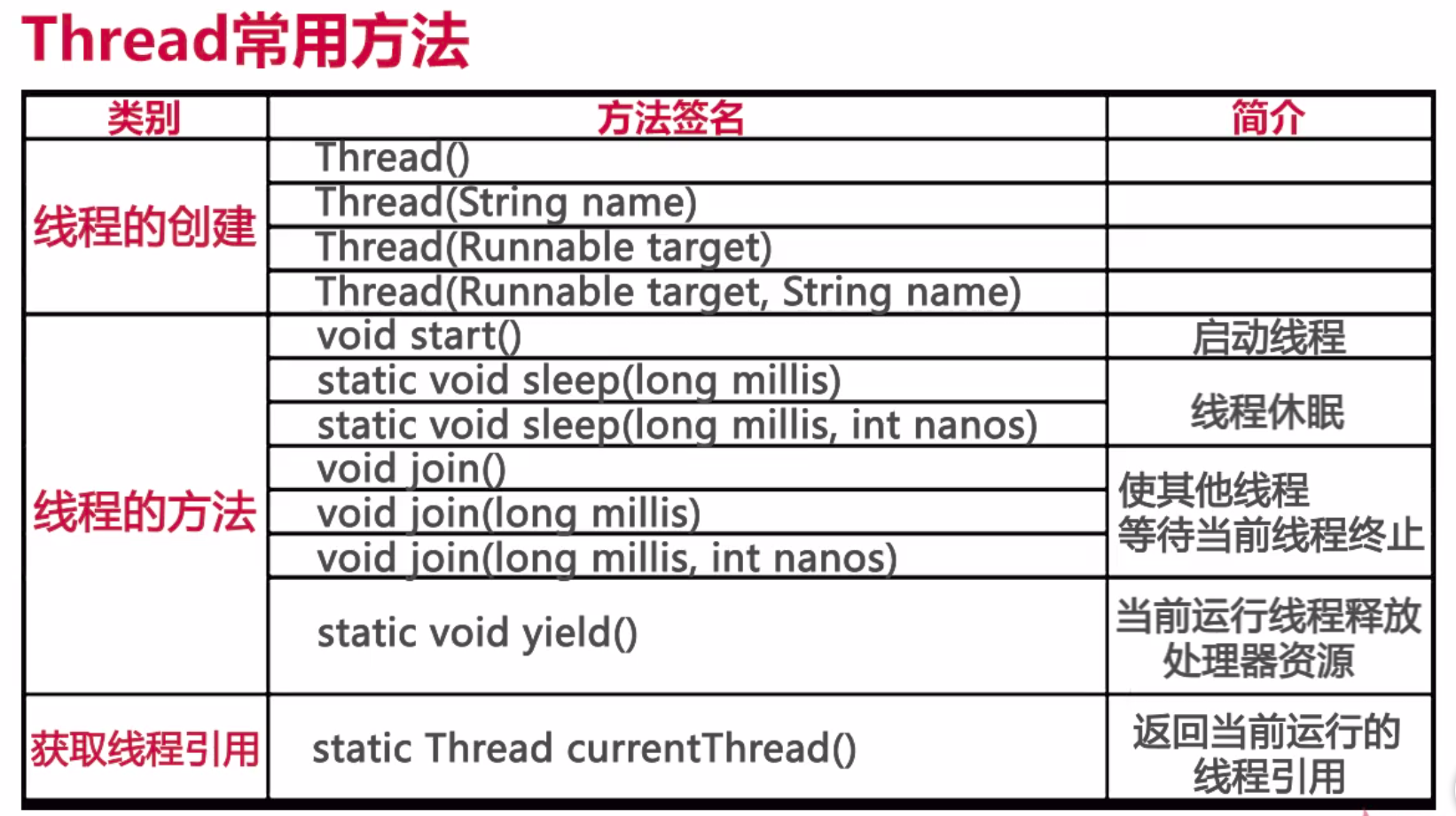
一.编写两种多线程的方法
(1).Thread(它是继承Runnable的子类)
class MyThread extends Thread{
private int ticket = 5;
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i=0 ; i<20;i++){
if(this.ticket>0)
System.out.println("卖出的票数为" + this.ticket--);
}
}
}
public class MyClass {
// 测试静态内部类
public static void main(String[] args) {
new MyThread().start();
new MyThread().start();
new MyThread().start();
}
}
卖出的票数为5
卖出的票数为4
卖出的票数为3
卖出的票数为2
卖出的票数为1
卖出的票数为5
卖出的票数为4
卖出的票数为3
卖出的票数为2
卖出的票数为1
卖出的票数为5
卖出的票数为4
卖出的票数为3
卖出的票数为2
卖出的票数为1
(2).继承Runnable接口的实现
class MyThread implements Runnable{
private int ticket = 5;
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i=0 ; i<20;i++){
if(this.ticket>0)
System.out.println("卖出的票数为" + this.ticket--);
}
}
}
public class MyClass {
// 测试静态内部类
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();
new Thread(myThread).start();
new Thread(myThread).start();
new Thread(myThread).start();
//myThread.start();
//myThread1.start();
//myThread2.start();
}
}
卖出的票数为4
卖出的票数为5
卖出的票数为2
卖出的票数为3
卖出的票数为1
二、两种线程的区别
Thread的方法:会受到单继承的局限性,且不方便表示出数据共享的概念
Runnable的方法 : 不会受到单继承的局限性,可以方便表示出数据共享的概念
它们最终都会调用Thread().start的方法。
三、常见的线程的编写
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.printf("这是hello world");
}
}).start();
四、线程的同步和死锁
1.线程同步的方法 : 同步代码块、同步方法
(1).同步代码的关键字 : synchronized
class Mythread implements Runnable{
private int ticket = 8 ;
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 0; i<20; i++) {
synchronized (this) {
if (this.ticket > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("剩余的票数" + this.ticket--);
}
}
}
}
}
public class MyClass {
// 测试静态内部类
public static void main(String[] args) {
Mythread mythread = new Mythread();
new Thread(mythread,"A").start();
new Thread(mythread,"B").start();
new Thread(mythread,"C").start();
new Thread(mythread,"D").start();
new Thread(mythread,"E").start();
}
}
(2).代码的同步的方法:在方法上面加synchronized的关键字
class Mythread implements Runnable{
private int ticket = 8 ;
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 0; i<20; i++) {
this.sale();
}
}
public synchronized void sale(){
if (this.ticket > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("剩余的票数" + this.ticket--);
}
}
}
public class MyClass {
// 测试静态内部类
public static void main(String[] args) {
Mythread mythread = new Mythread();
new Thread(mythread,"A").start();
new Thread(mythread,"B").start();
new Thread(mythread,"C").start();
new Thread(mythread,"D").start();
new Thread(mythread,"E").start();
}
}
五、线程的优先级
Thread.setPriority(int num) : 设置线程的优先级
六、生产者和消费者
1.解决重复的操作必须使用等待和唤醒的功能
Object类中含有使用的关键函数
1.等待的使用: wait()
2.唤醒第一个: notify()
3.唤醒全部 : notifyAll() : 谁的优先级高先执行谁
2.生产者消费者的代码
class Message{
private String name;
private String context;
private Boolean flag = true;
public synchronized void setName(String name , String context) {
if (this.flag == false){
try {
super.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
this.name = name;
this.context = context;
this.flag = false;
super.notify();
}
public synchronized void getName() {
if(this.flag == true){
try {
super.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(this.name + ":"+ context);
this.flag = true;
super.notify();
}
}
class Product implements Runnable{
private Message message;
public Product(Message msg){
this.message = msg;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0;i<100;i++){
if(i % 2 == 0 ) {
message.setName("想成为","诗人");
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}else {
message.setName("不想成为","囚犯");
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
class Custor implements Runnable{
private Message message;
public Custor(Message msg){
this.message = msg;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0;i<100;i++){
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
message.getName();
}
}
}
public class MyClass {
// 测试静态内部类
public static void main(String[] args) {
Message message = new Message();
// Product product = new Product(message);
// Custor custor = new Custor(message);
// Thread thread1 = new Thread(product);
// Thread thread2 = new Thread(custor);
// thread1.start();
// thread2.start();
new Thread(new Product(message)).start();
new Thread(new Custor(message)).start();
}
}
七、sleep()和wait()的区别
1.sleep() : 它是Thread的内部定义的,可以自动唤醒
2.wait() : 它是Object的内部定义的,需要手工用notify或notifyAll唤醒