前言
requests模块,也就是老污龟,为啥叫它老污龟呢,因为这个官网上的logo就是这只污龟,接下来就是学习它了。
一、环境安装
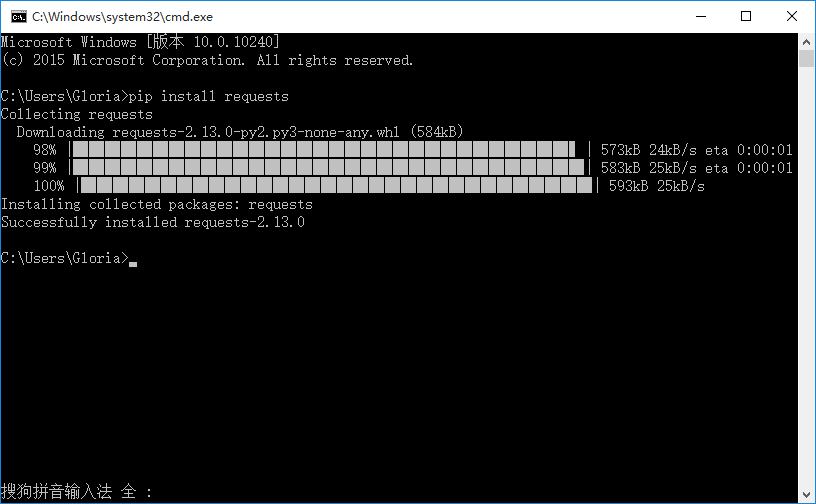
1.用pip安装requests模块
>>pip install requests
二、get请求
1.导入requests后,用get方法就能直接访问url地址,如:https://www.cnblogs.com/liunaixu,看起来是不是很酷
2.这里的r也就是response,请求后的返回值,可以调用response里的status_code方法查看状态码
3.状态码200只能说明这个接口访问的服务器地址是对的,并不能说明功能OK,一般要查看响应的内容,r.text是返回文本信息

# @Author:lsj
# @version V1.0
# -*- coding:UTF-8 -*-
import requests
# 请求我公司后台网站首页
r = requests.get("http://daxue.qysxy.com.cn/admin/static/front/html/index.html")
print(r.text)
print(r.status_code)
三、params
1.再发一个带参数的get请求,如在博客园搜索:python,url地址为:https://zzk.cnblogs.com/my/s/blogpost-p?Keywords=python
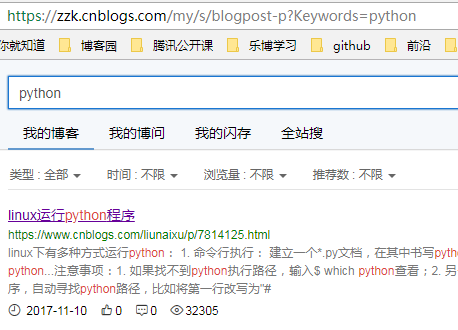
2.请求参数:Keywords=python,可以以字典的形式传参:{"Keywords":"python"}
3.多个参数格式:{"key1": "value1", "key2": "value2", "key3": "value3"}
四、content
1.百度首页如果用r.text会发现获取到的内容有乱码,因为百度首页响应内容是gzip压缩的(非text文本)
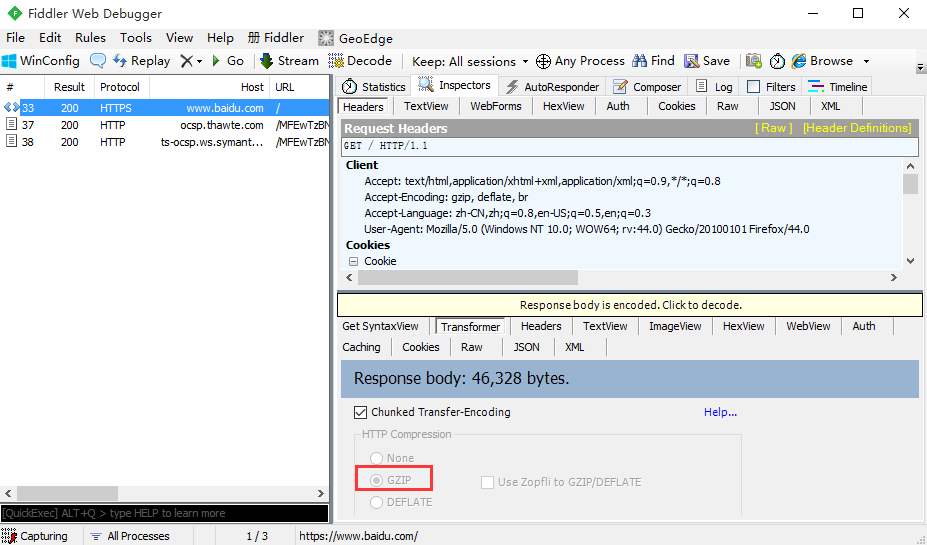
2.如果是在fiddler工具乱码,是可以点击后解码的,在代码里面可以用r.content这个方法,content会自动解码 gzip 和deflate压缩
五、response
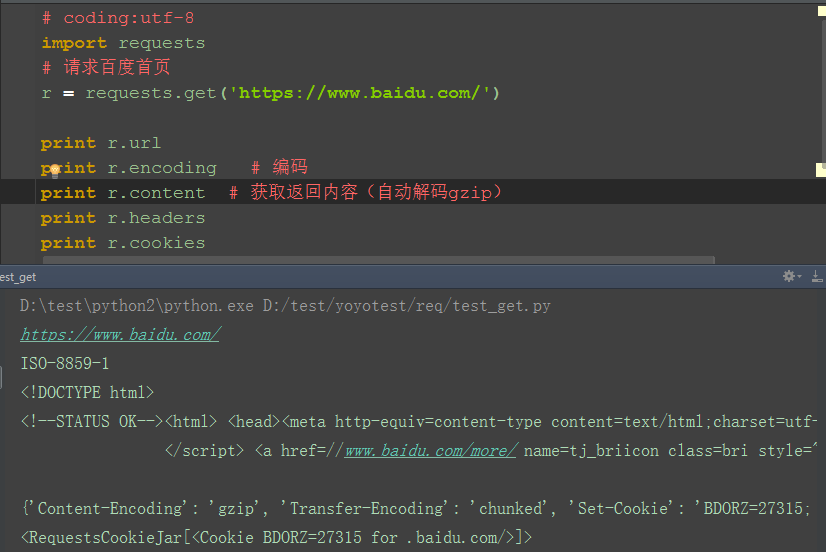
1.response的返回内容还有其它更多信息
-- r.status_code #响应状态码
-- r.content #字节方式的响应体,会自动为你解码 gzip 和 deflate 压缩
-- r.headers #以字典对象存储服务器响应头,但是这个字典比较特殊,字典键不区分大小写,若键不存在则返回None
-- r.json() #Requests中内置的JSON解码器
-- r.url # 获取url
-- r.encoding # 编码格式
-- r.cookies # 获取cookie
-- r.raw #返回原始响应体
-- r.text #字符串方式的响应体,会自动根据响应头部的字符编码进行解码
-- r.raise_for_status() #失败请求(非200响应)抛出异常