Link Cut Tree 是一种神奇的数据结构。感觉完全不会,写下模板题的学习笔记。
LCT 中,比较重要的一点是将树边划分成实边和虚边。
对于每个非叶节点 (u),我们选择一个儿子 (v) 作为 (u) 的实儿子。((u,v)) 是实边,(u) 到其它儿子的连边是虚边。
容易发现,实边组成了若干条实链,每个节点恰好在实链中出现了一次(链上只有一个节点仍然算作实链)。
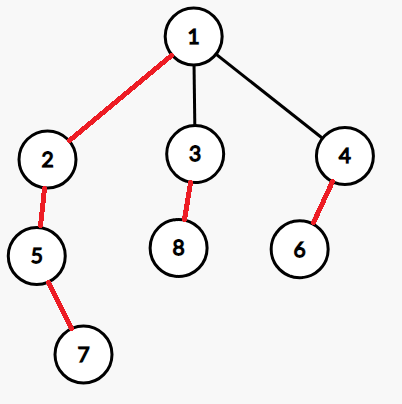
上图中,((1,2,5,7),(3,8),(4,6)) 是这棵树的实链。
对于每一条实链,我们用一棵 Splay 来维护节点。这棵 Splay 的中序遍历中,节点深度单调递增。
对于上图中的实链剖分,对应的 Splay 森林(注意形态可能不一样,但满足中序遍历节点深度单调递增):
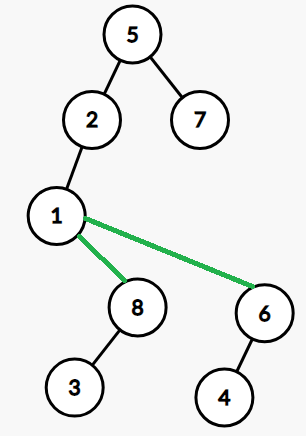
上图中绿色的边是虚边。
有一个显然的性质:如果 ((u,v)) 是实边且 (u) 的深度小于 (v),那么 (v) 是 Splay 中 (u) 的儿子。无论 ((u,v)) 是否是实边,(v) 的父亲都指向 (u)。
Access ~ 点与根的连接
LCT 的核心操作是 access()。access(x) 改变了原树的实链剖分,同时构造出一棵中序遍历以根节点开始,以 (x) 结束的 Splay。
首先把 (x) 与 (x) 的实儿子的连边改成虚边,因为要构造的 Splay 中序遍历以 (x) 结束。然后不断地从深度较大的 Splay 跳到深度较小的 Splay,并把跳的过程中经过的所有虚边改为实边。
inline void access(int x){
for(rr int y=0;x;y=x,x=fa(x)){
splay(x),rc(x)=y,update(x);
}
}
Makeroot ~ 换根
有了这个操作之后,我们可以来换根。makeroot(x) 的定义是让 (x) 成为原树的根。
我们怎么做呢?观察到,不在 (x) 到原来根路径上的点不会受到影响。于是我们只需要把 (x) 到原来根路径上的点拉出来,这就是 access(x)。然后我们将 (x) 旋转上去,这样 (x) 只有左子树(LCT 中 Splay 的性质:中序遍历节点深度单调递增)。我们想让 (x) 变成根,只需要翻转这棵 Splay。和做文艺平衡树时一样,打上翻转标记就行。
inline void rev(int x){
if(!x)
return;
std::swap(lc(x),rc(x));
tree[x].tag^=1;
return;
}
inline void makeroot(int x){
access(x),splay(x),rev(x);
return;
}
Findroot ~ 找根
findroot(x) 的定义是找到 (x) 所在树的根。因为维护过程中可能会出现森林,于是这个函数对判断连通性很有帮助。
access(x) 之后再 splay(x),按照上文,此时 (x) 只有左子树。往左子树一直走,就走到了根。
为了保证复杂度,找到原树的根之后要把根 splay() 成为 Splay 的根。
inline int findroot(int x){
access(x),splay(x);
while(lc(x))
pushdown(x),x=lc(x); // 记得下放翻转标记
splay(x);
return x;
}
Split ~ 提取路径
split(x,y) 的定义是拉出 (x,y) 在原树上的路径成为一个 Splay。通常要保证 (x,y) 连通。
很简单,makeroot(x) 之后在 access(y) 即可。为了保证复杂度,需要 splay(y)。
inline void split(int x,int y){
makeroot(x),access(y),splay(y);
return;
}
Link ~ 连边
link(x,y) 的定义是连接 (x,y)。如果 (x,y) 已经连通,则无需连接。
也很简单,因为是无根树,所以我们并不在乎 (x) 和 (y) 的祖孙关系。默认 (x) 的父亲变成 (y),makeroot(x) 再将 (x) 的父亲设为 (y) 就行。
如果 (x) 和 (y) 连通,那么 makeroot(x) 之后, findroot(y) 的结果一定为 (x)。特判即可。
inline void link(int x,int y){
makeroot(x);
if(findroot(y)==x){
return;
}
fa(x)=y,update(y); // 记得 update
return;
}
Cut ~ 断边
cut(x,y) 的定义是断掉 (x,y) 在原树上的边。如果没有边就不断。
首先用 findroot(y) 判掉 (x) 和 (y) 不连通的情况。接下来讨论 (x) 和 (y) 连通(即 findroot(y)==x)时:
findroot(y) 时已经执行了 access(y) 操作(见 findroot() 的实现),因此 (x) 到 (y) 的路径已经组成了一棵 Splay。此时若 (x,y) 之间有边,则:(x) 是 (y) 的父亲;(y) 没有左子树,否则这些点就会插在中序遍历中 (x) 和 (y) 的中间。
inline void cut(int x,int y){
makeroot(x);
if(findroot(y)==x&&fa(y)==x&&!lc(y)){
rc(x)=fa(y)=0;
update(x); // 记得 update
}
return;
}
模板题 Luogu P3690
题意
给定 (n) 个点以及每个点的权值,要你处理接下来的 (m) 个操作。
操作有四种,操作从 (0) 到 (3) 编号。点从 (1) 到 (n) 编号。
0 x y代表询问从 (x) 到 (y) 的路径上的点的权值的 ( ext{xor}) 和。保证 (x) 到 (y) 是联通的。1 x y代表连接 (x) 到 (y),若 (x) 到 (y) 已经联通则无需连接。2 x y代表删除边 ((x,y)),不保证边 ((x,y)) 存在。3 x y代表将点 (x) 上的权值变成 (y)。
(n,m leq 3 imes 10^5),值域 (10^9)
题解
update(x) 改成维护异或和就好了。
询问操作就是 split 出来之后 Splay 上点 (y) 的异或和(因为我们 Splay 过)。
(1,2) 操作都是板子。(3) 操作的话需要先把 (x) splay 上去再修改,否则 (x) 在 Splay 上父亲的信息都没有得到更新。
# include <bits/stdc++.h>
const int N=100010,INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
struct Node{
int son[2];
int val,sum,tag,fa;
}tree[N];
int sta[N];
inline int read(void){
int res,f=1;
char c;
while((c=getchar())<'0'||c>'9')
if(c=='-')f=-1;
res=c-48;
while((c=getchar())>='0'&&c<='9')
res=res*10+c-48;
return res*f;
}
inline int& fa(int x){
return tree[x].fa;
}
inline int& lc(int x){
return tree[x].son[0];
}
inline int& rc(int x){
return tree[x].son[1];
}
inline void update(int x){
tree[x].sum=tree[lc(x)].sum^tree[rc(x)].sum^tree[x].val;
return;
}
inline bool nroot(int x){
return (lc(fa(x))==x)||(rc(fa(x))==x);
}
inline void rotate(int x){
if(!nroot(x))
return;
int y=fa(x),z=fa(y),k=(rc(y)==x),ns=tree[x].son[!k];
if(nroot(y))
tree[z].son[rc(z)==y]=x;
tree[x].son[!k]=y,tree[y].son[k]=ns;
if(ns)
fa(ns)=y;
fa(y)=x,fa(x)=z;
update(y),update(x); // 顺序注意
return;
}
inline void rev(int x){
if(!x)
return;
std::swap(lc(x),rc(x));
tree[x].tag^=1;
return;
}
inline void pushdown(int x){
if(!tree[x].tag)
return;
rev(lc(x)),rev(rc(x)),tree[x].tag=0;
return;
}
inline void splay(int x){
int top=0;
int y=x;
for(;;){ // 记得这里要先下放标记
sta[++top]=y;
if(!nroot(y))
break;
y=fa(y);
}
while(top)
pushdown(sta[top--]);
while(nroot(x)){
int y=fa(x),z=fa(y);
if(nroot(y)){
((rc(y)==x)==(rc(z)==y))?rotate(y):rotate(x);
}
rotate(x);
}
return;
}
inline void access(int x){
for(int y=0;x;y=x,x=fa(x)){
splay(x),rc(x)=y,update(x);
}
return;
}
inline void makeroot(int x){
access(x),splay(x),rev(x);
return;
}
inline int findroot(int x){
access(x),splay(x);
while(lc(x))
pushdown(x),x=lc(x);
splay(x);
return x;
}
inline void split(int x,int y){
makeroot(x),access(y),splay(y);
return;
}
inline void link(int x,int y){
makeroot(x);
if(findroot(y)==x){
return;
}
fa(x)=y,update(y);
return;
}
inline void cut(int x,int y){
makeroot(x);
if(findroot(y)==x&&rc(x)==y&&!lc(y)){ // 顺序不能反
fa(y)=0,rc(x)=0;
update(x);
}
return;
}
int main(void){
int n=read(),m=read();
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){
tree[i].sum=tree[i].val=read();
}
int x,y,opt;
while(m--){
opt=read(),x=read(),y=read();
switch(opt){
case 0:{
split(x,y);
printf("%d
",tree[y].sum);
break;
}
case 1:{
link(x,y);
break;
}
case 2:{
cut(x,y);
break;
}
case 3:{
splay(x),tree[x].val=y,update(x);
break;
}
}
}
return 0;
}