1. 静态资源配置
1.1 访问静态资源

(1)默认访问静态资源的方式:当前项目根路径 / + 静态资源名
(2)请求会先去找 Controller 看有没有对应的 HandlerMapping,不能处理的所有请求又都交给静态资源处理器 ResourceHttpRequestHandler,若静态资源也找不到则响应 404 页面。

(3)自定义静态资源访问前缀(默认:this.staticPathPattern = "/**")
- 修改 application.yml 配置文件
spring: mvc: static-path-pattern: /res/** - 访问静态资源:当前项目 + static-path-pattern + 静态资源名 => 静态资源文件夹下找

(4)自定义静态资源存放目录

spring:
web:
resources:
static-locations: [classpath:/res/]
(5)根据上图源码中 CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS 的默认配置,故可以自动映射 /webjars/**


1.2 welcome & favicon
welcome & favicon ← 使用这俩功能之前,必须要禁用〈访问前缀〉,否则会导致功能失效。

1.3 源码分析
SpringBoot 启动默认加载 xxxAutoConfiguration 类(自动配置类)→ SpringMVC 功能的自动配置类 WebMvcAutoConfiguration 生效。
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@ConditionalOnClass({Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class})
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class})
@AutoConfigureOrder(-2147483638)
@AutoConfigureAfter({DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class,
TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration.class,ValidationAutoConfiguration.class})
public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration { ... }

1.3.1 WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Import({WebMvcAutoConfiguration.EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class}) // => #1.3.2
@EnableConfigurationProperties({
WebMvcProperties.class, ResourceProperties.class, WebProperties.class
})
@Order(0)
public static class WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter implements WebMvcConfigurer {
private final WebMvcProperties mvcProperties;
private final ListableBeanFactory beanFactory;
private final ObjectProvider<HttpMessageConverters> messageConvertersProvider;
private final ObjectProvider<DispatcherServletPath> dispatcherServletPath;
private final ObjectProvider<ServletRegistrationBean<?>> servletRegistrations;
final WebMvcAutoConfiguration.ResourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer
resourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer;
// ...
}
WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter 加载了如下 3 个配置类:

WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter 的唯一的构造器(有参构造器所有参数的值都会从容器中确定):
public WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter(
// 获取和 spring.web 绑定的所有的值的对象
WebProperties webProperties,
// 获取和 spring.mvc 绑定的所有的值的对象
WebMvcProperties mvcProperties,
// Spring 的 beanFactory
ListableBeanFactory beanFactory,
// 找到所有的 HttpMessageConverters
ObjectProvider<HttpMessageConverters> messageConvertersProvider,
// 找到「资源处理器的自定义器」
ObjectProvider<WebMvcAutoConfiguration.ResourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer>
resourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizerProvider,
// DispatcherServlet 能处理的请求路径
ObjectProvider<DispatcherServletPath> dispatcherServletPath,
// 给应用注册 Servlet、Filter ...
ObjectProvider<ServletRegistrationBean<?>> servletRegistrations) {
this.mvcProperties = mvcProperties;
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
this.messageConvertersProvider = messageConvertersProvider;
this.resourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer =
(WebMvcAutoConfiguration.ResourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer)
resourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizerProvider.getIfAvailable();
this.dispatcherServletPath = dispatcherServletPath;
this.servletRegistrations = servletRegistrations;
this.mvcProperties.checkConfiguration();
// ...
}
1.3.2 EnableWebMvcConfiguration
(1)静态资源的处理
@EnableConfigurationProperties({WebProperties.class})
public static class EnableWebMvcConfiguration
extends DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration implements ResourceLoaderAware {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(WebMvcConfigurer.class);
private final Resources resourceProperties;
private final WebMvcProperties mvcProperties;
private final WebProperties webProperties;
private final ListableBeanFactory beanFactory;
private final WebMvcRegistrations mvcRegistrations;
private final ResourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer resourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer;
private ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
// ...
protected void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
super.addResourceHandlers(registry);
// 若将 WebProperties.Resources.addMapping 设为 false,则禁用所有静态资源的配置!
// 对应到配置文件:spring.resource.add-mapping
if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) {
logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled");
}
else { // ↓ 静态资源映射规则 ↓
ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletContext();
this.addResourceHandler(registry, "/webjars/**", "classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/");
this.addResourceHandler(registry, this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern(),
(registration) -> {
registration.addResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations());
if (servletContext != null) {
registration.addResourceLocations(
new Resource[]{new ServletContextResource(servletContext, "/")});
}
});
}
}
private void addResourceHandler(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry, String pattern, String... locations) {
this.addResourceHandler(registry, pattern, (registration) -> {
registration.addResourceLocations(locations);
});
}
}
通过 debug 查看:

默认的静态资源存放的 4 个位置信息存放在 WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter 加载的三个配置类之一 WebProperties 中:
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.web")
public class WebProperties {
public static class Resources {
private static final String[] CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS = new String[] {
"classpath:/META-INF/resources/", "classpath:/resources/",
"classpath:/static/", "classpath:/public/"};
private String[] staticLocations;
// ...
}
(2)WelcomePage 处理规则
// HandlerMapping:处理器映射。保存了每一个 Handler 能处理哪些请求。
@Bean
public WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping(
ApplicationContext applicationContext,
FormattingConversionService mvcConversionService,
ResourceUrlProvider mvcResourceUrlProvider) {
// ====== ↓↓↓ StepInto ↓↓↓ ======
WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping = new WelcomePageHandlerMapping(
new TemplateAvailabilityProviders(applicationContext), applicationContext,
this.getWelcomePage(), this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern());
welcomePageHandlerMapping.setInterceptors(
this.getInterceptors(mvcConversionService, mvcResourceUrlProvider));
welcomePageHandlerMapping.setCorsConfigurations(this.getCorsConfigurations());
return welcomePageHandlerMapping;
}
private Resource getWelcomePage() {
for (String location : this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations()) {
Resource indexHtml = getIndexHtml(location);
if (indexHtml != null) {
return indexHtml;
}
}
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
if (servletContext != null) {
return getIndexHtml(new ServletContextResource(servletContext, SERVLET_LOCATION));
}
return null;
}
// ························································································
final class WelcomePageHandlerMapping extends AbstractUrlHandlerMapping {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(WelcomePageHandlerMapping.class);
private static final List<MediaType> MEDIA_TYPES_ALL;
WelcomePageHandlerMapping(TemplateAvailabilityProviders templateAvailabilityProviders,
ApplicationContext applicationContext, Resource welcomePage, String staticPathPattern) {
// '/**' 是在这里写死了的!所以就解释了为什么配置静态资源访问前缀后,WelcomePage 会失效的原因!
if (welcomePage != null && "/**".equals(staticPathPattern)) {
logger.info("Adding welcome page: " + welcomePage);
this.setRootViewName("forward:index.html");
} else if (this.welcomeTemplateExists(templateAvailabilityProviders, applicationContext)) {
logger.info("Adding welcome page template: index");
this.setRootViewName("index");
}
}
// ...
}
2. Rest 风格
2.1 使用
Rest 风格支持(使用 HTTP 请求方式动词来表示对资源的操作)
| 动作 | 以前 | 现在 |
|---|---|---|
| 获取用户 | /getUser | GET - /user |
| 删除用户 | /deleteUser | DELETE - /user |
| 修改用户 | /editUser | PUT - /user |
| 修改用户 | /saveUser | POST - /user |
【用法】表单 method=post、隐藏域 _method=put/delete
- WebMvcAutoConfiguration
@Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean({HiddenHttpMethodFilter.class}) @ConditionalOnProperty( prefix = "spring.mvc.hiddenmethod.filter", name = {"enabled"}, matchIfMissing = false ) // => 需要手动开启 public OrderedHiddenHttpMethodFilter hiddenHttpMethodFilter() { return new OrderedHiddenHttpMethodFilter(); } - application.yml
spring: mvc: hiddenmethod: filter: enabled: true
2.2 源码
OrderedHiddenHttpMethodFilter
public class OrderedHiddenHttpMethodFilter
extends HiddenHttpMethodFilter implements OrderedFilter {
public static final int DEFAULT_ORDER = -10000;
private int order = -10000;
public OrderedHiddenHttpMethodFilter() {}
public int getOrder() {
return this.order;
}
public void setOrder(int order) {
this.order = order;
}
}
HiddenHttpMethodFilter
private static final List<String> ALLOWED_METHODS; // PUT、DELETE、PATCH
public static final String DEFAULT_METHOD_PARAM = "_method";
private String methodParam = "_method";
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpServletRequest requestToUse = request;
if ("POST".equals(request.getMethod()) && request.getAttribute("javax.servlet.error.exception") == null) {
String paramValue = request.getParameter(this.methodParam);
if (StringUtils.hasLength(paramValue)) {
String method = paramValue.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH);
if (ALLOWED_METHODS.contains(method)) {
requestToUse = new HiddenHttpMethodFilter.HttpMethodRequestWrapper(request, method);
}
}
}
filterChain.doFilter((ServletRequest)requestToUse, response);
}
private static class HttpMethodRequestWrapper extends HttpServletRequestWrapper {
private final String method;
public HttpMethodRequestWrapper(HttpServletRequest request, String method) {
super(request);
this.method = method;
}
public String getMethod() {
return this.method;
}
}
- 表单提交会带上
_method=PUT,请求过来被 HiddenHttpMethodFilter 拦截- 请求是否正常,并且是 POST;
- 获取到 _method 的值 → 兼容以下请求:PUT、DELETE、PATCH
- 对原生 Request 采用包装模式(RequestWrapper),重写 getMethod 方法,使其返回的是
_method的值。FilterChain 放行的时候将代表本次请求的 Request 对象替换成了 RequesWrapper,所以,之后对于 Request 的调用实际是调用 RequesWrapper 的; - Rest 使用客户端工具(如 PostMan),可以直接发送 put、delete 等方式的请求(request.getMethod() 直接就是选定的请求方式),也即:无需进入 doFilter 方法。
2.3 扩展
请求参数名如果不想用 _method 呢?怎么实现?
问题切入点:

public class HiddenHttpMethodFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
private static final List<String> ALLOWED_METHODS;
public static final String DEFAULT_METHOD_PARAM = "_method";
private String methodParam = "_method";
public void setMethodParam(String methodParam) {
Assert.hasText(methodParam, "'methodParam' must not be empty");
this.methodParam = methodParam;
}
// ...
}
自己向容器中注册一个 HiddenHttpMethodFilter 类型的 Bean,并设置 methodParam 属性的值:
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public class MyConfig {
@Bean
public HiddenHttpMethodFilter hiddenHttpMethodFilter() {
HiddenHttpMethodFilter hiddenHttpMethodFilter = new HiddenHttpMethodFilter();
hiddenHttpMethodFilter.setMethodParam("_rest");
return hiddenHttpMethodFilter;
}
}
3. 请求映射原理
3.1 doDispatch
protected void doDispatch(request, response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
ModelAndView mv = null;
Object dispatchException = null;
processedRequest = this.checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = processedRequest != request;
// 调用 HandlerMapping 获取该 Handler 配置的所有相关对象(包括 Handler 以
// 及对应的 interceptors),最终以 HandlerExecutionChain 对象的形式返回。
mappedHandler = this.getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
this.noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
HandlerAdapter ha = this.getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if ((new ServletWebRequest(request, response)).checkNotModified(lastModified)&&isGet) {
return;
}
}
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) return;
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) return;
this.applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
this.processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
3.2 getHandler
- RequestMappingHandlerMapping:保存了所有 @RequestMapping 与 handler 的映射规则。
- WelcomePageHandlerMapping:有独立地处理主页请求的 HandlerMapping。

这两个 HandlerMapping 是在 WebMvcAutoConfiguration 中初始化的(也可以自定义 HandlerMapping)。

AbstractHandlerMapping
@Override
@Nullable
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) {
// ===== ↓↓↓↓↓ Step Into ↓↓↓↓↓ =====
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
if (handler == null) { handler = getDefaultHandler(); }
if (handler == null) { return null; }
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
// Ensure presence of cached lookupPath for interceptors and others
if (!ServletRequestPathUtils.hasCachedPath(request)) { initLookupPath(request); }
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Mapped to " + handler);
} else if (logger.isDebugEnabled()
&& !request.getDispatcherType().equals(DispatcherType.ASYNC)) {
logger.debug("Mapped to " + executionChain.getHandler());
}
if (hasCorsConfigurationSource(handler) || CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration config = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
if (getCorsConfigurationSource() != null) {
CorsConfiguration globalConfig = getCorsConfigurationSource().getCorsConfiguration(request);
config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(config) : config);
}
if (config != null) {
config.validateAllowCredentials();
}
executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}
RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping
@Override
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) {
request.removeAttribute(PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE);
try {
// ===== ↓↓↓↓↓ Step Into ↓↓↓↓↓ =====
return super.getHandlerInternal(request);
} finally {
ProducesRequestCondition.clearMediaTypesAttribute(request);
}
}
/**
* Look up a handler method for the given request.
*/
@Override
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) {
String lookupPath = initLookupPath(request);
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
try {
// ===== ↓↓↓↓↓ Step Into ↓↓↓↓↓ =====
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);
}
finally {
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
}
/**
* Look up the best-matching handler method for the current request.
* If multiple matches are found, the best match is selected.
* @param lookupPath mapping lookup path within the current servlet mapping
* @param request the current request
* @return the best-matching handler method, or null if no match
*/
@Nullable
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) {
List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<>();
List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByDirectPath(lookupPath);
if (directPathMatches != null) {
addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().keySet(), matches, request);
}
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
Match bestMatch = matches.get(0);
// @RequestMapping(value = "/user", method = RequestMethod.GET)
// @RequestMapping(value = "/user")
// 同时有上面这俩映射规则,就可以进到下面这个 if 了
if (matches.size() > 1) {
Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request));
matches.sort(comparator);
bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(matches.size() + " matching mappings: " + matches);
}
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
for (Match match : matches) {
if (match.hasCorsConfig()) {
return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH;
}
}
} else {
Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1);
if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) {
Method m1 = bestMatch.getHandlerMethod().getMethod();
Method m2 = secondBestMatch.getHandlerMethod().getMethod();
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Ambiguous handler methods mapped for '" + uri + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}");
}
}
}
request.setAttribute(BEST_MATCHING_HANDLER_ATTRIBUTE, bestMatch.getHandlerMethod());
handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);
return bestMatch.getHandlerMethod();
} else {
return handleNoMatch(
this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().keySet(), lookupPath, request);
}
}

3.3 处理方法形参
3.3.1 分为 4 类
- 注解修饰:@PathVariable、@RequestHeader、@CookieValue、@ModelAttribute、@RequestBody、@RequestParam、@RequestAttribute、@MatrixVariable
- Servlet API
- 复杂类型:Map、Model(里面的数据会被放在 request 的请求域 request.setAttribute)、Errors/BindingResult、RedirectAttributes( 重定向携带数据)、ServletResponse(response)、SessionStatus、UriComponentsBuilder、ServletUriComponentsBuilder
- 自定义对象
3.3.2 测试常用注解
// ==== @PathVariable、@RequestHeader、@RequestParam、@CookieValue ====
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/car/{id}/owner/{username}")
public Map<String,Object> getCar(
@PathVariable("id") Integer id,
@PathVariable("username") String name,
// If the method parameter is Map<String, String>, then the map
// is populated with all path variable names and values.
@PathVariable Map<String,String> pv,
@RequestHeader("User-Agent") String userAgent,
@RequestHeader Map<String,String> header, // 同上
@RequestParam("age") Integer age,
@RequestParam("inters") List<String> inters,
@RequestParam Map<String,String> params, // 同上
@CookieValue("_ga") String _ga,
@CookieValue("_ga") Cookie cookie) {
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
// map.put("id", id);
// map.put("name", name);
// map.put("pv", pv);
// map.put("userAgent", userAgent);
// map.put("headers", header);
map.put("age", age);
map.put("inters", inters);
map.put("params", params);
map.put("_ga", _ga);
System.out.println(cookie.getName() + "===>" + cookie.getValue());
return map;
}
// ================ @RequestBody ================
@ResponseBody
@PostMapping("/param")
public Map<String, String> handle(
@RequestParam Map<String, String> paramMap,
@RequestBody String reqContent) { // 请求体
System.out.println(reqContent); // username=aaa
return paramMap;
}
// ============== @RequestAttribute ==============
@GetMapping("reqScope")
public String gotoSuccess(HttpServletRequest request) {
request.setAttribute("abc", "123");
return "forward:/success";
}
@GetMapping("success")
@ResponseBody
public String success(@RequestAttribute("abc") String reqScope) {
return reqScope;
}
3.3.3 @MatrixVariable
/ 之间是一个整体,其中第一个 ; 之前是请求路径,即 @PathVariable 路径变量,之后每一个 ; 隔开的才是 @MatrixVariable 矩阵变量,也就是说是在每个路径变量里绑定多个矩阵变量。
@RestController
public class MatrixController {
// 请求路径:/cars/sell;low=34;brand=byd,audi,yd
@GetMapping("/cars/{path}")
public Map carsSell(
@PathVariable("path") String path,
@MatrixVariable("low") Integer low,
@MatrixVariable("brand") List<String> brand) {
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("path", path); // sell
map.put("low", low); // 34
map.put("brand", brand);
return map;
}
// 请求路径:/boss/1;age=20/2;age=10
@GetMapping("/boss/{bossId}/{empId}")
public Map boss(
@PathVariable("bossId") String bossId,
@PathVariable("empId") String empId,
@MatrixVariable(value = "age", pathVar = "bossId") Integer bossAge,
@MatrixVariable(value = "age", pathVar = "empId") Integer empAge) {
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("bossId", bossId);
map.put("empId", empId);
map.put("bossAge", bossAge);
map.put("empAge", empAge);
return map;
}
}
矩阵变量可以出现在任何路径片段中,每一个矩阵变量都用分号隔开。比如 “/cars;color=red;year=2012”。多个值可以用逗号隔开,比如 “color=red,green,blue”或者分开写 “color=red;color=green;color=blue”。
矩阵变量必须有〈url 路径变量〉才能被解析,但 SpringBoot 默认是禁用了矩阵变量的功能,所以须手动开启 → 对于路径的处理是用 UrlPathHelper 进行解析,属性 removeSemicolonContent(移除分号内容)用来支持矩阵变量的。
- WebMvcAutoConfiguration

- UrlPathHelper 的 removeSemicolonContent 属性默认值为 true

- 自定义 UrlPathHelper 开启矩阵变量的功能

3.4 getHandlerAdapter
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());

index=0 支持方法上标注 @RequestMapping 的 handler。
3.5 handle

3.5.1 参数&返回值
【参数解析器】 SpringMVC 目标方法能写多少种参数类型。取决于参数解析器。

Servlet API → ServletRequestMethodArgumentResolver
POJO → ModelAttributeMethodProcessor

【返回值处理器】

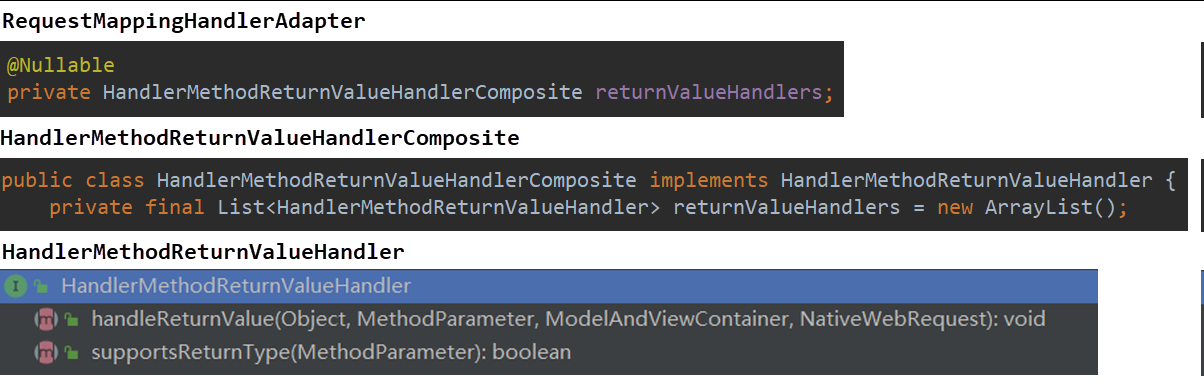
3.5.2 调用目标方法

InvocableHandlerMethod
/**
* Invoke the method after resolving its argument values in the context of the given request.
* <p>Argument values are commonly resolved through
* {@link HandlerMethodArgumentResolver HandlerMethodArgumentResolvers}.
* The {@code providedArgs} parameter however may supply argument values to be used directly,
* i.e. without argument resolution. Examples of provided argument values include a
* {@link WebDataBinder}, a {@link SessionStatus}, or a thrown exception instance.
* Provided argument values are checked before argument resolvers.
* <p>Delegates to {@link #getMethodArgumentValues} and calls {@link #doInvoke} with the
* resolved arguments.
*/
@Nullable
public Object invokeForRequest(NativeWebRequest request,
@Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
// ===== ↓↓↓↓ 获取参数值 ↓↓↓↓ =====
Object[] args = getMethodArgumentValues(request, mavContainer, providedArgs);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Arguments: " + Arrays.toString(args));
}
// ===== 执行目标方法 =====
return doInvoke(args);
}
3.5.3 先确定请求参数
InvocableHandlerMethod

/**
* Get the method argument values for the current request, checking the provided
* argument values and falling back to the configured argument resolvers.
*/
protected Object[] getMethodArgumentValues(NativeWebRequest request,
@Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
MethodParameter[] parameters = getMethodParameters();
if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(parameters)) {
return EMPTY_ARGS;
}
Object[] args = new Object[parameters.length];
for (int i = 0; i < parameters.length; i++) {
MethodParameter parameter = parameters[i];
parameter.initParameterNameDiscovery(this.parameterNameDiscoverer);
args[i] = findProvidedArgument(parameter, providedArgs);
if (args[i] != null) {
continue;
}
// ===== ↓↓↓↓↓ (1) 找出 27 个参数解析器中支持解析这个参数的(下图之后的代码块) ↓↓↓↓↓ =====
if (!this.resolvers.supportsParameter(parameter)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(formatArgumentError(parameter, "No suitable resolver"));
}
try {
// ===== ↓↓↓↓↓ (2) 下一个方法(url上参数的拆分结果放在uriTemplateVars) ↓↓↓↓↓ =====
args[i] = this.resolvers.resolveArgument(
parameter, mavContainer, request, this.dataBinderFactory);
} catch (Exception ex) {
// Leave stack trace for later, exception may actually be resolved and handled...
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String exMsg = ex.getMessage();
if (exMsg != null && !exMsg.contains(parameter.getExecutable().toGenericString())) {
logger.debug(formatArgumentError(parameter, exMsg));
}
}
throw ex;
}
}
return args;
}
/**
* Iterate over registered HandlerMethodArgumentResolvers
* and invoke the one that supports it.
*/
@Override
@Nullable
public Object resolveArgument(
MethodParameter parameter, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
NativeWebRequest webRequest, @Nullable WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) {
// 直接从上一步的缓存中拿出解析器对当前参数解析
HandlerMethodArgumentResolver resolver = getArgumentResolver(parameter);
if (resolver == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unsupported parameter type [" +
parameter.getParameterType().getName() + "]. supportsParameter should be called first.");
}
// 解析器处理参数 (详见 AbstractNamedValueMethodArgumentResolver,即下下个代码块)
return resolver.resolveArgument(parameter, mavContainer, webRequest, binderFactory);
}

HandlerMethodArgumentResolverComposite
@Override
public boolean supportsParameter(MethodParameter parameter) {
return getArgumentResolver(parameter) != null;
}
/**
* Find a registered HandlerMethodArgumentResolver that supports
* the given method parameter.
*/
@Nullable
private HandlerMethodArgumentResolver getArgumentResolver(MethodParameter parameter) {
// b. 下次再拿的时候,直接从缓存中拿,就不用进下面的代码了 -> 上一个代码块的(2)
HandlerMethodArgumentResolver result = this.argumentResolverCache.get(parameter);
if (result == null) {
for (HandlerMethodArgumentResolver resolver : this.argumentResolvers) {
if (resolver.supportsParameter(parameter)) {
result = resolver;
// a. [找到了~] 把参数处理的对应关系放到缓存中 -> 上一个代码块的(1)
this.argumentResolverCache.put(parameter, result);
break;
}
}
}
return result;
}
所有参数解析器都继承自 AbstractNamedValueMethodArgumentResolver(impl HandlerMethodArgumentResolver):
@Override
@Nullable
public final Object resolveArgument(
MethodParameter parameter, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
NativeWebRequest webRequest, @Nullable WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) {
NamedValueInfo namedValueInfo = getNamedValueInfo(parameter);
MethodParameter nestedParameter = parameter.nestedIfOptional();
// ===== ↓↓↓↓↓ Step Into ↓↓↓↓↓ =====
Object arg = resolveName(resolvedName.toString(), nestedParameter, webRequest);
// ... 省略一堆判断 ...
// ===== ↓↓↓↓↓ Step Into ↓↓↓↓↓ =====
handleResolvedValue(arg, namedValueInfo.name, parameter, mavContainer, webRequest);
return arg;
}
以 PathVariableMethodArgumentResolver.resolveArgument() 内部调用的 resolveName/handle 方法为例:

3.5.4 请求域里放数据
Model、Map 类型的参数,会分别被参数解析器中的 [19] ModelMethodProcessor 和 [20] MapMethodProcessor 所支持,底层给形参赋值时均是调用 mavContainer.getModel()。

将 Model/Map 中的数据放到请求域的时机是目标方法执行之后,页面跳转之前。

3.6 自定义参数类型
3.6.1 WebDataBinder
POJO 参数的解析器:ModelAttributeMethodProcessor
@Override
@Nullable
public final Object resolveArgument(
MethodParameter parameter, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
NativeWebRequest webRequest, @Nullable WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) {
String name = ModelFactory.getNameForParameter(parameter);
ModelAttribute ann = parameter.getParameterAnnotation(ModelAttribute.class);
if (ann != null) {
mavContainer.setBinding(name, ann.binding());
}
Object attribute = null;
BindingResult bindingResult = null;
if (mavContainer.containsAttribute(name)) {
attribute = mavContainer.getModel().get(name);
} else {
// Create attribute instance
attribute = createAttribute(name, parameter, binderFactory, webRequest);
}
if (bindingResult == null) {
// Bean property binding and validation;
// skipped in case of binding failure on construction.
WebDataBinder binder = binderFactory.createBinder(webRequest, attribute, name);
if (binder.getTarget() != null) {
if (!mavContainer.isBindingDisabled(name)) {
// ===== ↓↓↓↓↓ Step Into ↓↓↓↓↓ =====
bindRequestParameters(binder, webRequest);
}
validateIfApplicable(binder, parameter);
if (binder.getBindingResult().hasErrors() && isBindExceptionRequired(binder, parameter)) {
throw new BindException(binder.getBindingResult());
}
}
// Value type adaptation, also covering java.util.Optional
if (!parameter.getParameterType().isInstance(attribute)) {
attribute = binder.convertIfNecessary(
binder.getTarget(), parameter.getParameterType(), parameter);
}
bindingResult = binder.getBindingResult();
}
// Add resolved attribute and BindingResult at the end of the model
Map<String, Object> bindingResultModel = bindingResult.getModel();
mavContainer.removeAttributes(bindingResultModel);
mavContainer.addAllAttributes(bindingResultModel);
return attribute;
}
@Override
protected void bindRequestParameters(WebDataBinder binder, NativeWebRequest request) {
ServletRequest servletRequest = request.getNativeRequest(ServletRequest.class);
Assert.state(servletRequest != null, "No ServletRequest");
ServletRequestDataBinder servletBinder = (ServletRequestDataBinder) binder;
// ===== ↓↓↓↓↓ Step Into ↓↓↓↓↓ =====
servletBinder.bind(servletRequest);
}
ServletRequestBinder → WebDataBinder → DataBinder:

数据绑定分两步:① 将‘字符串’转换成指定‘属性类型’;② 通过反射赋值到属性。从上图中的 setPropertyValues 方法进去,就是下图 for 循环遍历 PropertyValue 的所在方法:

GenericConversionService:在设置字段值的时候,找它里面可以将这个数据类型转换到指定类型的 converter。

3.6.2 自定义类型转换器
index.html
<form action="/saveperson" method="post">
<input type="text" name="name">
<input type="text" name="age">
<input type="text" name="pet" value="猫猫,1">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
Converter<S, T>
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Converter<S, T> {
@Nullable
T convert(S var1);
default <U> Converter<S, U> andThen(Converter<? super T, ? extends U> after) {
Assert.notNull(after, "After Converter must not be null");
return (s) -> {
T initialResult = this.convert(s);
return initialResult != null ? after.convert(initialResult) : null;
};
}
}
WebMvcConfigurer

MyConfig
@Bean
public WebMvcConfigurer webMvcConfigurer() {
return new WebMvcConfigurer() {
@Override
public void configurePathMatch(PathMatchConfigurer configurer) {
UrlPathHelper urlPathHelper = new UrlPathHelper();
urlPathHelper.setRemoveSemicolonContent(false);
configurer.setUrlPathHelper(urlPathHelper);
}
@Override
public void addFormatters(FormatterRegistry registry) {
registry.addConverter(new Converter<String, Pet>() {
@Override
public Pet convert(String source) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(source)) {
Pet pet = new Pet();
String[] vars = source.split(",");
pet.setNickname(vars[0]);
pet.setAge(Integer.parseInt(vars[1]));
return pet;
}
return null;
}
});
}
};
}
