能量模型的概念从统计力学中得来,它描述着整个系统的某种状态,系统越有序,系统能量波动越小,趋近于平衡状态,系统越无序,能量波动越大。例如:一个孤立的物体,其内部各处的温度不尽相同,那么热就从温度较高的地方流向温度较低的地方,最后达到各处温度都相同的状态,也就是热平衡的状态。在统计力学中,系统处于某个状态的相对概率为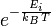 ,即玻尔兹曼因子,其中T表示温度,
,即玻尔兹曼因子,其中T表示温度,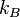 是玻尔兹曼常数,
是玻尔兹曼常数,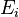 是状态
是状态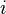 的能量。玻尔兹曼因子本身并不是一个概率,因为它还没有归一化。为了把玻尔兹曼因子归一化,使其成为一个概率,我们把它除以系统所有可能的状态的玻尔兹曼因子之和Z,称为配分函数(partition function)。这便给出了玻尔兹曼分布。
的能量。玻尔兹曼因子本身并不是一个概率,因为它还没有归一化。为了把玻尔兹曼因子归一化,使其成为一个概率,我们把它除以系统所有可能的状态的玻尔兹曼因子之和Z,称为配分函数(partition function)。这便给出了玻尔兹曼分布。
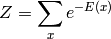

玻尔兹曼机(Boltzmann Machine,BM)是一种特殊形式的对数线性的马尔科夫随机场(Markov Random Field,MRF),即能量函数是自由变量的线性函数。 通过引入隐含单元,我们可以提升模型的表达能力,表示非常复杂的概率分布。限制性玻尔兹曼机(RBM)进一步加一些约束,在RBM中不存在可见单元与可见单元的链接,也不存在隐含单元与隐含单元的链接,如下图所示

能量函数在限制玻尔兹曼机中定义为,b,c,W为模型的参数,b,c分别为可见层和隐含层的偏置,W为可见层与隐含层的链接权重
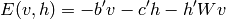
有了上述三个公式我们可以使用最大似然估计来求解模型的参数:设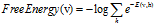 。把概率p(x)改写为
。把概率p(x)改写为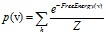 。
。
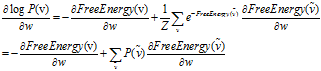
由于可见单元V和不可见单元h条件独立,利用这一性质,我们可以得到:
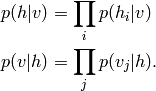
logistic回归估计v与h取一的概率:
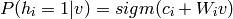
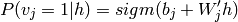
有了以上条件,我们可以推导出参数变化的梯度值:
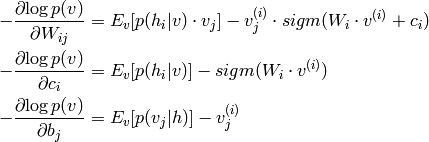
使用基于马尔可夫链的gibbs抽样,对于一个d维的随机向量x=(x1,x2,…xd),假设我们无法求得x的联合概率分布p(x),但我们知道给定x的其他分量是其第i个分量xi的条件分布,即p(xi|xi-),xi-=(x1,x2,…xi-1,xi+1…xd)。那么,我们可以从x的一个任意状态(如(x1(0),x2(0),…,xd(0)))开始,利用条件分布p(xi|xi-),迭代地对这状态的每个分量进行抽样,随着抽样次数n的增加,随机变量(x1(n),x2(n),…,xd(n))的概率分布将以n的几何级数的速度收敛到x的联合概率分布p(v)。
基于RBM模型的对称结构,以及其中节点的条件独立行,我们可以使用Gibbs抽样方法得到服从RBM定义的分布的随机样本。在RBM中进行k步Gibbs抽样的具体算法为:用一个训练样本(或者可视节点的一个随机初始状态)初始化可视节点的状态v0,交替进行下面的抽样:
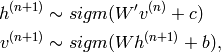
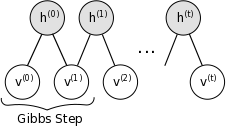
理论上,参数的每次更新需要让上面的链条图形遍历一次,这样带来的性能损耗毫无疑问是不能承受的。
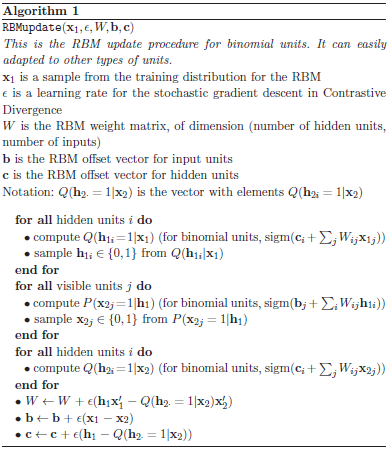
Hinton教授提出一种改进方法叫做对比分歧(Contrastive Divergence),即CD-K。他指出CD没有必要等待链收敛,样本可以通过k步 的gibbs抽样完成,仅需要较少的抽样步数(实验中使用一步)就可以得到足够好的效果。
下面给出RBM用到的CD-K算法伪代码。
关于deeplearning的c++实现放到了github上,由于时间关系只是实现了大致框架,细节方面有待改善,也欢迎大家的参与:https://github.com/loujiayu/deeplearning
下面附上Geoff Hinton提供的关于RBM的matlab代码
% Version 1.000 % % Code provided by Geoff Hinton and Ruslan Salakhutdinov % % Permission is granted for anyone to copy, use, modify, or distribute this % program and accompanying programs and documents for any purpose, provided % this copyright notice is retained and prominently displayed, along with % a note saying that the original programs are available from our % web page. % The programs and documents are distributed without any warranty, express or % implied. As the programs were written for research purposes only, they have % not been tested to the degree that would be advisable in any important % application. All use of these programs is entirely at the user's own risk. % This program trains Restricted Boltzmann Machine in which % visible, binary, stochastic pixels are connected to % hidden, binary, stochastic feature detectors using symmetrically % weighted connections. Learning is done with 1-step Contrastive Divergence. % The program assumes that the following variables are set externally: % maxepoch -- maximum number of epochs % numhid -- number of hidden units % batchdata -- the data that is divided into batches (numcases numdims numbatches) % restart -- set to 1 if learning starts from beginning epsilonw = 0.1; % Learning rate for weights epsilonvb = 0.1; % Learning rate for biases of visible units epsilonhb = 0.1; % Learning rate for biases of hidden units weightcost = 0.0002; initialmomentum = 0.5; finalmomentum = 0.9; [numcases numdims numbatches]=size(batchdata); if restart ==1, restart=0; epoch=1; % Initializing symmetric weights and biases. vishid = 0.1*randn(numdims, numhid); hidbiases = zeros(1,numhid); visbiases = zeros(1,numdims); poshidprobs = zeros(numcases,numhid); neghidprobs = zeros(numcases,numhid); posprods = zeros(numdims,numhid); negprods = zeros(numdims,numhid); vishidinc = zeros(numdims,numhid); hidbiasinc = zeros(1,numhid); visbiasinc = zeros(1,numdims); batchposhidprobs=zeros(numcases,numhid,numbatches); end for epoch = epoch:maxepoch, fprintf(1,'epoch %d ',epoch); errsum=0; for batch = 1:numbatches, fprintf(1,'epoch %d batch %d ',epoch,batch); %%%%%%%%% START POSITIVE PHASE %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% data = batchdata(:,:,batch); poshidprobs = 1./(1 + exp(-data*vishid - repmat(hidbiases,numcases,1))); batchposhidprobs(:,:,batch)=poshidprobs; posprods = data' * poshidprobs; poshidact = sum(poshidprobs); posvisact = sum(data); %%%%%%%%% END OF POSITIVE PHASE %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% poshidstates = poshidprobs > rand(numcases,numhid); %%%%%%%%% START NEGATIVE PHASE %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% negdata = 1./(1 + exp(-poshidstates*vishid' - repmat(visbiases,numcases,1))); neghidprobs = 1./(1 + exp(-negdata*vishid - repmat(hidbiases,numcases,1))); negprods = negdata'*neghidprobs; neghidact = sum(neghidprobs); negvisact = sum(negdata); %%%%%%%%% END OF NEGATIVE PHASE %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% err= sum(sum( (data-negdata).^2 )); errsum = err + errsum; if epoch>5, momentum=finalmomentum; else momentum=initialmomentum; end; %%%%%%%%% UPDATE WEIGHTS AND BIASES %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% vishidinc = momentum*vishidinc + ... epsilonw*( (posprods-negprods)/numcases - weightcost*vishid); visbiasinc = momentum*visbiasinc + (epsilonvb/numcases)*(posvisact-negvisact); hidbiasinc = momentum*hidbiasinc + (epsilonhb/numcases)*(poshidact-neghidact); vishid = vishid + vishidinc; visbiases = visbiases + visbiasinc; hidbiases = hidbiases + hidbiasinc; %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% END OF UPDATES %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% end fprintf(1, 'epoch %4i error %6.1f ', epoch, errsum); end;