springboot 与数据库访问
jdbc, mybatis, spring data jpa,
1.jdbc原生访问
新建项目 使用 springboot 快速构建工具 选中 web 组件 sql 选中 jdbc mysql
生成 pom.xml 文件依赖如下:
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies>
使用数据库只需要简单的配置:application.yml
spring: datasource: password: 101022li username: root url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.10.129:3306/jdbc driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
使用test 可以进行测试:
@Test public void contextLoads() throws Exception{ System.out.println(dataSource.getClass()); Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection(); System.out.println(connection); connection.close(); }
打印结果:
默认使用 org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource作为数据源
数据源的相关配置都在 DataSourceProperties里面
自动装配原理:org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc
1. 参考DataSourceConfiguration 根据配置创建数据源 默认使用tomcat链接池 可以使用 spring.datasource.type 指定自定义的数据源类型
2.springboot 默认可以支持:
org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource
HikariDataSource
BasicDataSource
3.自定义数据源
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({DataSource.class})
@ConditionalOnProperty(
name = {"spring.datasource.type"}
)
static class Generic {
Generic() {
}
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(DataSourceProperties properties) {
// 使用 DataSourceBuilder 创建数据源 利用反射响应type 数据源 并且绑定相关属性
return properties.initializeDataSourceBuilder().build();
}
}
4. DataSourceInitializer
实现 ApplicationListener 监听
作用:
1)runSchemaScripts() :方法运行建表语句
2)runDataScripts() : 运行插入数据的sql 语句
默认只需要将文件按规则命名:
创建表的sql : schema-*.sql
数据操作sql : data-*.sql
eg:
创建 department.sql 文件 并且放置于 resource文件夹下:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `department`; CREATE TABLE `department` ( `id` int(10) NOT NULL, `departmentName` char(25) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci;
在 yum 配置文件下加入
spring: datasource: password: 101022li username: root url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.10.129:3306/jdbc driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver schema: - classpath:department.sql
重新启动项目 则会自动执行指定的sql 文件
5)自动配置了jdbctemplate 操作数据库, (JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration 有数据源的情况下自动创建一个jdbctemplate)
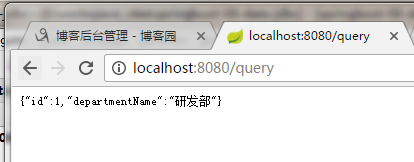
eg: 创建一个 HelloController.java 并且进行访问, 接收返回数据
package com.lixuchun.springboot06.controller; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; @Controller public class HelloController { @Autowired
// 有数据源 系统自动封装template 自动获取就可以 JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; @ResponseBody @GetMapping("/query") public Map<String, Object> map() { List<Map<String, Object>> depList = jdbcTemplate.queryForList("SELECT * FROM department"); return depList.get(0); } }
输出结果:
2. 整合Druid数据源
pom 文件引入 druid 数据源
<!-- 引入自定义的数据源 --> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid</artifactId> <version>1.1.8</version> </dependency>
yum文件 进行修改, 此时的yum文件配置是不好用的 必须单独写一个durid的配置类将数据参数加载金数据源
spring: datasource: password: 101022li username: root url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.10.129:3306/jdbc driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver # schema: # - classpath:department.sql type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource initialSize: 5 minIdle: 5 maxActive: 5 maxWait: 60000 timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000 minEvictableIdletimeMillis: 300000 validationQuery: SELECT 1 FROM DUAL testWhileIDle: true testOnBorrow: false testOnReturn: false poolPreparedStatements: true # 配置监控系统拦截的filters 去掉后监控界面sql无法统计 wall 用于防火墙 filters: stat,wall,log4j # maxPoolPreparedStatmentPerConnectionSize: 20 # useGlobalB
新建一个数据源配置类:
package com.lixuchun.springboot06.Config; import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource; import com.alibaba.druid.support.http.StatViewServlet; import com.alibaba.druid.support.http.WebStatFilter; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.FilterRegistrationBean; import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletRegistrationBean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import javax.servlet.ServletRegistration; import javax.sql.DataSource; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; @Configuration public class DruidConfig { // yum 配置文件中的配置和 注释类进行绑定, spring.datasource 下属性与数据源属性进行全部绑定 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource") @Bean public DataSource druid() { return new DruidDataSource(); } // 配置一个Druid 的监控,可以对数据库操作进行监控 // 1 配置一个管理后台的servlet @Bean public ServletRegistrationBean statViewServlet() { ServletRegistrationBean bean = new ServletRegistrationBean(new StatViewServlet(), "/druid/*"); Map<String , String> initParam = new HashMap<>(); initParam.put("loginUsername", "admin"); initParam.put("loginPassword", "123456"); // initParam.put("allow", ""); // 默认允许所有访问 // initParam.put("deny", "192.168.10."); 不允许访问 bean.setInitParameters(initParam); return bean; } // 2 配置一个监控的filter @Bean public FilterRegistrationBean webStatFilter() { FilterRegistrationBean bean = new FilterRegistrationBean(); bean.setFilter(new WebStatFilter()); Map<String , String> initParam = new HashMap<>(); initParam.put("exclusions", "*.js,*.css,/druid/*"); bean.setInitParameters(initParam); bean.setUrlPatterns(Arrays.asList("/*")); return bean; } }
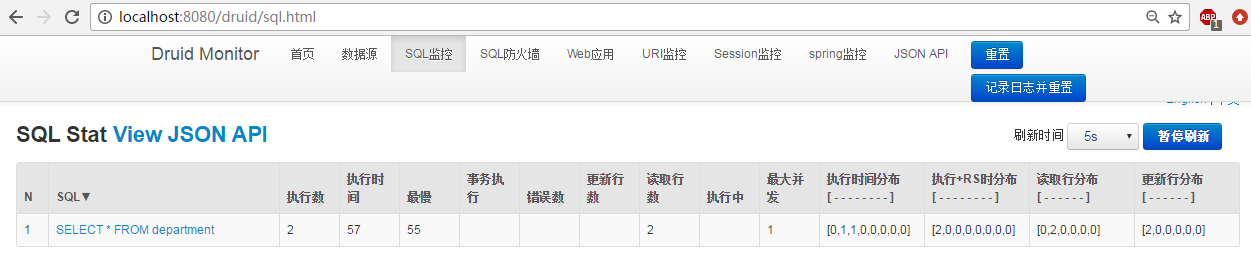
然后启动项目对 数据库进行操作 druid数据源监控后台进行观察
监控后台url : localhost:8080/durid

执行 sql 可以在sql监控中进行监控