基本操作
# 增
models.Tb1.objects.create(c1='xx', c2='oo') 增加一条数据,可以接受字典类型数据 **kwargs
obj = models.Tb1(c1='xx', c2='oo')
obj.save()
#查
models.Tb1.objects.get(id=123) # 获取单条数据,不存在则报错(不建议)
models.Tb1.objects.all() # 获取全部
models.Tb1.objects.filter(name='seven') # 获取指定条件的数据
models.Tb1.objects.exclude(name='seven') # 获取指定条件的数据
#删
models.Tb1.objects.filter(name='seven').delete() # 删除指定条件的数据
#改
models.Tb1.objects.filter(name='seven').update(gender='0') # 将指定条件的数据更新,均支持 **kwargs
obj = models.Tb1.objects.get(id=1)
obj.c1 = '111'
obj.save() # 修改单条数据
进阶操作
获取个数
models.Tb1.objects.filter(name='seven').count()
大于,小于
models.Tb1.objects.filter(id__gt=1) # 获取id大于1的值
models.Tb1.objects.filter(id__gte=1) # 获取id大于等于1的值
models.Tb1.objects.filter(id__lt=10) # 获取id小于10的值
models.Tb1.objects.filter(id__lte=10) # 获取id小于10的值
models.Tb1.objects.filter(id__lt=10, id__gt=1) # 获取id大于1 且 小于10的值
in
如果需要 in 很多连续值的话用range
models.Tb1.objects.filter(id__in=[11, 22, 33]) # 获取id等于11、22、33的数据
models.Tb1.objects.exclude(id__in=[11, 22, 33]) # not in
isnull, null 和 空不是一个概念
Entry.objects.filter(pub_date__isnull=True)
contains
models.Tb1.objects.filter(name__contains="ven")
models.Tb1.objects.filter(name__icontains="ven") # icontains大小写不敏感
models.Tb1.objects.exclude(name__icontains="ven")
range, 区别于 python range 的是 orm 的 range 的左右都是闭合标签
models.Tb1.objects.filter(id__range=[1, 2]) # 范围bettwen and
其他类似
startswith,istartswith, endswith, iendswith,
order by
models.Tb1.objects.filter(name='seven').order_by('id') # asc
models.Tb1.objects.filter(name='seven').order_by('-id') # desc
group by
from django.db.models import Count, Min, Max, Sum
models.Tb1.objects.filter(c1=1).values('id').annotate(c=Count('num'))
SELECT "app01_tb1"."id", COUNT("app01_tb1"."num") AS "c" FROM "app01_tb1" WHERE "app01_tb1"."c1" = 1 GROUP BY "app01_tb1"."id"
limit 、offset
models.Tb1.objects.all()[10:20]
regex正则匹配,iregex 不区分大小写
Entry.objects.get(title__regex=r'^(An?|The) +')
Entry.objects.get(title__iregex=r'^(an?|the) +')
date
Entry.objects.filter(pub_date__date=datetime.date(2005, 1, 1))
Entry.objects.filter(pub_date__date__gt=datetime.date(2005, 1, 1))
year
Entry.objects.filter(pub_date__year=2005)
Entry.objects.filter(pub_date__year__gte=2005)
month
Entry.objects.filter(pub_date__month=12)
Entry.objects.filter(pub_date__month__gte=6)
day
Entry.objects.filter(pub_date__day=3)
Entry.objects.filter(pub_date__day__gte=3)
week_day
Entry.objects.filter(pub_date__week_day=2)
Entry.objects.filter(pub_date__week_day__gte=2)
hour
Event.objects.filter(timestamp__hour=23)
Event.objects.filter(time__hour=5)
Event.objects.filter(timestamp__hour__gte=12)
minute
Event.objects.filter(timestamp__minute=29)
Event.objects.filter(time__minute=46)
Event.objects.filter(timestamp__minute__gte=29)
second
Event.objects.filter(timestamp__second=31)
Event.objects.filter(time__second=2)
Event.objects.filter(timestamp__second__gte=31)
其他操作
##################################################################
# PUBLIC METHODS THAT ALTER ATTRIBUTES AND RETURN A NEW QUERYSET #
##################################################################
def all(self)
# 获取所有的数据对象
def filter(self, *args, **kwargs)
# 条件查询
# 条件可以是:参数,字典,Q
def exclude(self, *args, **kwargs)
# 条件查询
# 条件可以是:参数,字典,Q
def select_related(self, *fields)
性能相关:表之间进行join连表操作,一次性获取关联的数据。
model.tb.objects.all().select_related()
model.tb.objects.all().select_related('外键字段')
model.tb.objects.all().select_related('外键字段__外键字段')
def prefetch_related(self, *lookups)
性能相关:多表连表操作时速度会慢,使用其执行多次SQL查询在Python代码中实现连表操作。
# 获取所有用户表
# 获取用户类型表where id in (用户表中的查到的所有用户ID)
models.UserInfo.objects.prefetch_related('外键字段')
from django.db.models import Count, Case, When, IntegerField
Article.objects.annotate(
numviews=Count(Case(
When(readership__what_time__lt=treshold, then=1),
output_field=CharField(),
))
)
students = Student.objects.all().annotate(num_excused_absences=models.Sum(
models.Case(
models.When(absence__type='Excused', then=1),
default=0,
output_field=models.IntegerField()
)))
def annotate(self, *args, **kwargs)
# 用于实现聚合group by查询
from django.db.models import Count, Avg, Max, Min, Sum
v = models.UserInfo.objects.values('u_id').annotate(uid=Count('u_id'))
# SELECT u_id, COUNT(ui) AS `uid` FROM UserInfo GROUP BY u_id
v = models.UserInfo.objects.values('u_id').annotate(uid=Count('u_id')).filter(uid__gt=1)
# SELECT u_id, COUNT(ui_id) AS `uid` FROM UserInfo GROUP BY u_id having count(u_id) > 1
v = models.UserInfo.objects.values('u_id').annotate(uid=Count('u_id',distinct=True)).filter(uid__gt=1)
# SELECT u_id, COUNT( DISTINCT ui_id) AS `uid` FROM UserInfo GROUP BY u_id having count(u_id) > 1 先distinct再count
def distinct(self, *field_names)
# 用于distinct去重
models.UserInfo.objects.values('nid').distinct()
# select distinct nid from userinfo
注:只有在PostgreSQL中才能使用distinct进行去重
def order_by(self, *field_names)
# 用于排序
models.UserInfo.objects.all().order_by('-id','age')
def extra(self, select=None, where=None, params=None, tables=None, order_by=None, select_params=None)
# 构造额外的查询条件或者映射,如:子查询
Entry.objects.extra(select={'new_id': "select col from sometable where othercol > %s"}, select_params=(1,))
Entry.objects.extra(where=['headline=%s'], params=['Lennon'])
Entry.objects.extra(where=["foo='a' OR bar = 'a'", "baz = 'a'"])
Entry.objects.extra(select={'new_id': "select id from tb where id > %s"}, select_params=(1,), order_by=['-nid'])
应对的情况是select nid 1 from tb; select nid, (select name from tb2 where tb2.id=tb.id) from tb where ... order by ...
按平均成绩从低到高 显示所有学生的“语文”、“数学”、“英语”三门的课程成绩,按如下形式显示: 学生ID,语文,数学,英语,有效课程数,有效平均分;
select sc.student_id,
(select num from score left join course on score.course_id = course.cid where course.cname = "生物" and score.student_id=sc.student_id) as sy,
(select num from score left join course on score.course_id = course.cid where course.cname = "物理" and score.student_id=sc.student_id) as wl,
(select num from score left join course on score.course_id = course.cid where course.cname = "体育" and score.student_id=sc.student_id) as ty,
count(sc.course_id),
avg(sc.num)
from score as sc
group by student_id desc
def reverse(self):
# 倒序
models.UserInfo.objects.all().order_by('-nid').reverse()
# 注:如果存在order_by,reverse则是倒序,如果多个排序则一一倒序
def defer(self, *fields):
models.UserInfo.objects.defer('username','id')
或
models.UserInfo.objects.filter(...).defer('username','id')
#映射中排除某列数据
def only(self, *fields):
#仅取某个表中的数据
models.UserInfo.objects.only('username','id')
或
models.UserInfo.objects.filter(...).only('username','id')
def using(self, alias):
指定使用的数据库,参数为别名(setting中的设置)
##################################################
# PUBLIC METHODS THAT RETURN A QUERYSET SUBCLASS #
##################################################
def raw(self, raw_query, params=None, translations=None, using=None):
# 执行原生SQL
models.UserInfo.objects.raw('select * from userinfo')
# 如果SQL是其他表时,必须将名字设置为当前UserInfo对象的主键列名
models.UserInfo.objects.raw('select id as nid from 其他表')
# 为原生SQL设置参数
models.UserInfo.objects.raw('select id as nid from userinfo where nid>%s', params=[12,])
# 将获取的到列名转换为指定列名
name_map = {'first': 'first_name', 'last': 'last_name', 'bd': 'birth_date', 'pk': 'id'}
Person.objects.raw('SELECT * FROM some_other_table', translations=name_map)
# 指定数据库
models.UserInfo.objects.raw('select * from userinfo', using="default")
################### 原生SQL ###################
from django.db import connection, connections
cursor = connection.cursor() # cursor = connections['default'].cursor()
cursor.execute("""SELECT * from auth_user where id = %s""", [1])
row = cursor.fetchone() # fetchall()/fetchmany(..)
def values(self, *fields):
# 获取每行数据为字典格式
def values_list(self, *fields, **kwargs):
# 获取每行数据为元祖
def dates(self, field_name, kind, order='ASC'):
# 根据时间进行某一部分进行去重查找并截取指定内容
# kind只能是:"year"(年), "month"(年-月), "day"(年-月-日)
# order只能是:"ASC" "DESC"
# 并获取转换后的时间
- year : 年-01-01
- month: 年-月-01
- day : 年-月-日
models.DatePlus.objects.dates('ctime','day','DESC')
def datetimes(self, field_name, kind, order='ASC', tzinfo=None):
# 根据时间进行某一部分进行去重查找并截取指定内容,将时间转换为指定时区时间
# kind只能是 "year", "month", "day", "hour", "minute", "second"
# order只能是:"ASC" "DESC"
# tzinfo时区对象
models.DDD.objects.datetimes('ctime','hour',tzinfo=pytz.UTC)
models.DDD.objects.datetimes('ctime','hour',tzinfo=pytz.timezone('Asia/Shanghai'))
"""
pip3 install pytz
import pytz
pytz.all_timezones
pytz.timezone(‘Asia/Shanghai’)
"""
def none(self):
# 空QuerySet对象
####################################
# METHODS THAT DO DATABASE QUERIES #
####################################
def aggregate(self, *args, **kwargs):
# 聚合函数,获取字典类型聚合结果
from django.db.models import Count, Avg, Max, Min, Sum
result = models.UserInfo.objects.aggregate(k=Count('u_id', distinct=True), n=Count('nid'))
===> {'k': 3, 'n': 4}
def count(self):
# 获取个数
def get(self, *args, **kwargs):
# 获取单个对象
def create(self, **kwargs):
# 创建对象
def bulk_create(self, objs, batch_size=None):
# 批量插入
# batch_size表示一次插入的个数
objs = [
models.DDD(name='r11'),
models.DDD(name='r22')
]
models.DDD.objects.bulk_create(objs, 10)
def get_or_create(self, defaults=None, **kwargs):
# 如果存在,则获取,否则,创建
# defaults 指定创建时,其他字段的值, created是True或者False,create只能create一条
obj, created = models.UserInfo.objects.get_or_create(username='root1',password='123456', defaults={'email': '1111111','u_id': 2, 't_id': 2})
def update_or_create(self, defaults=None, **kwargs):
# 如果存在,则更新,否则,创建
# defaults 指定创建时或更新时的其他字段
obj, created = models.UserInfo.objects.update_or_create(username='root1', username='root1',password='123456',defaults={'email': '1111111','u_id': 2, 't_id': 1})
def first(self):
# 获取第一个
def last(self):
# 获取最后一个
def in_bulk(self, id_list=None):
# 根据主键ID进行查找
id_list = [11,21,31]
models.DDD.objects.in_bulk(id_list)
def delete(self):
# 删除
def update(self, **kwargs):
# 更新
def exists(self):
# 是否有结果
select_related 和 prefetch_related 的用法
数据库
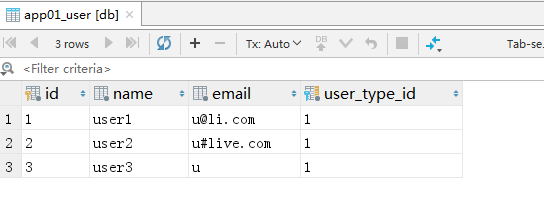
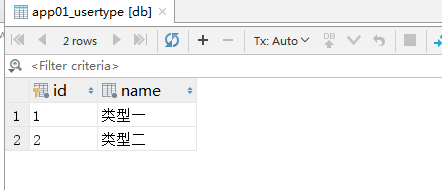
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
{% for item in v %}
{{ item.name }}{{ item.email }}{{ item.user_type.name }}
{% endfor %}
</body>
</html>
view.py
情况一
v = models.User.objects.all()
return render(request,'index.html',{'v': v})
发现执行了四次sql语句查询
SELECT "app01_user"."id", "app01_user"."name", "app01_user"."email", "app01_user"."user_type_id" FROM "app01_user";
SELECT "app01_usertype"."id", "app01_usertype"."name" FROM "app01_usertype" WHERE "app01_usertype"."id" = '1'
SELECT "app01_usertype"."id", "app01_usertype"."name" FROM "app01_usertype" WHERE "app01_usertype"."id" = '1'
SELECT "app01_usertype"."id", "app01_usertype"."name" FROM "app01_usertype" WHERE "app01_usertype"."id" = '1'
情况二
v = models.User.objects.all().select_related('user_type')
return render(request,'index.html',{'v': v})
发现只执行了一次sql查询
SELECT "app01_user"."id", "app01_user"."name", "app01_user"."email", "app01_user"."user_type_id",
"app01_usertype"."id", "app01_usertype"."name" FROM "app01_user"
INNER JOIN "app01_usertype" ON ("app01_user"."user_type_id" = "app01_usertype"."id")
情况三
v = models.User.objects.all().prefetch_related('user_type')
return render(request,'index.html',{'v': v})
发现执行了两次sql语句
SELECT "app01_user"."id", "app01_user"."name", "app01_user"."email", "app01_user"."user_type_id" FROM "app01_user"
SELECT "app01_usertype"."id", "app01_usertype"."name" FROM "app01_usertype" WHERE "app01_usertype"."id" IN ('1')
django会帮我们做整合
ORM函数操作
# ########### 基础函数 ###########
from django.db.models.functions import *
# 1. Concat,用于做类型转换
# v = models.UserInfo.objects.annotate(c=Cast('pwd', FloatField()))
# 2. Coalesce,从前向后,查询第一个不为空的值
# v = models.UserInfo.objects.annotate(c=Coalesce('name', 'pwd'))
# v = models.UserInfo.objects.annotate(c=Coalesce(Value('666'),'name', 'pwd'))
# 3. Concat,拼接
# models.UserInfo.objects.update(name=Concat('name', 'pwd'))
# models.UserInfo.objects.update(name=Concat('name', Value('666')))
# models.UserInfo.objects.update(name=Concat('name', Value('666'),Value('999')))
# 4.ConcatPair,拼接(仅两个参数)
# v = models.UserInfo.objects.annotate(c=ConcatPair('name', 'pwd'))
# v = models.UserInfo.objects.annotate(c=ConcatPair('name', Value('666')))
# 5.Greatest,获取比较大的值;least 获取比较小的值;
# v = models.UserInfo.objects.annotate(c=Greatest('id', 'pwd',output_field=FloatField()))
# 6.Length,获取长度
# v = models.UserInfo.objects.annotate(c=Length('name'))
# 7. Lower,Upper,变大小写
# v = models.UserInfo.objects.annotate(c=Lower('name'))
# v = models.UserInfo.objects.annotate(c=Upper('name'))
# 8. Now,获取当前时间
# v = models.UserInfo.objects.annotate(c=Now())
# 9. substr,子序列, 序号从1开始不是从0开始,2表示取几个字符串
# v = models.UserInfo.objects.annotate(c=Substr('name',1,2))
# ########### 时间类函数 ###########
# 1. 时间截取,不保留其他:Extract, ExtractDay, ExtractHour, ExtractMinute, ExtractMonth,ExtractSecond, ExtractWeekDay, ExtractYear,
# v = models.UserInfo.objects.annotate(c=functions.ExtractYear('ctime'))
# v = models.UserInfo.objects.annotate(c=functions.ExtractMonth('ctime'))
# v = models.UserInfo.objects.annotate(c=functions.ExtractDay('ctime'))
#
# v = models.UserInfo.objects.annotate(c=functions.Extract('ctime', 'year'))
# v = models.UserInfo.objects.annotate(c=functions.Extract('ctime', 'month'))
# v = models.UserInfo.objects.annotate(c=functions.Extract('ctime', 'year_month'))
"""
MICROSECOND
SECOND
MINUTE
HOUR
DAY
WEEK
MONTH
QUARTER
YEAR
SECOND_MICROSECOND
MINUTE_MICROSECOND
MINUTE_SECOND
HOUR_MICROSECOND
HOUR_SECOND
HOUR_MINUTE
DAY_MICROSECOND
DAY_SECOND
DAY_MINUTE
DAY_HOUR
YEAR_MONTH
"""
# 2. 时间截图,保留其他:Trunc, TruncDate, TruncDay,TruncHour, TruncMinute, TruncMonth, TruncSecond, TruncYear
# v = models.UserInfo.objects.annotate(c=functions.TruncHour('ctime'))
# v = models.UserInfo.objects.annotate(c=functions.TruncDate('ctime'))
# v = models.UserInfo.objects.annotate(c=functions.Trunc('ctime','year'))