一点一点看JDK源码(五)java.util.ArrayList 后篇之sort与Comparator
liuyuhang原创,未经允许禁止转载
本文举例使用的是JDK8的API
目录:一点一点看JDK源码(〇)
Comparator为额外实现的比较接口,与类本身无关
该接口在ArrayList的sort中有应用(很多时候都可以用的,只是以此举例)
Comparator接口主要用途有两种,
1、比较有序集合内任意两个元素A、B(完全遍历的compareTo方法,于compare方法内实现)
若A元素小于B元素,则返回1,donothing
若A元素等于B元素,则返回0,donothing
若A元素小于B元素,则返回-1,交换元素位置
若compare方法的返回值遵循以上原则,则进行排序
示例代码如下:
1 package com.FM.ArrayListStudy; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Comparator; 5 6 public class ComparatorInArrayListStudy01 { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>(); 9 list.add(1); 10 list.add(12); 11 list.add(3); 12 list.add(4); 13 list.add(3); 14 list.add(11); 15 list.add(7); 16 System.out.println(list);//排序之前的list 17 18 list.sort(new Comparator<Integer>() {//使用Comparator进行自然排序 19 @Override 20 public int compare(Integer one, Integer anotherOne) { 21 int compareTo = one.compareTo(anotherOne);//正序排序 22 //int compareTo = anotherOne.compareTo(one);//逆序排序 23 24 //比较结果为1则不操作 25 //比较结果为0则相等 26 //比较结果为-1则交换位置 27 System.out.println(anotherOne + " -- " + one + " --- " + compareTo); 28 return compareTo; 29 } 30 }); 31 System.out.println(list);//排序之后的list 32 } 33 }
运行结果:
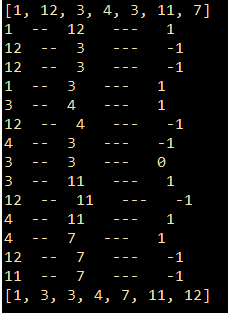
2、依照比较的结果(-1,0,1)进行判断分组
示例代码如下:Apple类
1 package com.FM.ArrayListStudy; 2 3 public class Apple { 4 5 private Integer id; 6 private Integer size; 7 8 public Integer getId() { 9 return id; 10 } 11 12 public void setId(Integer id) { 13 this.id = id; 14 } 15 16 public Integer getSize() { 17 return size; 18 } 19 20 public void setSize(Integer size) { 21 this.size = size; 22 } 23 24 public Apple(Integer id, Integer size) { 25 super(); 26 this.id = id; 27 this.size = size; 28 } 29 30 @Override 31 public String toString() { 32 return "Apple [id=" + id + ", size=" + size + "]"; 33 } 34 35 }
示例代码如下:利用Comparator接口分组
1 package com.FM.ArrayListStudy; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Comparator; 5 import java.util.List; 6 7 public class ComparatorInArrayListStudy02 { 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 ArrayList<Apple> list = new ArrayList<Apple>(); 10 list.add(new Apple(1, 81)); 11 list.add(new Apple(2, 76)); 12 list.add(new Apple(3, 91)); 13 list.add(new Apple(4, 84)); 14 list.add(new Apple(5, 79)); 15 list.add(new Apple(6, 87)); 16 list.add(new Apple(7, 85)); 17 list.add(new Apple(8, 83)); 18 list.add(new Apple(9, 91)); 19 System.out.println(list);//排序之前的list 20 21 List<List<Apple>> disPartList = disPart(list,new Comparator<Apple>(){ 22 @Override 23 public int compare(Apple o1, Apple o2) {//这里写具体的分组接口,分组方式可以使用对象内的属性的组合方式 24 if(o1.getSize()/10 == o2.getSize()/10){//将苹果Apple按照size分组,每10个size分为一组 25 return 0; 26 } 27 return 1; 28 } 29 }); 30 for(List lis : disPartList){//分别遍历每一组 31 System.out.println(lis); 32 } 33 } 34 35 /** 36 * 按照comparator进行分组的方法 37 */ 38 public static <T> List<List<T>> disPart(List<T> list, Comparator<? super T> c) { 39 ArrayList<List<T>> resultList = new ArrayList<List<T>>(); 40 for (T t : list) { 41 boolean flag = false; 42 for (int i = 0; i < resultList.size(); i++) { 43 if (c.compare(t, resultList.get(i).get(0)) == 0) {// 若匹配成功则加入resultList中的子元素 44 flag = true; 45 resultList.get(i).add(t); 46 break; 47 } 48 } 49 if (flag == false) {// 若flag为false则将此元素加入resultList为新元素 50 List<T> listIn = new ArrayList<T>(); 51 listIn.add(t); 52 resultList.add(listIn); 53 } 54 } 55 return resultList; 56 } 57 }
运行结果:

分组的方式很多,很多人也喜欢自己写遍历来分组
利用好Comparator接口进行分组能更好的重用,也更容易扩展!
以上!!