DNS域名解析服务的三种服务器:
主服务器:管理域名和IP地址的对应关系
从服务器:同步域名和IP地址的对应关系(缓解跟服务器压力,提高解析速度)
缓存服务器:转发域名和IP地址的对应关系(缓解根服务器压力,提高解析速度)
DNS从服务器要解决的问题:
从主服务器中获取指定的区域数据文件,起到备份同步和负载均衡的作用,缓解主服务器压力,提高DNS解析效率。
下面实验中要用到两台虚拟机,分别为PC1(主服务器)和PC2(从服务器)。IP分别为192.168.10.10和192.168.10.20。
1、查看主服务器和从服务器基本信息,测试联通性
[root@PC1 ~]# ifconfig | head -n 3 ## 查看主服务器IP
eno16777728: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.10.10 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.10.255
inet6 fe80::20c:29ff:fe66:37f7 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
[root@PC2 ~]# ifconfig | head -n 3 ## 查看从服务器IP
eno16777728: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.10.20 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.10.255
inet6 fe80::20c:29ff:fe25:bb3e prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
[root@PC2 ~]# ping -c 3 192.168.10.10 ## 测试从服务器和主服务器的连通性,没有问题
PING 192.168.10.10 (192.168.10.10) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 192.168.10.10: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.222 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.10.10: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.202 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.10.10: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.228 ms
--- 192.168.10.10 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2001ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.202/0.217/0.228/0.016 ms
2、主服务器上一实验已经配置好BIND服务,只需给从服务器配置好BIND服务。
[root@PC2 network-scripts]# yum install bind-chroot ## 安装bind服务
Loaded plugins: langpacks, product-id, subscription-manager
This system is not registered to Red Hat Subscription Management. You can use subscription-manager to register.
Resolving Dependencies
--> Running transaction check
---> Package bind-chroot.x86_64 32:9.9.4-14.el7 will be installed
--> Processing Dependency: bind = 32:9.9.4-14.el7 for package: 32:bind-chroot-9.9.4-14.el7.x86_64
--> Running transaction check
---> Package bind.x86_64 32:9.9.4-14.el7 will be installed
--> Finished Dependency Resolution
Dependencies Resolved
==============================================================================================
Package Arch Version Repository Size
==============================================================================================
Installing:
bind-chroot x86_64 32:9.9.4-14.el7 rhel7 81 k
Installing for dependencies:
bind x86_64 32:9.9.4-14.el7 rhel7 1.8 M
Transaction Summary
==============================================================================================
Install 1 Package (+1 Dependent package)
Total download size: 1.8 M
Installed size: 4.3 M
Is this ok [y/d/N]: y
Downloading packages:
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total 189 MB/s | 1.8 MB 00:00:00
Running transaction check
Running transaction test
Transaction test succeeded
Running transaction
Installing : 32:bind-9.9.4-14.el7.x86_64 1/2
Installing : 32:bind-chroot-9.9.4-14.el7.x86_64 2/2
rhel7/productid | 1.6 kB 00:00:00
Verifying : 32:bind-9.9.4-14.el7.x86_64 1/2
Verifying : 32:bind-chroot-9.9.4-14.el7.x86_64 2/2
Installed:
bind-chroot.x86_64 32:9.9.4-14.el7
Dependency Installed:
bind.x86_64 32:9.9.4-14.el7
Complete!
[root@PC2 network-scripts]# vim /etc/named.conf ## 修改主配置文件,修改第11行和第17行
1 //
2 // named.conf
3 //
4 // Provided by Red Hat bind package to configure the ISC BIND named(8) DNS
5 // server as a caching only nameserver (as a localhost DNS resolver only).
6 //
7 // See /usr/share/doc/bind*/sample/ for example named configuration files.
8 //
9
10 options {
11 listen-on port 53 { any; }; ## 表示服务器上的所有的IP(网卡)均可提供DNS服务
12 listen-on-v6 port 53 { ::1; };
13 directory "/var/named";
14 dump-file "/var/named/data/cache_dump.db";
15 statistics-file "/var/named/data/named_stats.txt";
16 memstatistics-file "/var/named/data/named_mem_stats.txt";
17 allow-query { any; }; ## 表示允许任何人使用DNS查询服务
18
19 /*
20 - If you are building an AUTHORITATIVE DNS server, do NOT enable recursion.
21 - If you are building a RECURSIVE (caching) DNS server, you need to enable
22 recursion.
修改从服务器网卡参数,将DNS服务改为本机的IP:
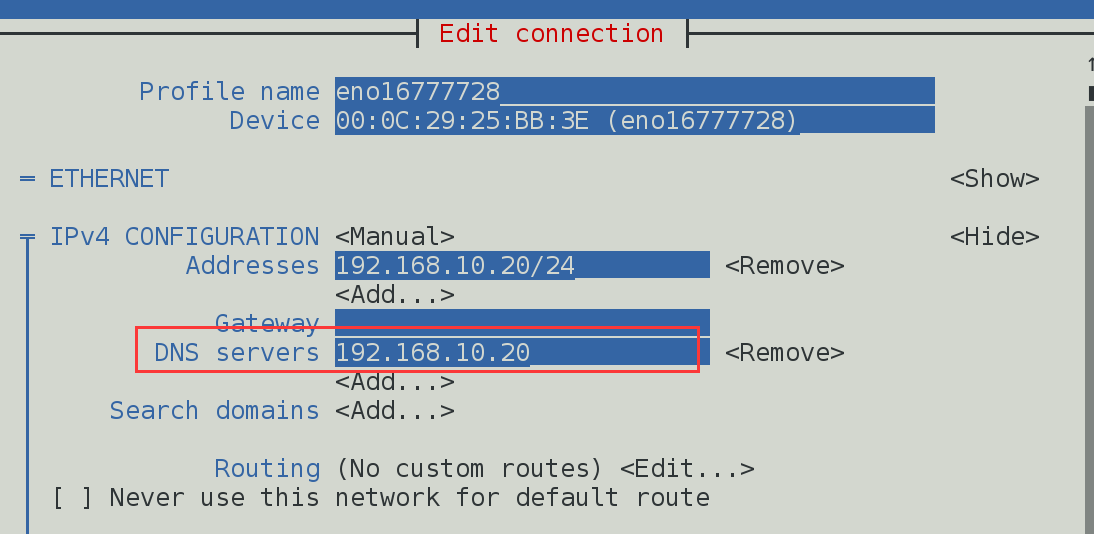
[root@PC2 Desktop]# systemctl restart named ## 重启bind服务
[root@PC2 Desktop]# systemctl restart network ## 重启网卡服务
2、在主服务器中修改区域配置文件,允许从服务器的更新请求,并重启bind服务程序
[root@PC1 ~]# vim /etc/named.rfc1912.zones zone "linuxprobe.com" IN { type master; file "linuxprobe.com.zone"; allow-update {192.168.10.20;}; }; zone "10.168.192.in-addr.arpa" IN { type master; file "192.168.10.arpa"; allow-update {192.168.10.20;}; };
[root@PC1 ~]# systemctl restart named ## 重启服务,加入开机自启
[root@PC1 ~]# systemctl enable named
ln -s '/usr/lib/systemd/system/named.service' '/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/named.service'
3、修改从服务器的区域配置文件,指定将要去主服务器同步的信息
[root@PC2 ~]# vim /etc/named.rfc1912.zones ## 修改从服务器的区域配置文件,删除原始的信息,按照如下进行编辑
zone "linuxprobe.com" IN { ## 指定同步域名
type slave; ## 指定服务器类型为从服务器
masters { 192.168.10.10; }; ## 指定主服务器的IP
file "slaves/linuxprobe.com.zone"; ## 指定从主服务器同步数据的保存路径
};
zone "10.168.192.in-addr.arpa" IN { ## 指定反向解析的IP
type slave; ## 指定服务器类型为从服务器
masters { 192.168.10.10; }; ## 指定主服务器的IP
file "slaves/192.168.10.arpa"; ## 指定从主服务器同步数据的保存路径
};
[root@PC2 ~]# systemctl restart named ## 重启服务
[root@PC2 ~]# systemctl enable named ## 设定开机自启
ln -s '/usr/lib/systemd/system/named.service' '/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/named.service'
[root@PC2 ~]# cd /var/named/slaves/ ## 进入指定同步数据的目录检查是否同步,没有
[root@PC2 slaves]# ls
4、 清空主服务器防火墙
[root@PC1 ~]# iptables -F ## 这一步很重要,不知道为啥
5、 在从服务器中重新启动bind服务,检查是否同步
[root@PC2 slaves]# systemctl restart named ## 重启服务
[root@PC2 slaves]# ls ## 检查,已经同步
192.168.10.arpa linuxprobe.com.zone
6、测试从服务器的同步备份效果
[root@PC2 slaves]# nslookup ## 测试从服务的备份效果,通过
> www.linuxprobe.com
Server: 192.168.10.20
Address: 192.168.10.20#53
Name: www.linuxprobe.com
Address: 192.168.10.10
> 192.168.10.10
Server: 192.168.10.20
Address: 192.168.10.20#53
10.10.168.192.in-addr.arpa name = www.linuxprobe.com.
> xxx.linuxprobe.com
Server: 192.168.10.20
Address: 192.168.10.20#53
Name: xxx.linuxprobe.com
Address: 111.123.145.23
> 192.168.10.20
Server: 192.168.10.20
Address: 192.168.10.20#53
20.10.168.192.in-addr.arpa name = mmm.xxxxxxxx.com.
以上测试说明了以上部署方法可以实现从服务器的备份效果。