(接上篇《架构设计:系统间通信(13)——RPC实例Apache Thrift 下篇(1)》)
3、正式开始编码
我已经在CSDN的资源区上传了这个示例工程的所有代码(http://download.csdn.net/detail/yinwenjie/9289999)。读者可以直接到资源下载站进行下载(不收积分哦~~^_^)。这篇文章将紧接上文,主要介绍这个工程几个主要的类代码。
3-1、编写服务端主程序
服务端主程序的类名:processor.MainProcessor,它负责在服务端启动Apache Thrift并且在服务监听启动成功后,连接到zookeeper,注册这个服务的基本信息。
这里要注意一下,Apache Thrift的服务监听是阻塞式的,所以processor.MainProcessor的Apache Thrift操作应该另起线程进行(processor.MainProcessor.StartServerThread),并且通过线程间的锁定操作,保证zookeeper的连接一定是在Apache Thrift成功启动后才进行。
package processor;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import net.sf.json.JSONObject;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.apache.log4j.BasicConfigurator;
import org.apache.thrift.TProcessor;
import org.apache.thrift.protocol.TBinaryProtocol;
import org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol;
import org.apache.thrift.server.ServerContext;
import org.apache.thrift.server.TServerEventHandler;
import org.apache.thrift.server.TThreadPoolServer;
import org.apache.thrift.server.TThreadPoolServer.Args;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TServerSocket;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TTransport;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TTransportException;
import org.apache.zookeeper.CreateMode;
import org.apache.zookeeper.KeeperException;
import org.apache.zookeeper.WatchedEvent;
import org.apache.zookeeper.Watcher;
import org.apache.zookeeper.ZooKeeper;
import org.apache.zookeeper.ZooDefs.Ids;
import org.apache.zookeeper.data.Stat;
import business.BusinessServicesMapping;
import thrift.iface.DIYFrameworkService;
import thrift.iface.DIYFrameworkService.Iface;
public class MainProcessor {
static {
BasicConfigurator.configure();
}
/**
* 日志
*/
private static final Log LOGGER = LogFactory.getLog(MainProcessor.class);
private static final Integer SERVER_PORT = 8090;
/**
* 专门用于锁定以保证这个主线程不退出的一个object对象
*/
private static final Object WAIT_OBJECT = new Object();
/**
* 标记apache thrift是否启动成功了
* 只有apache thrift启动成功了,才需要连接到zk
*/
private boolean isthriftStart = false;
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
* 主程序要做的事情:
*
* 1、启动thrift服务。并且服务调用者的请求
* 2、连接到zk,并向zk注册自己提供的服务名称,告知zk真实的访问地址、访问端口
* (向zk注册的服务,存储在BusinessServicesMapping这个类的K-V常量中)
* */
//1、========启动thrift服务
MainProcessor mainProcessor = new MainProcessor();
mainProcessor.startServer();
// 一直等待,apache thrift启动完成
synchronized (mainProcessor) {
try {
while(!mainProcessor.isthriftStart) {
mainProcessor.wait();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
MainProcessor.LOGGER.error(e);
System.exit(-1);
}
}
//2、========连接到zk
try {
mainProcessor.connectZk();
} catch (IOException | KeeperException | InterruptedException e) {
MainProcessor.LOGGER.error(e);
System.exit(-1);
}
// 这个wait在业务层面,没有任何意义。只是为了保证这个守护线程不会退出
synchronized (MainProcessor.WAIT_OBJECT) {
try {
MainProcessor.WAIT_OBJECT.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
MainProcessor.LOGGER.error(e);
System.exit(-1);
}
}
}
/**
* 这个私有方法用于连接到zk上,并且注册相关服务
* @throws IOException
* @throws InterruptedException
* @throws KeeperException
*/
private void connectZk() throws IOException, KeeperException, InterruptedException {
// 读取这个服务提供者,需要在zk上注册的服务
Set<String> serviceNames = BusinessServicesMapping.SERVICES_MAPPING.keySet();
// 如果没有任何服务需要注册到zk,那么这个服务提供者就没有继续注册的必要了
if(serviceNames == null || serviceNames.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
// 默认的监听器
MyDefaultWatcher defaultWatcher = new MyDefaultWatcher();
// 连接到zk服务器集群,添加默认的watcher监听
ZooKeeper zk = new ZooKeeper("192.168.61.128:2181", 120000, defaultWatcher);
//创建一个父级节点Service
Stat pathStat = null;
try {
pathStat = zk.exists("/Service", defaultWatcher);
//如果条件成立,说明节点不存在(只需要判断一个节点的存在性即可)
//创建的这个节点是一个“永久状态”的节点
if(pathStat == null) {
zk.create("/Service", "".getBytes(), Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE, CreateMode.PERSISTENT);
}
} catch(Exception e) {
System.exit(-1);
}
// 开始添加子级节点,每一个子级节点都表示一个这个服务提供者提供的业务服务
for (String serviceName : serviceNames) {
JSONObject nodeData = new JSONObject();
nodeData.put("ip", "127.0.0.1");
nodeData.put("port", MainProcessor.SERVER_PORT);
zk.create("/Service/" + serviceName, nodeData.toString().getBytes(), Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE, CreateMode.EPHEMERAL);
}
//执行到这里,说明所有的service都启动完成了
MainProcessor.LOGGER.info("===================所有service都启动完成了,主线程开始启动===================");
}
/**
* 这个私有方法用于开启Apache thrift服务端,并进行持续监听
* @throws TTransportException
*/
private void startServer() {
Thread startServerThread = new Thread(new StartServerThread());
startServerThread.start();
}
private class StartServerThread implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
MainProcessor.LOGGER.info("看到这句就说明thrift服务端准备工作 ....");
// 服务执行控制器(只要是调度服务的具体实现该如何运行)
TProcessor tprocessor = new DIYFrameworkService.Processor<Iface>(new DIYFrameworkServiceImpl());
// 基于阻塞式同步IO模型的Thrift服务,正式生产环境不建议用这个
TServerSocket serverTransport = null;
try {
serverTransport = new TServerSocket(MainProcessor.SERVER_PORT);
} catch (TTransportException e) {
MainProcessor.LOGGER.error(e);
System.exit(-1);
}
// 为这个服务器设置对应的IO网络模型、设置使用的消息格式封装、设置线程池参数
Args tArgs = new Args(serverTransport);
tArgs.processor(tprocessor);
tArgs.protocolFactory(new TBinaryProtocol.Factory());
tArgs.executorService(Executors.newFixedThreadPool(100));
// 启动这个thrift服务
TThreadPoolServer server = new TThreadPoolServer(tArgs);
server.setServerEventHandler(new StartServerEventHandler());
server.serve();
}
}
/**
* 为这个TThreadPoolServer对象,设置是一个事件处理器。
* 以便在TThreadPoolServer正式开始监听服务请求前,通知mainProcessor:
* “Apache Thrift已经成功启动了”
* @author yinwenjie
*
*/
private class StartServerEventHandler implements TServerEventHandler {
@Override
public void preServe() {
/*
* 需要实现这个方法,以便在服务启动成功后,
* 通知mainProcessor: “Apache Thrift已经成功启动了”
* */
MainProcessor.this.isthriftStart = true;
synchronized (MainProcessor.this) {
MainProcessor.this.notify();
}
}
/* (non-Javadoc)
* @see org.apache.thrift.server.TServerEventHandler#createContext(org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol, org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol)
*/
@Override
public ServerContext createContext(TProtocol input, TProtocol output) {
/*
* 无需实现
* */
return null;
}
@Override
public void deleteContext(ServerContext serverContext, TProtocol input, TProtocol output) {
/*
* 无需实现
* */
}
@Override
public void processContext(ServerContext serverContext, TTransport inputTransport, TTransport outputTransport) {
/*
* 无需实现
* */
}
}
/**
* 这是默认的watcher,什么也没有,也不需要有什么<br>
* 因为按照功能需求,服务器端并不需要监控zk上的任何目录变化事件
* @author yinwenjie
*/
private class MyDefaultWatcher implements Watcher {
public void process(WatchedEvent event) {
}
}
}
3-2、编写服务具体实现
服务端具体实现的代码很简单,就是在IDL脚本生成了java代码后,对DIYFrameworkService接口进行的实现。
package processor;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import net.sf.json.JSONObject;
import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.apache.thrift.TException;
import business.BusinessService;
import business.BusinessServicesMapping;
import business.exception.BizException;
import business.exception.ResponseCode;
import business.pojo.AbstractPojo;
import business.pojo.BusinessResponsePojo;
import business.pojo.DescPojo;
import thrift.iface.DIYFrameworkService.Iface;
import thrift.iface.EXCCODE;
import thrift.iface.RESCODE;
import thrift.iface.Reponse;
import thrift.iface.Request;
import thrift.iface.ServiceException;
import utils.JSONUtils;
/**
* IDL文件中,我们定义的唯一服务接口DIYFrameworkService.Iface的唯一实现
* @author yinwenjie
*
*/
public class DIYFrameworkServiceImpl implements Iface {
/**
* 日志
*/
public static final Log LOGGER = LogFactory.getLog(DIYFrameworkServiceImpl.class);
/* (non-Javadoc)
* @see thrift.iface.DIYFrameworkService.Iface#send(thrift.iface.Request)
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public Reponse send(Request request) throws ServiceException, TException {
/*
* 由于MainProcessor中,在Apache Thrift 服务端启动时已经加入了线程池,所以这里就不需要再使用线程池了
* 这个服务方法的实现,需要做以下事情:
*
* 1、根据request中,描述的具体服务名称,在配置信息中查找具体的服务类
* 2、使用java的反射机制,调用具体的服务类(BusinessService接口的实现类)。
* 3、根据具体的业务处理结构,构造Reponse对象,并进行返回
* */
//1、===================
String serviceName = request.getServiceName();
String className = BusinessServicesMapping.SERVICES_MAPPING.get(serviceName);
//未发现服务
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(className)) {
return this.buildErrorReponse("无效的服务" , null);
}
//2、===================
// 首先得到以json为描述格式的请求参数信息
JSONObject paramJSON = null;
try {
byte [] paramJSON_bytes = request.getParamJSON();
if(paramJSON_bytes != null && paramJSON_bytes.length > 0) {
String paramJSON_string = new String(paramJSON_bytes);
paramJSON = JSONObject.fromObject(paramJSON_string);
}
} catch(Exception e) {
DIYFrameworkServiceImpl.LOGGER.error(e);
// 向调用者抛出异常
throw new ServiceException(EXCCODE.PARAMNOTFOUND, e.getMessage());
}
// 试图进行反射
BusinessService<AbstractPojo> businessServiceInstance = null;
try {
businessServiceInstance = (BusinessService<AbstractPojo>)Class.forName(className).newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
DIYFrameworkServiceImpl.LOGGER.error(e);
// 向调用者抛出异常
throw new ServiceException(EXCCODE.SERVICENOTFOUND, e.getMessage());
}
// 进行调用
AbstractPojo returnPojo = null;
try {
returnPojo = businessServiceInstance.handle(paramJSON);
} catch (BizException e) {
DIYFrameworkServiceImpl.LOGGER.error(e);
return this.buildErrorReponse(e.getMessage() , e.getResponseCode());
}
// 构造处理成功情况下的返回信息
BusinessResponsePojo responsePojo = new BusinessResponsePojo();
responsePojo.setData(returnPojo);
DescPojo descPojo = new DescPojo("", ResponseCode._200);
responsePojo.setDesc(descPojo);
// 生成json
String returnString = JSONUtils.toString(responsePojo);
byte[] returnBytes = returnString.getBytes();
ByteBuffer returnByteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(returnBytes.length);
returnByteBuffer.put(returnBytes);
returnByteBuffer.flip();
// 构造response
Reponse reponse = new Reponse(RESCODE._200, returnByteBuffer);
return reponse;
}
/**
* 这个私有方法,用于构造“Thrift中错误的返回信息”
* @param erroe_mess
* @return
*/
private Reponse buildErrorReponse(String erroe_mess , ResponseCode responseCode) {
// 构造返回信息
BusinessResponsePojo responsePojo = new BusinessResponsePojo();
responsePojo.setData(null);
DescPojo descPojo = new DescPojo(erroe_mess, responseCode == null?ResponseCode._504:responseCode);
responsePojo.setDesc(descPojo);
// 存储byteBuffer;
String responseJSON = JSONUtils.toString(responsePojo);
byte[] responseJSON_bytes = responseJSON.getBytes();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(responseJSON_bytes.length);
byteBuffer.put(byteBuffer);
byteBuffer.flip();
Reponse reponse = new Reponse(RESCODE._500, byteBuffer);
return reponse;
}
}3-3、编写客户端实现
在上文中已经介绍过了,客户端有两件事情需要做:连接到zookeeper查询注册的服务该如何访问;然后向真实的服务提供者发起请求。代码如下:
package client;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.util.List;
import net.sf.json.JSONObject;
import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.apache.log4j.BasicConfigurator;
import org.apache.thrift.protocol.TBinaryProtocol;
import org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TSocket;
import org.apache.zookeeper.CreateMode;
import org.apache.zookeeper.WatchedEvent;
import org.apache.zookeeper.Watcher;
import org.apache.zookeeper.ZooKeeper;
import org.apache.zookeeper.ZooDefs.Ids;
import org.apache.zookeeper.data.Stat;
import thrift.iface.DIYFrameworkService.Client;
import thrift.iface.Reponse;
import thrift.iface.Request;
import utils.JSONUtils;
public class ThriftClient {
/**
* 日志
*/
private static final Log LOGGER = LogFactory.getLog(ThriftClient.class);
private static final String SERVCENAME = "queryUserDetailService";
static {
BasicConfigurator.configure();
}
public static final void main(String[] main) throws Exception {
/*
* 服务治理框架的客户端示例,要做以下事情:
*
* 1、连接到zk,查询当前zk下提供的服务列表中是否有自己需要的服务名称(queryUserDetailService)
* 2、如果没有找到需要的服务名称,则客户端终止工作
* 3、如果找到了服务,则通过服务给出的ip,port,基于Thrift进行正式请求
* (这时,和zookeeper是否断开,关系就不大了)
* */
// 1、===========================
// 默认的监听器
ClientDefaultWatcher defaultWatcher = new ClientDefaultWatcher();
// 连接到zk服务器集群,添加默认的watcher监听
ZooKeeper zk = new ZooKeeper("192.168.61.128:2181", 120000, defaultWatcher);
/*
* 为什么客户端连接上来以后,也可能创建一个Service根目录呢?
* 因为正式的环境下,不能保证客户端一点就在服务器端全部准备好的情况下,再来做调用请求
* */
Stat pathStat = null;
try {
pathStat = zk.exists("/Service", defaultWatcher);
//如果条件成立,说明节点不存在(只需要判断一个节点的存在性即可)
//创建的这个节点是一个“永久状态”的节点
if(pathStat == null) {
zk.create("/Service", "".getBytes(), Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE, CreateMode.PERSISTENT);
}
} catch(Exception e) {
System.exit(-1);
}
// 2、===========================
//获取服务列表(不需要做任何的事件监听,所以第二个参数可以为false)
List<String> serviceList = zk.getChildren("/Service", false);
if(serviceList == null || serviceList.isEmpty()) {
ThriftClient.LOGGER.info("未发现相关服务,客户端退出");
return;
}
//然后查看要找寻的服务是否在存在
boolean isFound = false;
byte[] data;
for (String serviceName : serviceList) {
if(StringUtils.equals(serviceName, ThriftClient.SERVCENAME)) {
isFound = true;
break;
}
}
if(!isFound) {
ThriftClient.LOGGER.info("未发现相关服务,客户端退出");
return;
} else {
data = zk.getData("/Service/" + ThriftClient.SERVCENAME, false, null);
}
/*
* 执行到这里,zk的工作就完成了,接下来zk是否断开,就不重要了
* */
zk.close();
if(data == null || data.length == 0) {
ThriftClient.LOGGER.info("未发现有效的服务端地址,客户端退出");
return;
}
// 得到服务器地值说明
JSONObject serverTargetJSON = null;
String serverIp;
String serverPort;
try {
serverTargetJSON = JSONObject.fromObject(new String(data));
serverIp = serverTargetJSON.getString("ip");
serverPort = serverTargetJSON.getString("port");
} catch(Exception e) {
ThriftClient.LOGGER.error(e);
return;
}
//3、===========================
TSocket transport = new TSocket(serverIp, Integer.parseInt(serverPort));
TProtocol protocol = new TBinaryProtocol(transport);
// 准备调用参数
JSONObject jsonParam = new JSONObject();
jsonParam.put("username", "yinwenjie");
byte[] params = jsonParam.toString().getBytes();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(params.length);
buffer.put(params);
buffer.flip();
Request request = new Request(buffer, ThriftClient.SERVCENAME);
// 开始调用
Client client = new Client(protocol);
// 准备传输
transport.open();
// 正式调用接口
Reponse reponse = client.send(request);
byte[] responseBytes = reponse.getResponseJSON();
// 一定要记住关闭
transport.close();
// 将返回信息显示出来
ThriftClient.LOGGER.info("respinse value = " + new String(responseBytes));
}
}
/**
* 这是默认的watcher,什么也没有,也不需要有什么<br>
* 因为按照功能需求,客户端并不需要监控zk上的任何目录变化事件
* @author yinwenjie
*/
class ClientDefaultWatcher implements Watcher {
public void process(WatchedEvent event) {
}
}3-4、工程结构说明
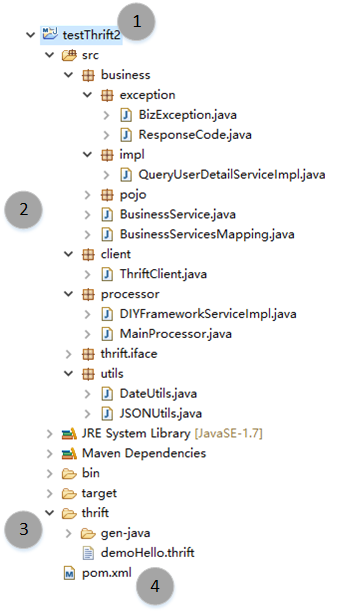
以上代码是服务器端、客户端的主要代码。整个工程还有其他的辅助代码,为了让各位读者能够看得清楚直接,我们将整个工程结构进行一下说明,下载后导入的工程结构如下图所示:
这是一个典型的JAVA工程。请使用 JDK 1.6+ 版本。我们将讲解整个工程结构。首先来看看这个工程中主要的package和它们的作用。
business:具体的业务层逻辑都在这个包里面,其中exception包含了一个业务层异常的定义BizException,还有错误代码ResponseCode;impl包中放置具体的业务层实现,它们都必须实现BusinessService接口;Pojo是业务层对象模型。client:为了简单起见,我将服务端的实现和客户端的实现放置在一个工程中,client这个包就是客户端的实现代码了;utils包放置了两个工具类,用来进行日期格式化的DataUtils和用来进行json转换的JSONUtils。
定义的apache thrift IDL文件放置在thrift文件夹下面,名字叫做:demoHello.thrift;您可以使用它生成各种语言的代码;
工程需要maven的支持。
2016年08月08日,由网友OneZhous发现了一个程序的bug,这是由于Apache Thrift内部并不会在进行org.apache.thrift.TBaseHelper.copyBinary执行时,将java.nio.ByteBuffer自动进行flip()。所以在完成request和response对象设置后,需要开发人员自行进行flip()。感谢OneZhous对文章中的问题进行纠正,但是CSDN由于无法修改已上传的资源,所以还请各位读者在下载运行时注意这个问题:
......
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(params.length);
buffer.put(params);
buffer.flip();
// 以及位置
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(responseJSON_bytes.length);
byteBuffer.put(byteBuffer);
byteBuffer.flip();
......