1:SpringDataJPA是JPA规范的再次封装抽象,底层还是使用了Hibernate的JPA技术实现,是属于Spring的生成体系中的一部分
2:SpringData的结构(七个接口)
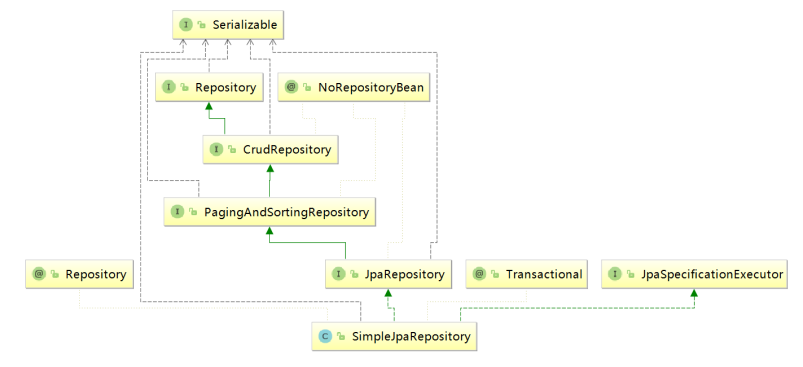
操作数据库的方式一:继承JpaRepository口后操作数据库
1:在Repository层新建一个基础接口
1 @NoRepositoryBean //告诉JPA不要创建对应接口的bean对象 2 public interface BaseReposittory <T,ID extends Serializable> extends JpaRepository<T,ID>{ 3 }
2:再建一个你所要操作的类型的接口去继承 这里以实体类Employee举例 这里Long是数据库中主键的类型 完成后就已经具备了基础的CRUD 和分页排序的功能
1 public interface EmployeeRepository extends BaseReposittory<Employee,Long>{
注意:在操作数据库时 添加和修改所使用的都是save()方法 ;可以自行测试 这里测试一个分页排序
1 @Test//分页排序 2 public void pageAndSort() throws Exception{ 3 Sort sort = new Sort(Sort.Direction.DESC,"age"); 4 Pageable page = new PageRequest(0,10,sort); 5 Page<Employee> employees = employeeRepository.findAll(page); 6 employees.forEach(e->{ 7 System.out.println(e); 8 }); 9 }
基础查询和分页排序底层已经定义好可以直接使用 现在我们来自定义查询; 查询方法写在EmployeeRepository 中
自定义查询
方式一:按照规范创建查询方法,一般按照java驼峰式书写规范加一些特定关键字
例:
1 //根据名称模糊查询 2 List<Employee> findByUsernameLike(String username); 3 //根据名称进行查询 4 List<Employee> findByUsername(String username);
查询规则如下:
|
表达式 |
例子 |
hql查询语句 |
|
And |
findByLastnameAndFirstname |
… where x.lastname = ?1 and x.firstname = ?2 |
|
Or |
findByLastnameOrFirstname |
… where x.lastname = ?1 or x.firstname = ?2 |
|
Is,Equals |
findByFirstname,findByFirstnameIs,findByFirstnameEqual |
… where x.firstname = 1? |
|
Between |
findByStartDateBetween |
… where x.startDate between 1? and ?2 |
|
LessThan(lt) |
findByAgeLessThan |
… where x.age < ?1 |
|
LessThanEqual(le) |
findByAgeLessThanEqual |
… where x.age <= ?1 |
|
GreaterThan |
findByAgeGreaterThan |
… where x.age > ?1 |
|
GreaterThanEqual |
findByAgeGreaterThanEqual |
… where x.age >= ?1 |
|
After |
findByStartDateAfter |
… where x.startDate > ?1 |
|
Before |
findByStartDateBefore |
… where x.startDate < ?1 |
|
IsNull |
findByAgeIsNull |
… where x.age is null |
|
IsNotNull,NotNull |
findByAge(Is)NotNull |
… where x.age not null |
|
Like |
findByFirstnameLike |
… where x.firstname like ?1 |
|
NotLike |
findByFirstnameNotLike |
… where x.firstname not like ?1 |
|
StartingWith |
findByFirstnameStartingWith |
… where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound with appended %) |
|
EndingWith |
findByFirstnameEndingWith |
… where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound with prepended %) |
|
Containing |
findByFirstnameContaining |
… where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound wrapped in %) |
|
OrderBy |
findByAgeOrderByLastnameDesc |
… where x.age = ?1 order by x.lastname desc |
|
Not |
findByLastnameNot |
… where x.lastname <> ?1 |
|
In |
findByAgeIn(Collection ages) |
… where x.age in ?1 |
|
NotIn |
findByAgeNotIn(Collection age) |
… where x.age not in ?1 |
|
True |
findByActiveTrue() |
… where x.active = true |
|
False |
findByActiveFalse() |
… where x.active = false |
|
IgnoreCase |
findByFirstnameIgnoreCase |
… where UPPER(x.firstame) = UPPER(?1) |
方式二:@Query注解查询
在EmployeeRepository 按照查询方法的命名规则,其实是比较麻烦的如果我们想不遵循 查询方法的命名规则,还可以使用@Query的方法进行查询。只需要将@Query定义在Respository的方法之上即可
1:使用jpql语句操作数据库
例:
1 //根据用户名查询(这里写必需在问号后加顺序) 2 @Query("select e from Employee e where e.username = ?1") 3 Employee query01(String name); 4 //根据用户名模糊查询(这里写必需在问号后加顺序) 5 @Query("select e from Employee e where e.username like ?1") 6 List<Employee> query02(String name); 7 //根据用户名与邮件进行模糊查询(这里写必需在问号后加顺序) 8 @Query("select e from Employee e where e.username like ?1 and e.email like ?2") 9 List<Employee> query03(String name, String email);
2:如果想用原生sql操作数据库只需在注解@Query中加nativeQuery =true
例:
1 //查询所有 2 @Query(nativeQuery =true,value = "select * from employee where username=?;") 3 Employee query04(String name);
方式三:继承接口JpaSpecificationExecutor
JpaSpecificationExecutor的认识
JpaSpecificationExecutor(JPA规则执行者)是JPA2.0提供的Criteria API的使用封装,可以用于动态生成Query来满足我们业务中的各种复杂场景。
Spring Data JPA为我们提供了JpaSpecificationExecutor接口,只要简单实现toPredicate方法就可以实现复杂的查询。所有查询都要求传入一个Specification对象
1:BaseReposittory的操作
@NoRepositoryBean //告诉JPA不要创建对应接口的bean对象 public interface BaseReposittory <T,ID extends Serializable> extends JpaRepository<T,ID>,JpaSpecificationExecutor<T> { }
2:测试:直接来个多条件查询
1 /** 2 * 根据相应的规则(Specification) 查询对应数据 3 * Predicate: where username=? and email =? 4 * root : 根 -> 可以获取到类中的属性(username,email) 5 * criteriaQuery: 如select,from,where,group by ,order by 等 6 * criteriaBuilder:解决 username=? / username like ? / age > ? 7 * 多个条件结合 username=? and/or age > ? 8 */ 9 @Test//多条件查询+分页+排序 10 public void testJpaSpecificationExecutor() throws Exception{ 11 //先定义规范 12 Specification spec= new Specification<Employee>() { 13 @Override 14 public Predicate toPredicate(Root<Employee> root, CriteriaQuery<?> cq, CriteriaBuilder cd) { 15 Path usernamePath = root.get("username"); 16 Predicate p1 = cd.like(usernamePath, "%1%"); 17 Path emailPath = root.get("email"); 18 Predicate p2 = cd.like(emailPath, "%2%"); 19 Path agePath = root.get("age"); 20 Predicate p3 = cd.ge(agePath, 18);//le 表示小于 ge表示大于 21 //多个条件连接起来 22 Predicate p = cd.and(p1, p2, p3); 23 return p; 24 } 25 }; 26 //进行排序 27 Sort sort = new Sort(Sort.Direction.ASC,"username"); 28 //进行分页 29 Pageable page=new PageRequest(0,10,sort); 30 //查询数据库 31 Page p = employeeRepository.findAll(spec, page); 32 p.forEach(e->{ 33 System.out.println(e); 34 }); 35 }
Root:查询哪个表(定位到表和字段-> 用于拿到表中的字段)
* 可以查询和操作的实体的根
* Root接口:代表Criteria查询的根对象,Criteria查询的查询根定义了实体类型,能为将来导航获得想要的结果,它与SQL查询中的FROM子句类似
* Root<Employee> 相当于 from Employee
* Root<Product> 相当于 from Product
* CriteriaQuery:查询哪些字段,排序是什么(主要是把多个查询的条件连系起来)
* CriteriaBuilder:字段之间是什么关系,如何生成一个查询条件,每一个查询条件都是什么方式
* 主要判断关系(和这个字段是相等,大于,小于like等)
* Predicate(Expression):单独每一条查询条件的详细描述 整个 where xxx=xx and yyy=yy ...
方式四:使用jpa-spec插件的前提是要实现JpaSpecificationExecutor接口(我这里是接口继承了接口)
1:在Maven项目中pom.xml引入包
<!-- jpa的SpecificationSpecification功能封装 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.wenhao</groupId>
<artifactId>jpa-spec</artifactId>
<version>3.1.1</version>
<!-- 把所有依赖都过滤 -->
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>*</groupId>
<artifactId>*</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
2:功能测试:
1 @Test// 多个条件查询 +分页+排序 2 public void testSpec() throws Exception{ 3 Specification<Employee> spec = Specifications.<Employee>and() 4 .like("username","%1%") 5 .like("email","%2%") 6 .ge("age", 20) 7 .build(); 8 Sort sort = new Sort(Sort.Direction.DESC,"age");//根据年龄排序 9 Pageable page = new PageRequest(0,10,sort); 10 Page<Employee> list = employeeRepository.findAll(spec, page); 11 list.forEach(e->{ 12 System.out.println(e); 13 }); 14 }