shiro(java安全框架)
以下都是综合之前的人加上自己的一些小总结
Apache Shiro是一个强大且易用的Java安全框架,执行身份验证、授权、密码学和会话管理。使用Shiro的易于理解的API,您可以快速、轻松地获得任何应用程序,从最小的移动应用程序到最大的网络和企业应用程序。
Shiro 主要分为来个部分就是认证和授权,在个人感觉来看就是查询数据库做相应的判断而已,Shiro只是一个框架而已,其中的内容需要自己的去构建,前后是自己的,中间是Shiro帮我们去搭建和配置好的
个人认为需要看一下其中的一些源码,更有帮助的深入的去了解Shiro的原理。
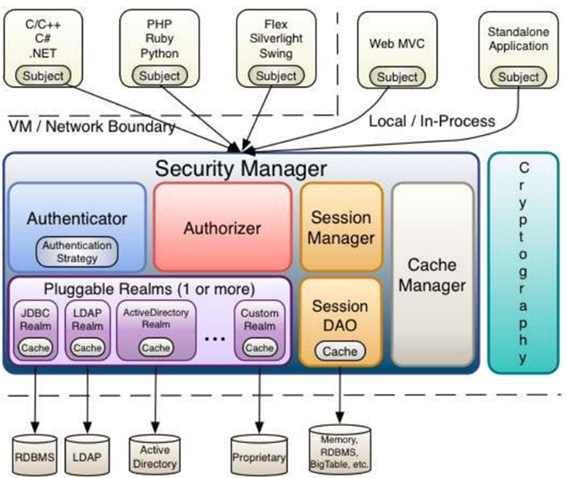
Shiro的主要框架图:
subject:主体,可以是用户也可以是程序,主体要访问系统,系统需要对主体进行认证、授权。
securityManager:安全管理器,主体进行认证和授权都 是通过securityManager进行。
authenticator:认证器,主体进行认证最终通过authenticator进行的。
authorizer:授权器,主体进行授权最终通过authorizer进行的。
sessionManager:web应用中一般是用web容器对session进行管理,shiro也提供一套session管理的方式。
SessionDao: 通过SessionDao管理session数据,针对个性化的session数据存储需要使用sessionDao。
cache Manager:缓存管理器,主要对session和授权数据进行缓存,比如将授权数据通过cacheManager进行缓存管理,和ehcache整合对缓存数据进行管理。
realm:域,领域,相当于数据源,通过realm存取认证、授权相关数据。
方法类的走向:
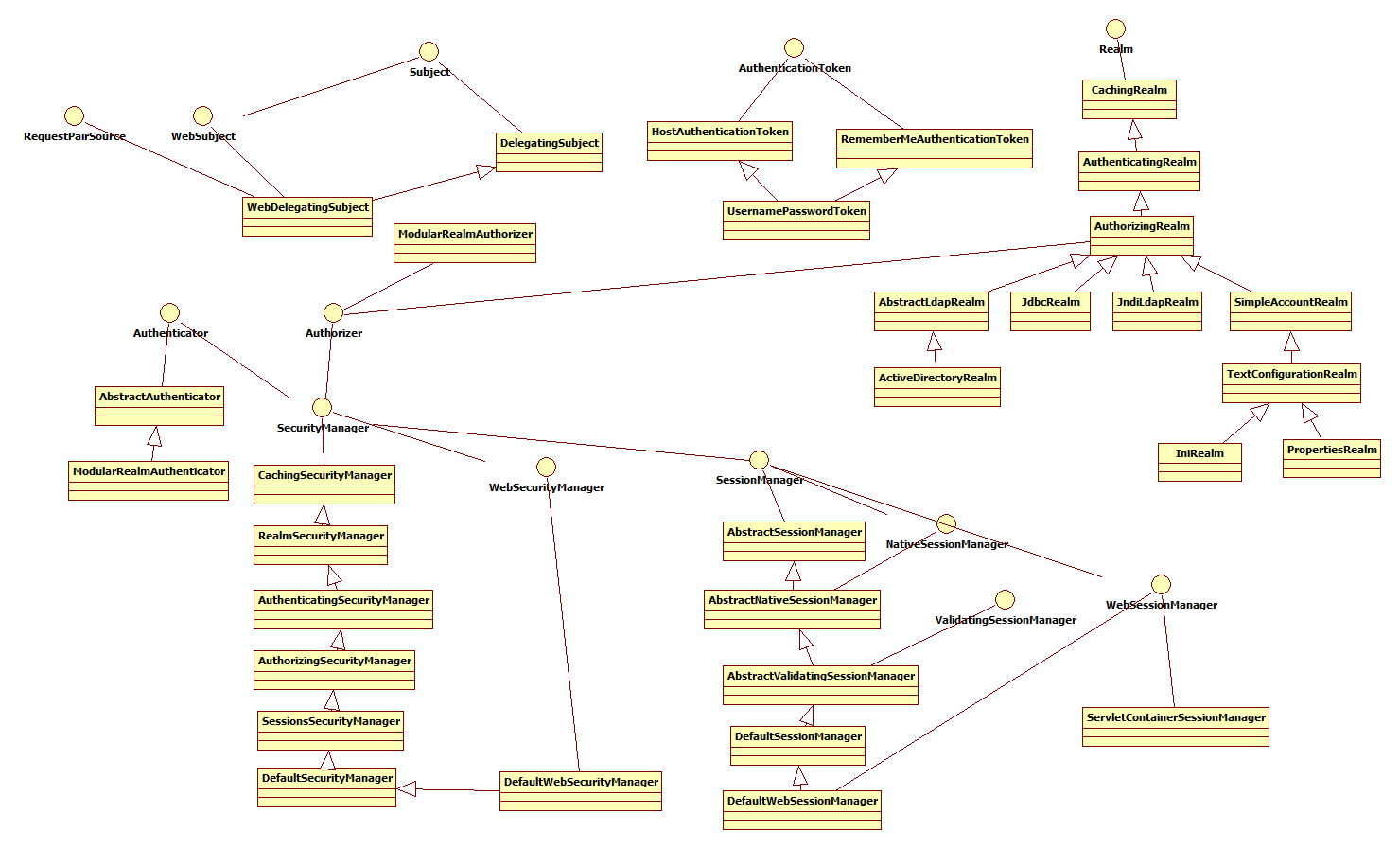
对一些其中的方法的简单说明:
Subject
Subject即主体,外部应用与subject进行交互,subject记录了当前操作用户,将用户的概念理解为当前操作的主体,可能是一个通过浏览器请求的用户,也可能是一个运行的程序。 Subject在shiro中是一个接口,接口中定义了很多认证授相关的方法,外部程序通过subject进行认证授,而subject是通过SecurityManager安全管理器进行认证授权
SecurityManager
SecurityManager即安全管理器,对全部的subject进行安全管理,它是shiro的核心,负责对所有的subject进行安全管理。通过SecurityManager可以完成subject的认证、授权等,实质上SecurityManager是通过Authenticator进行认证,通过Authorizer进行授权,通过SessionManager进行会话管理等。
SecurityManager是一个接口,继承了Authenticator, Authorizer, SessionManager这三个接口。
Authenticator
Authenticator即认证器,对用户身份进行认证,Authenticator是一个接口,shiro提供ModularRealmAuthenticator实现类,通过ModularRealmAuthenticator基本上可以满足大多数需求,也可以自定义认证器。
Authorizer
Authorizer即授权器,用户通过认证器认证通过,在访问功能时需要通过授权器判断用户是否有此功能的操作权限。
realm
Realm即领域,相当于datasource数据源,securityManager进行安全认证需要通过Realm获取用户权限数据,比如:如果用户身份数据在数据库那么realm就需要从数据库获取用户身份信息。
注意:不要把realm理解成只是从数据源取数据,在realm中还有认证授权校验的相关的代码。
sessionManager
sessionManager即会话管理,shiro框架定义了一套会话管理,它不依赖web容器的session,所以shiro可以使用在非web应用上,也可以将分布式应用的会话集中在一点管理,此特性可使它实现单点登录。
SessionDAO
SessionDAO即会话dao,是对session会话操作的一套接口,比如要将session存储到数据库,可以通过jdbc将会话存储到数据库。
CacheManager
CacheManager即缓存管理,将用户权限数据存储在缓存,这样可以提高性能。
Cryptography
Cryptography即密码管理,shiro提供了一套加密/解密的组件,方便开发。比如提供常用的散列、加/解密等功能。
shiro认证与授权的在Web中实现
第一步:添加jar包
<!-- shiro -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-core</artifactId>
<version>1.4.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-spring</artifactId>
<version>1.4.0</version>
</dependency>
第二步:配置web.xml
<!-- shiro 过滤器 start -->
<filter>
<filter-name>shiroFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</filter-class>
<!-- 设置true由servlet容器控制filter的生命周期 -->
<init-param>
<param-name>targetFilterLifecycle</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>shiroFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<!-- shiro 过滤器 end -->
第三步:自定义Realm 继承AuthorizingRealm 重写 AuthorizationInfo(授权) 和 AuthenticationInfo(认证)
以下只是简单的测试
以下都是根据个人的设置和需求改变的。现在数据是死的,运用的时候需要从数据库中得到
/**
* @author zhouguanglin
* @date 2018/2/26 14:05
*/
public class CustomRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
/**
* 授权
* @param principalCollection
* @return
*/
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
String userName = (String) principalCollection.getPrimaryPrincipal();
List<String> permissionList=new ArrayList<String>();
permissionList.add("user:add");
permissionList.add("user:delete");
if (userName.equals("zhou")) {
permissionList.add("user:query");
}
SimpleAuthorizationInfo info=new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
info.addStringPermissions(permissionList);
info.addRole("admin");
return info;
}
/**
* 认证
* @param authenticationToken
* @return
* @throws AuthenticationException
*/
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException {
String userName = (String) authenticationToken.getPrincipal();
if ("".equals(userName)) {
return null;
}
SimpleAuthenticationInfo info = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(userName,"123456",this.getName());
return info;
}
}
第四步:配置spring-shiro.xml
这里面都是按照自己的需求去配置的
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--开启shiro的注解-->
<bean id="advisorAutoProxyCreator" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator">
<property name="proxyTargetClass" value="true"></property>
</bean>
<bean class="org.apache.shiro.spring.security.interceptor.AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor"/>
<!--注入自定义的Realm-->
<bean id="customRealm" class="com.test.realm.CustomRealm"></bean>
<bean id="securityManager" class="org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.DefaultWebSecurityManager">
<property name="realm" ref="customRealm"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置ShiroFilter-->
<bean id="shiroFilter" class="org.apache.shiro.spring.web.ShiroFilterFactoryBean">
<property name="securityManager" ref="securityManager"></property>
<!--登入页面-->
<property name="loginUrl" value="/login.jsp"></property>
<!--登入成功页面-->
<property name="successUrl" value="/index.jsp"/>
<property name="filters">
<map>
<!--退出过滤器-->
<entry key="logout" value-ref="logoutFilter" />
</map>
</property>
<!--URL的拦截-->
<property name="filterChainDefinitions" >
<value>
/share = authc
/logout = logout
</value>
</property>
</bean>
<!--自定义退出LogoutFilter-->
<bean id="logoutFilter" class="com.test.filter.SystemLogoutFilter">
<property name="redirectUrl" value="/login"/>
</bean>
</beans>
一些属性的意义:
securityManager: 这个属性是必须的。
loginUrl: 没有登录的用户请求需要登录的页面时自动跳转到登录页面,不是必须的属性,不输入地址的话会自动寻找项目web项目的根目录下的”/login.jsp”页面。
successUrl: 登录成功默认跳转页面,不配置则跳转至”/”。如果登陆前点击的一个需要登录的页面,则在登录自动跳转到那个需要登录的页面。不跳转到此。
unauthorizedUrl: 没有权限默认跳转的页面。
Shiro中默认的过滤器:
| 过滤器名称 | 过滤器类 | 描述 |
| anon | org.apache.shiro.web.filter.authc.AnonymousFilter | 匿名过滤器 |
| authc | org.apache.shiro.web.filter.authc.FormAuthenticationFilter | 如果继续操作,需要做对应的表单验证否则不能通过 |
| authcBasic | org.apache.shiro.web.filter.authc.BasicHttpAuthenticationFilter | 基本http验证过滤,如果不通过,跳转屋登录页面 |
| logout | org.apache.shiro.web.filter.authc.LogoutFilter | 登录退出过滤器 |
| noSessionCreation | org.apache.shiro.web.filter.session.NoSessionCreationFilter | 没有session创建过滤器 |
| perms | org.apache.shiro.web.filter.authz.PermissionsAuthorizationFilter | 权限过滤器 |
| port | org.apache.shiro.web.filter.authz.PortFilter | 端口过滤器,可以设置是否是指定端口如果不是跳转到登录页面 |
| rest | org.apache.shiro.web.filter.authz.HttpMethodPermissionFilter | http方法过滤器,可以指定如post不能进行访问等 |
| roles | org.apache.shiro.web.filter.authz.RolesAuthorizationFilter | 角色过滤器,判断当前用户是否指定角色 |
| ssl | org.apache.shiro.web.filter.authz.SslFilter | 请求需要通过ssl,如果不是跳转回登录页 |
| user | org.apache.shiro.web.filter.authc.UserFilter | 如果访问一个已知用户,比如记住我功能,走这个过滤器 |
在spring中直接引入<import resource="spring-shiro.xml"></import>
第五步:在spring-mvc.xml中配置权限的控制 异常的跳转
<!-- 未认证或未授权时跳转必须在springmvc里面配,spring-shiro里的shirofilter配不生效 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleMappingExceptionResolver">
<property name="exceptionMappings">
<props>
<!--表示捕获的异常 -->
<prop key="org.apache.shiro.authz.UnauthorizedException">
<!--捕获该异常时跳转的路径 -->
/403
</prop>
<!--表示捕获的异常 -->
<prop key="org.apache.shiro.authz.UnauthenticatedException">
<!--捕获该异常时跳转的路径 -->
/403
</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
403是错误页面
第六步:在controller中测试使用的验证登入
@RequestMapping(value = "/login", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String login(String userName, String passwd, Model model) {
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken(userName, passwd);
try {
subject.login(token);
} catch (UnknownAccountException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
model.addAttribute("userName", "用户名错误!");
return "login";
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
model.addAttribute("passwd", "密码错误");
return "login";
}
return "index";
}
之后的都是HTML页面的跳转
有关HTML中的一些shiro设置:
在使用Shiro标签库前,首先需要在JSP引入shiro标签:
<%@ taglib prefix="shiro" uri="http://shiro.apache.org/tags" %>1、介绍Shiro的标签guest标签 :验证当前用户是否为“访客”,即未认证(包含未记住)的用户。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
<shiro:guest> Hi there! Please <a href="login.jsp">Login</a> or <a href="signup.jsp">Signup</a> today! </shiro:guest> |
2、user标签 :认证通过或已记住的用户。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
<shiro:user> Welcome back John! Not John? Click <a href="login.jsp">here<a> to login. </shiro:user> |
3、authenticated标签 :已认证通过的用户。不包含已记住的用户,这是与user标签的区别所在。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
<shiro:authenticated> <a href="updateAccount.jsp">Update your contact information</a>. </shiro:authenticated> |
4、notAuthenticated标签 :未认证通过用户,与authenticated标签相对应。与guest标签的区别是,该标签包含已记住用户。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
<shiro:notAuthenticated> Please <a href="login.jsp">login</a> in order to update your credit card information. </shiro:notAuthenticated> |
5、principal 标签 :输出当前用户信息,通常为登录帐号信息。
|
1
|
Hello, <shiro:principal/>, how are you today? |
6、hasRole标签 :验证当前用户是否属于该角色。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
<shiro:hasRole name="administrator"> <a href="admin.jsp">Administer the system</a> </shiro:hasRole> |
7、lacksRole标签 :与hasRole标签逻辑相反,当用户不属于该角色时验证通过。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
<shiro:lacksRole name="administrator"> Sorry, you are not allowed to administer the system. </shiro:lacksRole> |
8、hasAnyRole标签 :验证当前用户是否属于以下任意一个角色。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
<shiro:hasAnyRoles name="developer, project manager, administrator"> You are either a developer, project manager, or administrator. </shiro:lacksRole> |
9、hasPermission标签 :验证当前用户是否拥有指定权限。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
<shiro:hasPermission name="user:create"> <a href="createUser.jsp">Create a new User</a> </shiro:hasPermission> |
10、lacksPermission标签 :与hasPermission标签逻辑相反,当前用户没有制定权限时,验证通过。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
<shiro:hasPermission name="user:create"> <a href="createUser.jsp">Create a new User</a> </shiro:hasPermission> |
参考文章 :
http://www.cnblogs.com/yangang2013/p/5716928.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/jifeng/p/4500410.html