写在前面:今天突然发现还没有写过最小生成树的博客,然后调堆优化prim板子好久才调出来……赶紧写篇博客来保命。
一、最小生成树概念:
在一个n个点的有向图中,选取n-1条边使所有顶点两两联通,那么这个边集叫做这个图的一个生成树
在所有的生成树中,边权和最小的那一个叫做图的最小生成树。
二、Kruskal算法
求图的最小生成树的常用方法有两种,Kruskal和Prim
kruskal算法的步骤如下:
(1)将所有边按边权从小到大排序
(2)选取一条边权最小且两顶点未联通的边并把它连上
(3)重复步骤2,直到连上了n-1条边为止;若所有的边都找完仍未连n-1条边,则图不连通
看图:
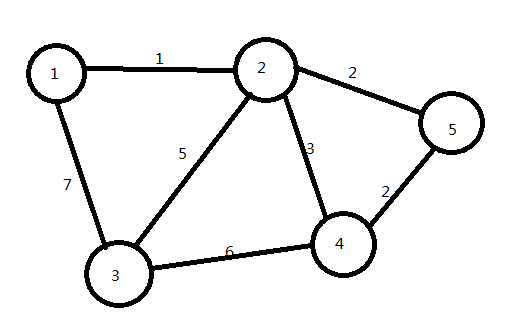
我们对该图进行Kruskal算法:
(1)选取一条边权最小且两顶点未联通的边并把它连上
即边1→2
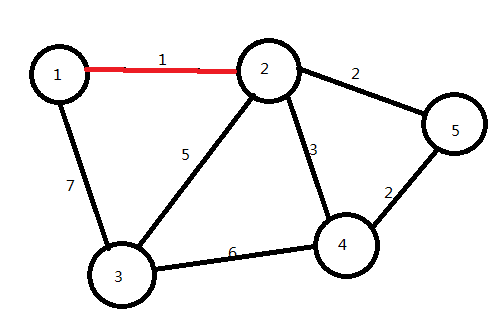
重复以上步骤:

下面我们找到最短的边是2→4
我们要连它吗?
不要!
因为点2和点4已经联通,如果再连就会形成环,显然不是最优解。
我们将它跳过,选取2→3
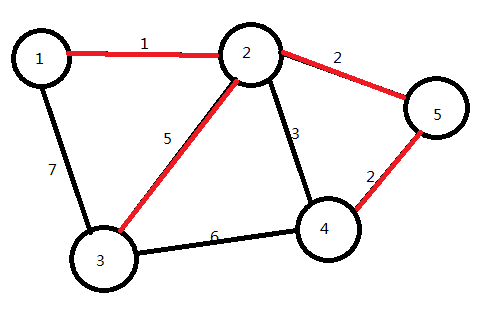
已选取n-1条边,算法结束。红色边即为图的最小生成树
以上判断两点是否联通可以用并查集来实现
代码如下:

#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstdlib> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> #include<cmath> using namespace std; inline int read() { int f=1,x=0; char ch=getchar(); while(ch<'0' || ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') f=-1; ch=getchar();} while(ch>='0' && ch<='9') {x=x*10+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();} return x*f; } struct node { int u,v,w; }r[400005]; bool cmp(node a,node b) { return a.w<b.w; } int n,m,cnt,ans; int f[5005]; int i,j; int f_ancestor(int x) { return x==f[x] ? x : f[x]=f_ancestor(f[x]); } int main() { n=read(); m=read(); for(i=1;i<=n;i++) f[i]=i; for(i=1;i<=m;i++) { r[i].u=read(); r[i].v=read(); r[i].w=read(); r[i+m].v=r[i].u; r[i+m].u=r[i].v; r[i+m].w=r[i].w; } m*=2; sort(r+1,r+m+1,cmp); for(i=1;i<=m;i++) { int f1=f_ancestor(r[i].u),f2=f_ancestor(r[i].v); if(f1!=f2) { f[f2]=f1; cnt++; ans+=r[i].w; } if(cnt==n-1) break; } if(cnt==n-1) printf("%d",ans); else printf("orz");//图不连通 return 0; }
kruskal算法的时间复杂度为O(MlogM+并查集查询时间*N)
三、Prim算法
Prim算法的步骤如下:
(1)定义两个集合U和V,开始时U集合为空,V集合中有所有点
定义dis数组表示每个点距离U集合中点的最短距离
(2)选取一个未选取过且dis值最小的点(起始时可以是任意点),设该点为点k
(3)将点k加入U集合中
(4)k为中间点,修改V集合中点的dis值。即dis[j]=min(dis[j],w(k,j)) (j为V集合中的点)
(5)重复步骤234,直到U集合中有了n个点(若U集合最后meiyoun个点,则图不连通)
看图:

进行Prim算法
(1)选取任意一个点,如点1
dis赋初值
(2)将点1加入U集合,更新dis值
U={1}

(3)选取dis值最小的点(点2),将它加入U集合,连接边1→2,更新dis值
ans=1
U={1,2}

(4)选取dis值最小的点(点5),将它加入U集合,连接边2→5,更新dis值
ans=3
U={1,2,5}

(5)选取dis值最小的点(点4),将它加入U集合,连接边5→4,更新dis值
ans=5
U={1,2,5,4}
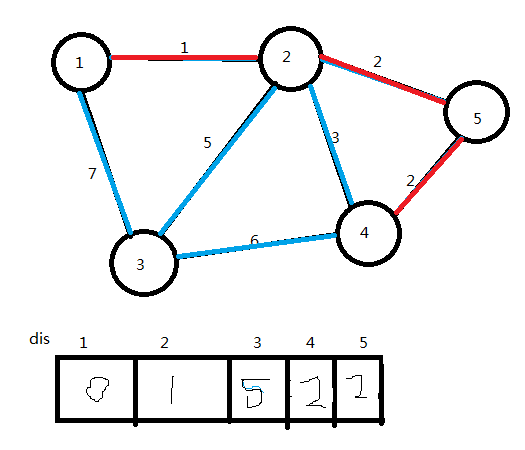
(6)选取dis值最小的点(点3),将它加入U集合,连接边2→3,更新dis值
ans=10
U={1,2,5,4,3}
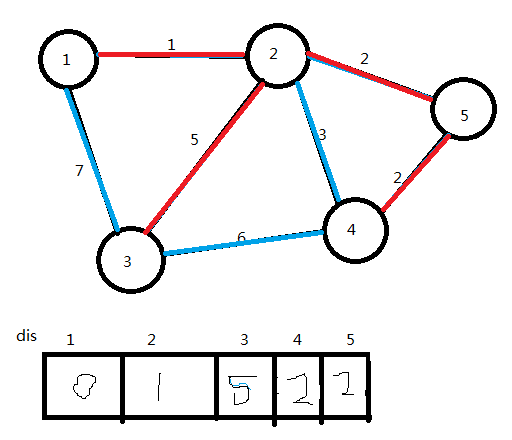
U集合中已有了n个点,算法结束。图中红色部分即为图的最小生成树
代码如下:

#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstdlib> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> #include<cmath> #include<queue> using namespace std; inline int read() { int f=1,x=0; char ch=getchar(); while(ch<'0' || ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') f=-1; ch=getchar();} while(ch>='0' && ch<='9') {x=x*10+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();} return x*f; } struct node { int dis,h; bool operator < (const node &a) const { return a.dis<dis; } }d[5005]; int v[400005],w[400005],head[5005],nxt[400005]; bool book[5005]; int n,m,cnt,ans,tot; int i,j; priority_queue <node> Q; void add(int a,int b,int c) { v[++cnt]=b; w[cnt]=c; nxt[cnt]=head[a]; head[a]=cnt; } int main() { memset(head,-1,sizeof(head)); n=read(); m=read(); int a,b,c; for(i=1;i<=m;i++) { a=read();b=read();c=read(); add(a,b,c); add(b,a,c); } for(i=1;i<=n;i++) d[i].dis=1000000000,d[i].h=i; d[1].dis=0; Q.push(d[1]); while(!Q.empty()) { node x=Q.top(); Q.pop(); if(x.dis!=d[x.h].dis) continue;//处理重边 book[x.h]=1; ans+=d[x.h].dis; tot++; for(j=head[x.h];j!=-1;j=nxt[j]) { if(!book[v[j]] && d[v[j]].dis>w[j]) { d[v[j]].dis=w[j]; Q.push(d[v[j]]); } } } if(tot==n) printf("%d",ans); else printf("orz");//图不连通 return 0; }
Prim算法的时间复杂度为O((N+M)logM)
四、总结
两种算法都是基于贪心的思想
若要彻底掌握这两种算法,不仅要非常熟悉它们的流程,还要会在适当的时刻使用
本文部分内容参考《信息学奥赛一本通.提高篇》第三部分第一章 最小生成树
若需转载,请注明https://www.cnblogs.com/llllllpppppp/p/9749533.html
~祝大家编程顺利~
