本文内容
- 创建测试数据表
- 测试 B-tree 索引
- 测试 Bitmap 索引
- Bitmap 索引与分组
- 总结
本文演示数据列值的特点对索引类型的影响。若数据列的取值范围是可以穷举的,则 Bitmap 索引比 B-tree 索引更合适。
创建测试数据表
代码段一:
CREATE TABLE TESTIDX_A AS
SELECT *
FROM (SELECT ROWNUM as id, t.object_name, t.object_type FROM dba_objects t);
利用 dba_objects 系统表生成测试数据表 testidx_a,并以同样方式生成表 testidx_b 和 testidx_c。用下面语句查看一下数据量。
代码段二:
SQL> select count(*) from TESTIDX_A;
COUNT(*)
----------
69448
SQL>
以这样方式生成的测试数据,即便是新创建的数据库实例,也有将近 7 万行。
另外,本测试数据有个特点。object_type 列值的取值范围是可以枚举、穷举的,比如 FUNCTION、INDEX、PACKAGE 等,而 object_name 是不能穷举的。这个特点对创建并使用哪种索引类型很重要。
将按如下方式为三个表创建索引:
- testidx_a 表不创建任何索引。
- testidx_b 表分别为 object_name 和 object_type 列创建 B-tree 索引。
- testidx_c 表分别为 object_name 和 object_type 列创建 Bitmap 索引。
测试 B-tree 索引
首先,testidx_a 表,不创建任何索引。其次,为 testidx_b 表的 object_name 和 object_type 列分别建立 idx_tb_on 和 idx_tb_ot 的 B-tree 索引。Oracle 默认创建 B-tree 索引。
代码段三:
SQL> create index idx_tb_on on TESTIDX_B(object_name);
索引已创建。
SQL> create index idx_tb_ot on TESTIDX_B(object_type);
索引已创建。
SQL>
检索 testidx_a 和 testidx_b 表 object_name 字段值 'EMP' 表。如下所示,查找 testidx_a:
代码段四:
SQL> select * from TESTIDX_A where object_name='EMP';
执行计划
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 1043052094
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 5 | 450 | 119 (1)| 00:00:02 |
|* 1 | TABLE ACCESS FULL| TESTIDX_A | 5 | 450 | 119 (1)| 00:00:02 |
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
1 - filter("OBJECT_NAME"='EMP')
Note
-----
- dynamic sampling used for this statement
统计信息
----------------------------------------------------------
0 recursive calls
0 db block gets
418 consistent gets
0 physical reads
0 redo size
565 bytes sent via SQL*Net to client
416 bytes received via SQL*Net from client
4 SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client
0 sorts (memory)
0 sorts (disk)
1 rows processed
SQL>
注意:
- 执行计划中 Rows、Bytes、Cost 列。其中,Rows 和 Bytes 列表示选择多少行及其大小;Cost 是该 SQL 的代价,它仅仅是根据 CPU、IO 等代价计算出来一个值。
- 统计信息部分是可变的,也就是,初次与再次执行 SQL 时,consistent gets 值可能不同。但无论怎么样,执行计划的值不会变。
查找 testidx_b,如下所示:
代码段五:
SQL> select * from TESTIDX_B where object_name='EMP';
执行计划
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 4045461513
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 90 | 4 (0)| 00:00:01 |
| 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| TESTIDX_B | 1 | 90 | 4 (0)| 00:00:01 |
|* 2 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | IDX_TB_ON | 1 | | 3 (0)| 00:00:01 |
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
2 - access("OBJECT_NAME"='EMP')
Note
-----
- dynamic sampling used for this statement
统计信息
----------------------------------------------------------
0 recursive calls
0 db block gets
5 consistent gets
0 physical reads
0 redo size
569 bytes sent via SQL*Net to client
416 bytes received via SQL*Net from client
4 SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client
0 sorts (memory)
0 sorts (disk)
1 rows processed
SQL>
说明:
- 执行计划 Operations 列,因为,testidx_a 表没有建立任何索引,所以代码段四进行了全表扫描;而代码段五,使用了索引 idx_tb_on。
- 这样,执行计划 Cost 列的值,差距很大。创建索引后,SQL 执行的明显快。
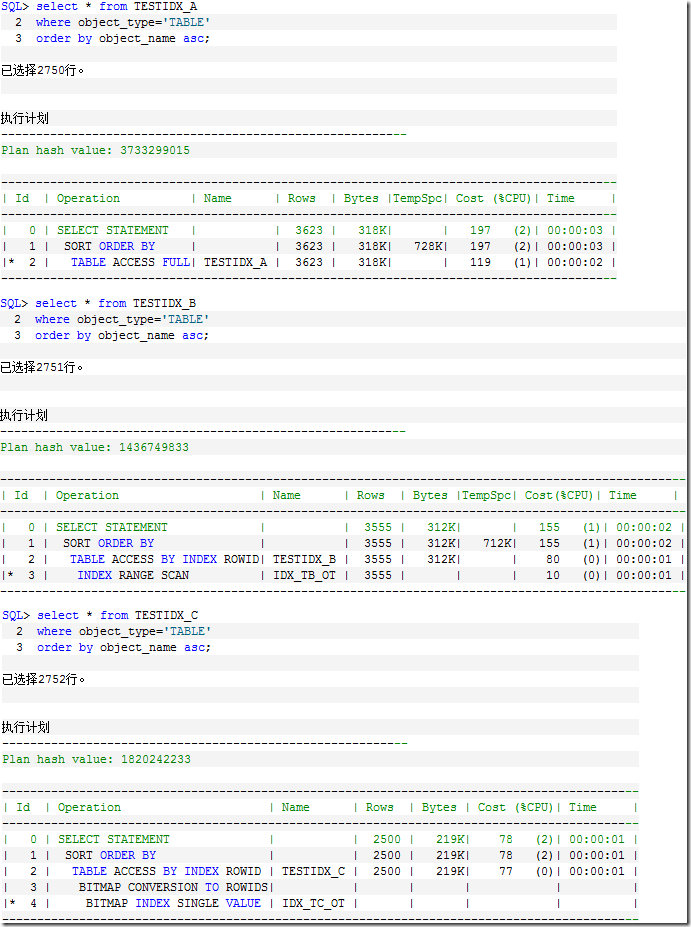
检索 testidx_a 和 testidx_b 表 object_type 列为 'TABLE' 的记录。检索 testidx_a 如下所示:
代码段六:
SQL> select * from TESTIDX_A
2 where object_type='TABLE'
3 order by object_name asc;
已选择2750行。
执行计划
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 3733299015
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes |TempSpc| Cost (%CPU)| Time |
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 3623 | 318K| | 197 (2)| 00:00:03 |
| 1 | SORT ORDER BY | | 3623 | 318K| 728K| 197 (2)| 00:00:03 |
|* 2 | TABLE ACCESS FULL| TESTIDX_A | 3623 | 318K| | 119 (1)| 00:00:02 |
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
2 - filter("OBJECT_TYPE"='TABLE')
Note
-----
- dynamic sampling used for this statement
统计信息
----------------------------------------------------------
0 recursive calls
0 db block gets
417 consistent gets
0 physical reads
0 redo size
104070 bytes sent via SQL*Net to client
2429 bytes received via SQL*Net from client
186 SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client
1 sorts (memory)
0 sorts (disk)
2750 rows processed
SQL>
检索 testidx_b 表,如下所示:
代码段七:
SQL> select * from TESTIDX_B
2 where object_type='TABLE'
3 order by object_name asc;
已选择2751行。
执行计划
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 1436749833
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes |TempSpc| Cost(%CPU)| Time |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 3555 | 312K| | 155 (1)| 00:00:02 |
| 1 | SORT ORDER BY | | 3555 | 312K| 712K| 155 (1)| 00:00:02 |
| 2 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| TESTIDX_B | 3555 | 312K| | 80 (0)| 00:00:01 |
|* 3 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | IDX_TB_OT | 3555 | | | 10 (0)| 00:00:01 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
3 - access("OBJECT_TYPE"='TABLE')
Note
-----
- dynamic sampling used for this statement
统计信息
----------------------------------------------------------
9 recursive calls
0 db block gets
178 consistent gets
8 physical reads
0 redo size
104086 bytes sent via SQL*Net to client
2429 bytes received via SQL*Net from client
186 SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client
1 sorts (memory)
0 sorts (disk)
2751 rows processed
SQL>
测试 Bitmap 索引
接下来,为 testidx_c 表的 object_name 和 object_type 列都建立 Bitmap 索引。如下所示。
代码段八:
SQL> create bitmap index idx_tc_on on TESTIDX_C(object_name);
索引已创建。
SQL> create bitmap index idx_tc_ot on TESTIDX_C(object_type);
索引已创建。
SQL>
同代码段六和七执行同样的操作——查找 object_type 列为 TABLE 的记录,如下所示。
代码段九:
SQL> select * from TESTIDX_C
2 where object_type='TABLE'
3 order by object_name asc;
已选择2752行。
执行计划
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 1820242233
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 2500 | 219K| 78 (2)| 00:00:01 |
| 1 | SORT ORDER BY | | 2500 | 219K| 78 (2)| 00:00:01 |
| 2 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID | TESTIDX_C | 2500 | 219K| 77 (0)| 00:00:01 |
| 3 | BITMAP CONVERSION TO ROWIDS| | | | | |
|* 4 | BITMAP INDEX SINGLE VALUE | IDX_TC_OT | | | | |
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
4 - access("OBJECT_TYPE"='TABLE')
Note
-----
- dynamic sampling used for this statement
统计信息
----------------------------------------------------------
103 recursive calls
0 db block gets
170 consistent gets
1 physical reads
0 redo size
104107 bytes sent via SQL*Net to client
2429 bytes received via SQL*Net from client
186 SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client
1 sorts (memory)
0 sorts (disk)
2752 rows processed
说明:
- 代码段六,没有创建任何索引;代码段七,创建的是 B-tree 索引;代码段九,创建的是 Bitmap 索引。
- 当检索作用在 object_type 列时,Bitmap 索引比 B-tree 索引的效果更好。这是因为 object_type 的列决定的。该列的值是可以枚举,或是说穷举出来的。
因此,对某个列,它的值若有范围,可穷举,用 Bitmap 索引比较合适。否则,Bitmap 索引的效果,就不是很明显。如下所示,执行同代码段四和五同样的操作,查找 object_name 列为 EMP 的记录。
代码段十:
SQL> select * from testidx_c
2 where object_name='EMP';
执行计划
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 2697327847
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)|Time |
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 90 | 77 (0)|00:00:01 |
| 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID | TESTIDX_C | 1 | 90 | 77 (0)|00:00:01 |
| 2 | BITMAP CONVERSION TO ROWIDS| | | | | |
|* 3 | BITMAP INDEX SINGLE VALUE | IDX_TC_ON | | | | |
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
3 - access("OBJECT_NAME"='EMP')
Note
-----
- dynamic sampling used for this statement
统计信息
----------------------------------------------------------
9 recursive calls
0 db block gets
76 consistent gets
1 physical reads
0 redo size
569 bytes sent via SQL*Net to client
416 bytes received via SQL*Net from client
4 SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client
0 sorts (memory)
0 sorts (disk)
1 rows processed
说明:看代码段四、五和十的执行计划,Cost 列的值,代码段十还是不如代码段五。因为,object_name 列的值不能穷举,不具有像 object_type 列那样的特点。所以,虽然 SQL 使用了 Bitmap 索引,但效果明显不如 B-tree 索引。
这样,我们会想到一个问题,是不是 Bitmap 索引对分组语句效果很好?
Bitmap 索引与分组
分别对 testidx_b 和 testidx_c 表的 object_type 字段进行分组。如下所示,分组 testidx_b:
代码段十一:
SQL> select t.object_type,count(*) from testidx_b t
2 group by t.object_type;
已选择41行。
执行计划
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 141313140
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 79998 | 859K| 122 (4)| 00:00:02 |
| 1 | HASH GROUP BY | | 79998 | 859K| 122 (4)| 00:00:02 |
| 2 | TABLE ACCESS FULL| TESTIDX_B | 79998 | 859K| 119 (1)| 00:00:02 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Note
-----
- dynamic sampling used for this statement
统计信息
----------------------------------------------------------
5 recursive calls
0 db block gets
492 consistent gets
0 physical reads
0 redo size
1449 bytes sent via SQL*Net to client
438 bytes received via SQL*Net from client
5 SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client
0 sorts (memory)
0 sorts (disk)
41 rows processed
分组 testidx_c,如下所示:
SQL> select t.object_type,count(*) from testidx_c t
2 group by t.object_type;
已选择41行。
执行计划
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 3862313015
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 72610 | 779K| 9 (0)| 00:00:01 |
| 1 | SORT GROUP BY NOSORT | | 72610 | 779K| 9 (0)| 00:00:01 |
| 2 | BITMAP CONVERSION COUNT| | 72610 | 779K| 9 (0)| 00:00:01 |
| 3 | BITMAP INDEX FULL SCAN| IDX_TC_OT | | | | |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Note
-----
- dynamic sampling used for this statement
统计信息
----------------------------------------------------------
5 recursive calls
0 db block gets
78 consistent gets
3 physical reads
0 redo size
1449 bytes sent via SQL*Net to client
438 bytes received via SQL*Net from client
8 SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client
0 sorts (memory)
0 sorts (disk)
41 rows processed
说明:从执行计划的 Cost 列看,效果果然很明显。但是,当执行分组的同时,还有过滤条件,SQL 就不会使用 Bitmap 索引,除非将过滤条件中的列与分组列同时建立 Bitmap 索引。
总结
- testidx_a 表不创建任何索引。
- testidx_b 表分别为 object_name 和 object_type 列创建 B-tree 索引。
- testidx_c 表分别为 object_name 和 object_type 列创建 Bitmap 索引。
如图 1 所示,在三个表的 object_name 列执行相同的操作,查找值为 emp 的记录。B-tree 索引的效果更好。因为,当像 object_name 这样不能枚举其值的列,B-tree 索引对 SQL 的执行效率很高。不能枚举其值意思是 distinct 该列的值与 count 该列,相差无几。这反映在执行计划的基数列。另外,对 object_name 列创建 Bitmap 索引,效果比 B-tree 索引差很多。
图 1
如图 2 所示,在三个表的 object_type 列执行相同的操作,查找值为 TABLE 的记录。Bitmap 索引的效果更好。因为,当为 object_type 这样可能枚举其值的列,Bitmap 索引对 SQL 的执行效率很高。可能枚举其值意思是 distinct 该列的值与 count 该列,相差很多。
图 2
如图 3 所示,在 testidx_b 和 testidx_c 执行相同的操作。按 object_type 分组,Bitmap 索引对分组操作更好。
图 3