一、概述
LinkedList和ArrayList一样,都实现了List接口,但其内部的数据结构有本质的不同。LinkedList是基于链表实现的(通过名字也能区分开来),所以它的插入和删除操作比ArrayList更加高效。但也是由于其为基于链表的,所以随机访问的效率要比ArrayList差。
看一下LinkedList的类的定义:
public class LinkedList<E> extends AbstractSequentialList<E> implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {}
LinkedList继承自AbstractSequenceList,实现了List、Deque、Cloneable、java.io.Serializable接口。AbstractSequenceList提供了List接口骨干性的实现以减少实现List接口的复杂度,Deque接口定义了双端队列的操作。
在LinkedList中除了本身自己的方法外,还提供了一些可以使其作为栈、队列或者双端队列的方法。这些方法可能彼此之间只是名字不同,以使得这些名字在特定的环境中显得更加合适。
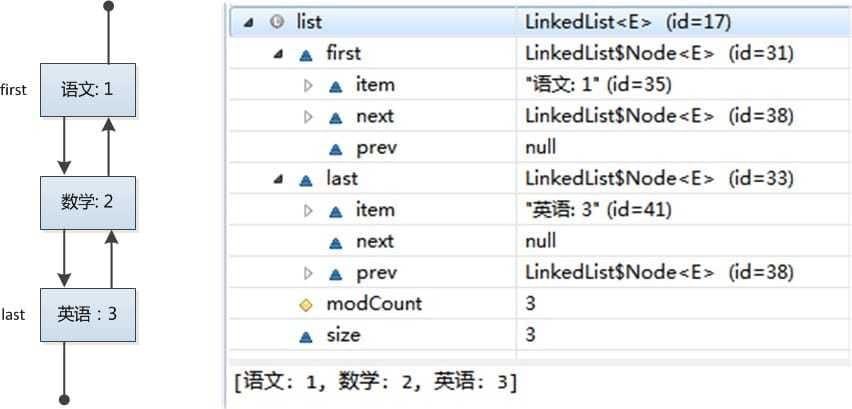
LinkedList<String> list = new LinkedList<String>(); list.add("语文: 1"); list.add("数学: 2"); list.add("英语: 3");
结构也相对简单一些,如下图所示:
二、数据结构
LinkedList是基于链表结构实现,所以在类中包含了first和last两个指针(Node)。Node中包含了上一个节点和下一个节点的引用,这样就构成了双向的链表。每个Node只能知道自己的前一个节点和后一个节点,但对于链表来说,这已经足够了。
transient int size = 0; transient Node<E> first; //链表的头指针 transient Node<E> last; //尾指针 //存储对象的结构 Node, LinkedList的内部类 private static class Node<E> { E item; Node<E> next; // 指向下一个节点 Node<E> prev; //指向上一个节点 Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) { this.item = element; this.next = next; this.prev = prev; } }
三、存储
3.1 add(E e)
该方法是在链表的end添加元素,其调用了自己的方法linkLast(E e)。
该方法首先将last的Node引用指向了一个新的Node(l),然后根据l新建了一个newNode,其中的元素就为要添加的e;而后,我们让last指向了newNode。接下来是自身进行维护该链表。
/** * Appends the specified element to the end of this list. * * <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}. * * @param e element to be appended to this list * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add}) */ public boolean add(E e) { linkLast(e); return true; } /** * Links e as last element. */ void linkLast(E e) { final Node<E> l = last; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); last = newNode; if (l == null) first = newNode; else l.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; }
3.2 add(int index, E element)
该方法是在指定index位置插入元素。如果index位置正好等于size,则调用linkLast(element)将其插入末尾;否则调用 linkBefore(element, node(index))方法进行插入。
/** * Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list. * Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and any * subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices). * * @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted * @param element element to be inserted * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public void add(int index, E element) { checkPositionIndex(index); if (index == size) linkLast(element); else linkBefore(element, node(index)); } /** * Inserts element e before non-null Node succ. */ void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) { // assert succ != null; final Node<E> pred = succ.prev; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ); succ.prev = newNode; if (pred == null) first = newNode; else pred.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; }
LinkedList的方法有很多,有机会再续。
参考与推荐: