Given a syntax tree (binary), you are supposed to output the corresponding infix expression, with parentheses reflecting the precedences of the operators.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (≤ 20) which is the total number of nodes in the syntax tree. Then N lines follow, each gives the information of a node (the i-th line corresponds to the i-th node) in the format:
data left_child right_child
where data is a string of no more than 10 characters, left_child and right_child are the indices of this node's left and right children, respectively. The nodes are indexed from 1 to N. The NULL link is represented by −. The figures 1 and 2 correspond to the samples 1 and 2, respectively.
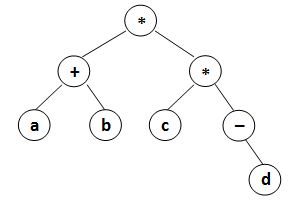 | 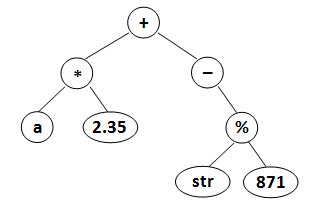 |
|---|---|
| Figure 1 | Figure 2 |
Output Specification:
For each case, print in a line the infix expression, with parentheses reflecting the precedences of the operators. Note that there must be no extra parentheses for the final expression, as is shown by the samples. There must be no space between any symbols.
Sample Input 1:
8
* 8 7
a -1 -1
* 4 1
+ 2 5
b -1 -1
d -1 -1
- -1 6
c -1 -1
Sample Output 1:
(a+b)*(c*(-d))
Sample Input 2:
8
2.35 -1 -1
* 6 1
- -1 4
% 7 8
+ 2 3
a -1 -1
str -1 -1
871 -1 -1
Sample Output 2:
(a*2.35)+(-(str%871))这题考察语法树的转换。我们已知一棵语法树,如何求中缀表达式。仅需要判断右子树存不存在(存在就可以递归),和左子树无关。
#include <iostream> #include <vector> using namespace std; int N, root; struct node { string data; int left = -1, right = -1; }*tree = NULL; vector<node> v; string dfs(int n) { if(n == -1) return ""; if(v[n].right != -1) { v[n].data = dfs(v[n].left) + v[n].data + dfs(v[n].right); if(n != root) v[n].data = '(' + v[n].data + ')'; } return v[n].data; } int main() { cin >> N; v.resize(N + 1); vector<bool> judge(N + 1, 0); for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++) { cin >> v[i].data >> v[i].left >> v[i].right; if(v[i].left != -1) judge[v[i].left] = 1; if(v[i].right != -1) judge[v[i].right] = 1; } for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++) if(!judge[i]) root = i; string ans = dfs(root); printf("%s", ans.c_str()); return 0; }