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,0}, {0,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,1,0}, {0,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,0}, {0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,1,0}, {0,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0}, {0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0} }; int i,j,ti,tj; InitStack(&S); /* 初始化栈为空 */ e.i=1;e.j=1; /* 搜索的起点位置 */ Push(&S,e); /* 把起点位置入栈,准备搜索*/ while(Pop(&S,&e)){ /* 当栈不空,则出栈并保存到e中 */ if (maze[e.i][e.j]==1) { /* 迷宫的当前位置不是墙壁并且没走过 */ maze[e.i][e.j]=2; /* 标记已走过 */ if (e.i==8 && e.j==8) /* 如果已经到达终点,退出循环 */ break; else { /* 把相邻的四个位置压入栈,依次等待搜索,深度优先 */ ti=e.i; tj=e.j; e.i=ti-1; e.j=tj; Push(&S,e); e.i=ti+1; e.j=tj; Push(&S,e); e.i=ti; e.j=tj-1; Push(&S,e); e.i=ti; e.j=tj+1; Push(&S,e); /* 最先搜索:右边位置 */ } } } /* 打印出整个迷宫,2表示搜索过的位置。但是没有显示具体路径 */ printf(" "); for(i=0;i<10;i++) { for(j=0;j<10;j++) printf("%2d ",maze[i][j]); printf(" "); } getch(); }
另一种写法

#include "stdio.h" #define StackSize 100 typedef struct{ int i,j; }PosType; typedef struct{ PosType pos; int di; } ElemType; typedef struct { ElemType elem[StackSize]; int top; }SqStack; InitStack(SqStack *pS) { pS->top=0; /* top指向栈顶的上一个元素 */ } int Push(SqStack *pS,ElemType e) { if (pS->top==StackSize-1) /* 栈满 */ return 0; pS->elem[pS->top]=e; pS->top=pS->top+1; return 1; } int Pop(SqStack *pS,ElemType* pe) { if (pS->top==0) /* 栈空 */ return 0; pS->top = pS->top - 1; *pe = pS->elem[pS->top]; return 1; } main() { SqStack S; ElemType e; PosType pos,pos_end; int maze[10][10]={ /* 离散迷宫矩阵,0表示墙壁 */ {0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0}, {0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0}, {0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0}, {0,1,1,1,1,0,0,1,1,0}, {0,1,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,0}, {0,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,1,0}, {0,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,0}, {0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,1,0}, {0,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0}, {0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0} }; int i,j; InitStack(&S); pos_end.i=8;pos_end.j=8; pos.i=1;pos.j=1; do { if (maze[pos.i][pos.j]==1) { /* 当前位置不是墙壁并且没走过 */ maze[pos.i][pos.j]=2; /* 标记已走过 */ e.pos = pos; e.di = 1; Push(&S,e); /* 加入路径 */ if (pos.i==pos_end.i && pos.j==pos_end.j) /* 如果已经到达终点,退出循环,求得的路径放在栈中 */ break; else pos.j++; /* 下一个位置是当前位置的右邻 */ } else{ /* 当前位置不能通过 */ if(S.top>0){ Pop(&S,&e); while(e.di==4 && S.top>0){ maze[e.pos.i][e.pos.j]=-1; /* 留下不能通过的标记,并退回一步 */ Pop(&S,&e); } if (e.di<4){ e.di++; Push(&S,e); /* 换下一个方向搜索 */ pos.i=e.pos.i; pos.j=e.pos.j; if (e.di==2) pos.i++; /* 设定当前位置是该方向上的相邻块“右下左上” */ else if (e.di==3) pos.j--; else if (e.di==4) pos.i--; } } } }while(S.top>0); /* 求得的路径放在栈中 */ printf(" "); while(Pop(&S,&e)) printf(" (%d,%d)",e.pos.i,e.pos.j); /* 打印出整个迷宫,2的是所找到的路径,-1是走过的不通的路径 */ printf(" "); for(i=0;i<10;i++) { for(j=0;j<10;j++) printf("%2d ",maze[i][j]); printf(" "); } getch(); }
队列的方式——广度

#include"stdio.h" #include"stdlib.h" #define Maxsize 100 typedef struct{ int i; int j; int pre;//记录前一个结点下标 }DataType;//记录位置 typedef struct { DataType data[Maxsize]; int front,rear; }Queue; //初始化队列 void InitQueue(Queue *Q) { Q->front=Q->rear=0; } //入队 int InQueue(Queue *Q,DataType x) { if((Q->rear+1)%Maxsize==Q->front) return 0; Q->rear=(Q->rear+1)%Maxsize; //if (Q->rear+1)==Maxsize,Q->rear=0 Q->data[Q->rear]=x; return 1; } //判断空队列 int EmptyQueue(Queue *Q) { if(Q->rear==Q->front) return 1; else return 0; } //出队 int OutQueue(Queue *Q,DataType *x) { if(EmptyQueue(Q)) return 0; Q->front=(Q->front+1)%Maxsize; *x=Q->data[Q->front]; return 1; } void main() { Queue Q; DataType x; int maze[10][10]={ /* 离散迷宫矩阵,0表示墙壁,1表示可以走的道路 */ {0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0}, {0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0}, {0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0}, {0,1,1,1,1,0,0,1,1,0}, {0,1,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,0}, {0,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,1,0}, {0,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,0}, {0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,1,0}, {0,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0}, {0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0} }; InitQueue(&Q); int i,j,ti,tj; int di; x.i=1; x.j=1; //起始位置(1,1) x.pre=0; InQueue(&Q,x); while(OutQueue(&Q,&x)) { if(x.i==8&&x.j==8) break; ti=x.i; tj=x.j; for(di=0;di<4;di++) { switch(di) { case 0://上 x.i=ti-1; x.j=tj; break; case 1://下 x.i=ti+1; x.j=tj; break; case 2://左 x.i=ti; x.j=tj-1; break; case 3://右 x.i=ti; x.j=tj+1; break; } if(1==maze[x.i][x.j])//如果有路并且没有访问过 { x.pre=Q.front; x.i=x.i;x.j=x.j; InQueue(&Q,x); maze[x.i][x.j]=2; //表示已经访问过 } }//for } printf(" 搜索过后的迷宫: "); for(i=0;i<10;i++) { for(j=0;j<10;j++) printf("%2d ",maze[i][j]); printf(" "); } printf(" 所走路线为(最短路线): "); //* do { printf("(%d,%d) ",Q.data[Q.front].i,Q.data[Q.front].j); Q.front=Q.data[Q.front].pre; }while(Q.front!=0); //*/ }

递归的方式——深度优先

#include "stdio.h" int SearchFun(int maze[][10],int i, int j) { if (maze[i][j]==1) { /* 迷宫的当前位置不是墙壁并且没走过 */ maze[i][j]=2; /* 标记已走过 */ if (i==8 && j==8) /* 如果已经到达终点,返回 */ return 1; else { /* 依次搜索相邻的四个位置,深度优先 */ if (SearchFun(maze,i,j+1)) /* 最先搜索:右边位置 */ return 1; if (SearchFun(maze,i,j-1)) return 1; if (SearchFun(maze,i+1,j)) return 1; if (SearchFun(maze,i-1,j)) return 1; } } return 0; } main() { int maze[10][10]={ /* 离散迷宫矩阵,0表示墙壁,1表示可以走的道路 */ {0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0}, {0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0}, {0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0}, {0,1,1,1,1,0,0,1,1,0}, {0,1,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,0}, {0,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,1,0}, {0,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,0}, {0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,1,0}, {0,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0}, {0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0} }; int i,j; SearchFun(maze,1,1); /* 打印出整个迷宫,2表示搜索过的位置。但是没有显示具体路径 */ printf(" "); for(i=0;i<10;i++) { for(j=0;j<10;j++) printf("%2d ",maze[i][j]); printf(" "); } getch(); }
