jdbc DAO设计实现增删改查
1.DAO模式的作用:
1.隔离业务逻辑代码和数据访问代码;
2.隔离不同数据库的实现。:
2.不用DAO模式也可以实现数据的增删改查那为什么要用DAO呢:
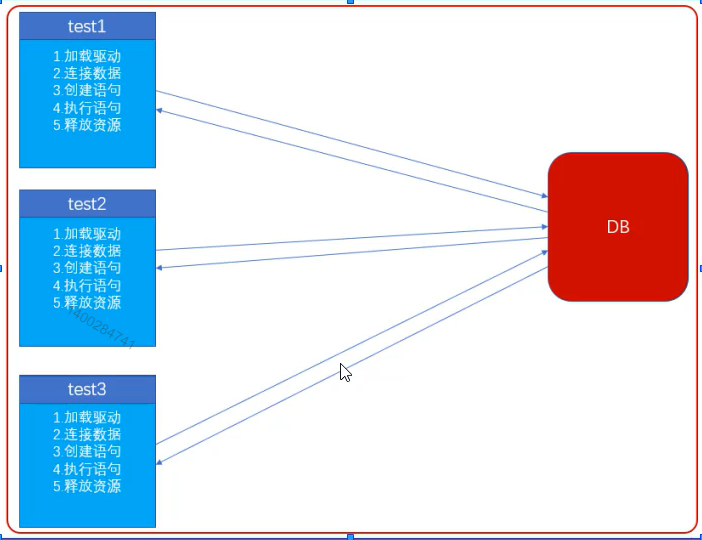
在没有使用DAO的时候 程序是直接对数据库进行操作的 而每个程序需要操作数据库都需要 1.加载驱动、2.连接数据库
3.创建语句、4.执行语句、5.释放资源 这样非常的繁琐。

在用了DAO之后 将数据库的1.加载驱动、2.连接数据库、3.创建语句、4.执行语句、5.释放资源 和
(增删该查)的操作都写在Dao里 程序只需要告诉DAO要干什么(增删改查)然后DAO再去操作数据库
这样既方便了程序的编写也减少了代码的复写。
3.DAO的实现步骤:
先建立模型的对象domain
package com.xiaofu.servlet; public class User { Integer id; String name; Integer age; public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } }
类中的一个属性对应 数据库表中的一个字段 称之为ORM对象关系映射 拥有get set方法的可以称之为domain。
编写DAO接口
public interface UserDao { //保存用户 void save(User user); //删除用户 void delete(Integer id); //更改用户 void update(int id, User newUser); //更具id查询单个用户 void get(Integer id); //查询所有用户 List<User> getAll(); }
定义DAO实现类
import java.sql.*; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class UserRell implements UserDao { //保存用户 @Override public void save(User user) { String url = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8"; String username = "root"; String password = "1234"; Connection conn = null; Statement st = null; try { //1.加载驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //2.连接数据库 conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password); //3.创建sql语句 Integer id = user.getId(); Integer age = user.getAge(); String name = user.getName(); String sql = "insert into user values(" + id + ",'" + name + "'," + age + ")"; System.out.println(sql); st = conn.createStatement(); //4.执行语句 int now = st.executeUpdate(sql); System.out.println(now); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //5.释放资源 if (st != null) { try { st.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (conn != null) { try { conn.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } //删除用户 @Override public void delete(Integer id) { String url = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8"; String username = "root"; String password = "1234"; Connection conn = null; Statement st = null; try { //1.加载驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //2.连接数据库 conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password); //3.创建sql语句 String sql = "delete from user where id=" + id + ""; System.out.println(sql); st = conn.createStatement(); //4.执行语句 int now = st.executeUpdate(sql); System.out.println(now); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //5.释放资源 if (st != null) { try { st.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (conn != null) { try { conn.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } //更改用户 @Override public void update(Integer id, User newUser) { String url = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8"; String username = "root"; String password = "1234"; Connection conn = null; Statement st = null; try { //1.加载驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //2.连接数据库 conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password); //3.创建sql语句 String sql = "update user set name='" + newUser.getName() + "', age=" + newUser.getAge() + " where id=" + id + ""; System.out.println(sql); st = conn.createStatement(); //4.执行语句 int now = st.executeUpdate(sql); System.out.println(now); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //5.释放资源 if (st != null) { try { st.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (conn != null) { try { conn.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } //根据id查询单个用户 @Override public User get(Integer id) { String url = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8"; String username = "root"; String password = "1234"; Connection conn = null; Statement st = null; ResultSet resultSet = null; try { //1.加载驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //2.连接数据库 conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password); //3.创建sql语句 String sql = "select * from user where id= " + id + ""; System.out.println(sql); st = conn.createStatement(); //4.执行语句 resultSet = st.executeQuery(sql); if (resultSet.next()) { User user = new User(); user.setName(resultSet.getString("name")); user.setAge(resultSet.getInt("age")); user.setId(resultSet.getInt("id")); return user; } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //5.释放资源 if (resultSet != null) { try { resultSet.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (st != null) { try { st.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (conn != null) { try { conn.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } return null; } //查询所有用户 @Override public List<User> getAll() { String url = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8"; String username = "root"; String password = "1234"; Connection conn = null; Statement st = null; ResultSet resultSet = null; try { //1.加载驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //2.连接数据库 conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password); //3.创建sql语句 String sql = "select * from user "; System.out.println(sql); st = conn.createStatement(); //4.执行语句 resultSet = st.executeQuery(sql); //创建一个集合 存放User对象 List<User> list = new ArrayList<User>(); while (resultSet.next()) { User user = new User(); user.setName(resultSet.getString("name")); user.setAge(resultSet.getInt("age")); user.setId(resultSet.getInt("id")); list.add(user); } return list; } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //5.释放资源 if (resultSet != null) { try { resultSet.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (st != null) { try { st.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (conn != null) { try { conn.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } return null; } }
在测试类中测试方法
public class Text { public static void main(String[] args) { User user = new User(); user.name = "haha"; user.age = 2; UserRell userRell = new UserRell(); userRell.get(2); userRell.delete(2); userRell.save(user); userRell.update(1,user); List<User> all = userRell.getAll(); for (User userlist : all) { System.out.println(user); } } }