附录一个:Keras学习随笔 http://blog.csdn.net/niuwei22007/article/details/49045909
参考 《Python Machine Learning》这本书的第13章
Theano是Bengio大神课题组弄得。
一、Theano初步
Theano编程三个步骤: 初始化、编译和执行,就是定义符号(变量对象)、编译代码和执行代码
举个例子:计算 z=x1*w1+wo 代码如下:
1 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 2 __author__ = 'Administrator' 3 4 import theano 5 import theano.tensor as T 6 import random 7 import numpy as np 8 from itertools import izip 9 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 10 11 #初始化 12 x1 = T.scalar() 13 w1 = T.scalar() 14 w0 = T.scalar() 15 z = w1*x1+w0 16 17 #编译 18 19 net_input = theano.function( 20 inputs=[w1, x1, w0], 21 outputs=z 22 ) 23 24 #执行 25 26 print 'net input %.2f'% (net_input(2.0, 1.0 ,0.5))
在写Theano代码时,要注意变量的类型 dtype ,要分清楚我们要使用 64或者32为的int or floats
二、 配置Theano
一般来说 采用CPU时,我们设置float64 ,采用GPU时,需要设置float32
print (theano.config.floatX)
print (theano.config.device)
在window中设置CPU or GPU模式,是在运行cmd后出现的路径下,新建一个.theanorc.txt的文件。文件内容如下图所示

三、使用array结构
一个简单的求和例子
1 #初始化 2 x = T.fmatrix(name ='x') 3 x_sum = T.sum(x, axis=1) # 0 是按列 1 是按行 4 5 #编译 6 calc_sum = theano.function( 7 inputs=[x], 8 outputs=x_sum 9 ) 10 11 #执行 12 ary = np.array([[1,2,4],[1,2,3]],dtype=theano.config.floatX) 13 print calc_sum(ary)
shared variable 和 权值更新
1 #初始化 2 x = T.fmatrix('x') 3 w = theano.shared(np.asarray([[0.0,0.0,0.0]],dtype=theano.config.floatX)) 4 5 z = T.dot(x,w.T) # 这个就是两个矩阵相乘 w是1*3 x是1*3 6 7 update = [[w, w+1.0]] 8 9 # 编译 10 net_input = theano.function( 11 inputs=[x], 12 updates=update, 13 outputs=z 14 ) 15 16 # 执行 17 18 data = np.array([[1,2,3]],dtype=theano.config.floatX) 19 for i in range(5): 20 print w.get_value() 21 print '%d %.2f' % (i,net_input(data))
可以提取指定数据,代码如下
1 #初始化 2 data = np.array([[1,2,3]],dtype=theano.config.floatX) 3 x = T.fmatrix('x') 4 w = theano.shared(np.asarray([[0.0,0.0,0.0]],dtype=theano.config.floatX)) 5 6 z = T.dot(x,w.T) # 这个就是两个矩阵相乘 w是1*3 x是1*3 7 8 update = [[w, w+1.0]] 9 10 # 编译 11 net_input = theano.function( 12 inputs=[], 13 updates=update, 14 givens={x : data}, 15 outputs=z 16 ) 17 18 # 执行 19 20 for i in range(5): 21 print w.get_value() 22 print '%d %.2f' % (i,net_input())
四、 一个线性回归的例子
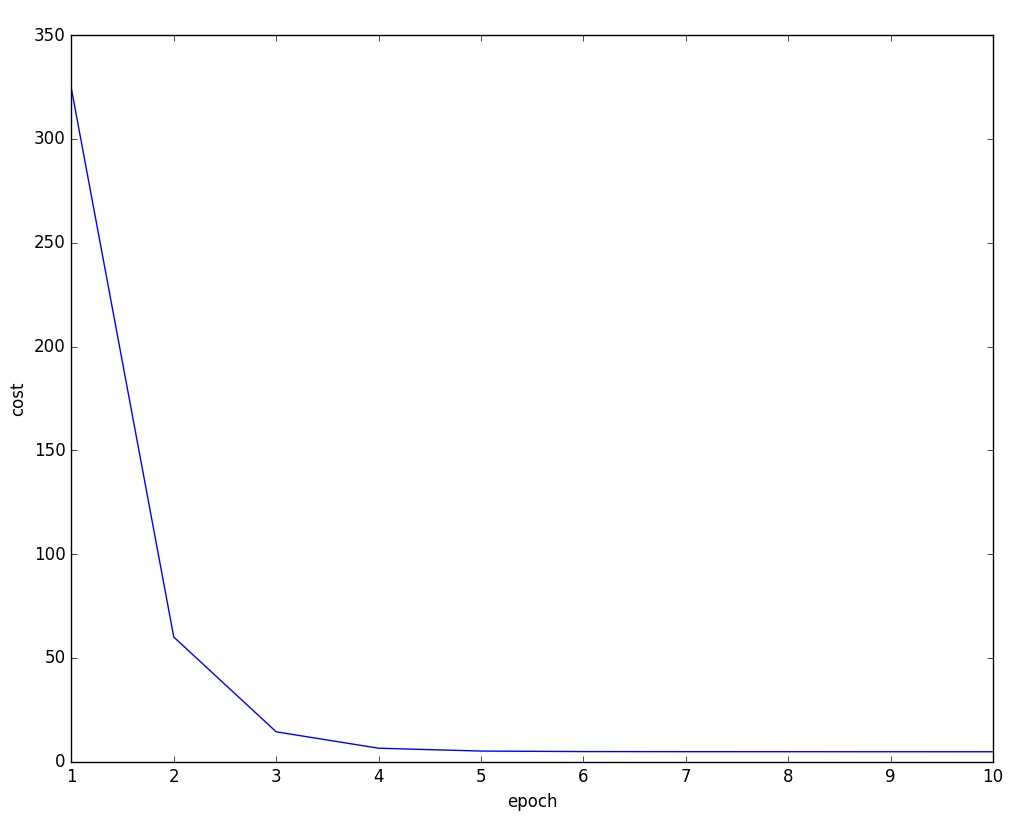
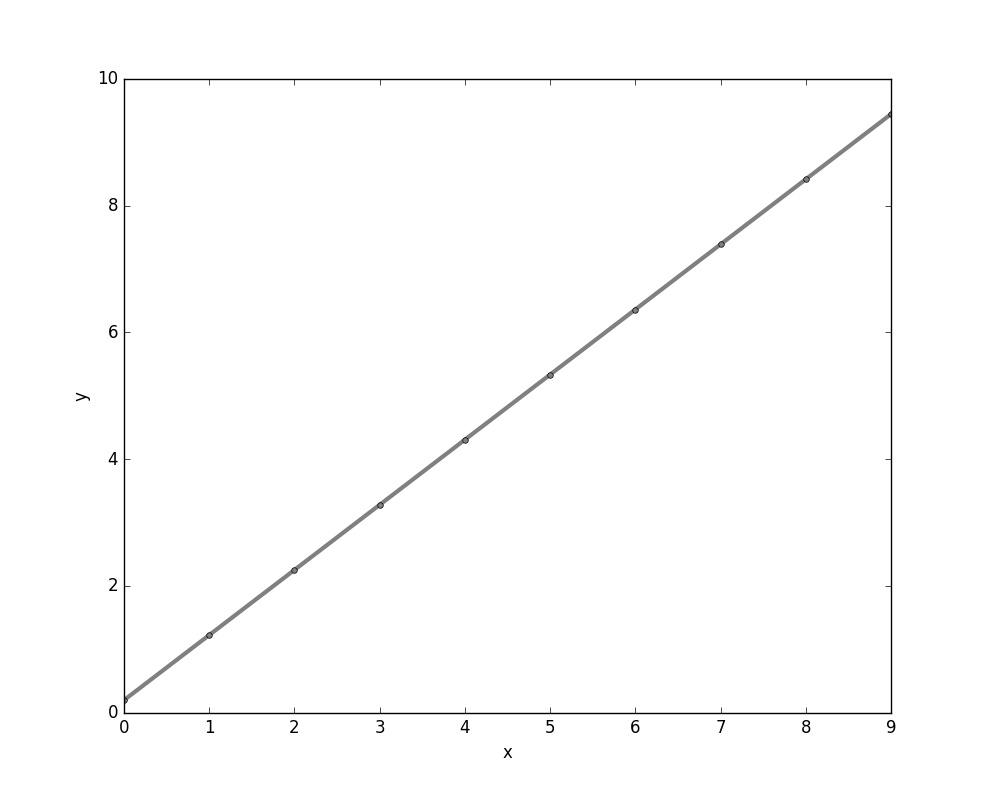
1 X_train = np.asarray( 2 [ [0,0] , [1, 0], 3 [2,0] , [3, 0], 4 [4,0] , [5, 0], 5 [6,0] , [7, 0], 6 [8,0] , [9, 0]], 7 dtype= theano.config.floatX 8 ) 9 10 y_train = np.asarray( 11 [ 1.0,1.3,3.1,2.0, 12 5.0,6.3,6.6,7.4, 13 8.0,9.0], 14 dtype= theano.config.floatX 15 ) 16 17 y_train_new = np.asarray( 18 [ [1.0],[1.3],[3.1],[2.0], 19 [5.0],[6.3],[6.6],[7.4], 20 [8.0],[9.0]], 21 dtype= theano.config.floatX 22 ) 23 print X_train.shape[1] # shape 0 获取行 shape 1 获取列 24 25 def train_linreg(X_train, y_train ,eta, epochs): 26 costs = [] 27 #初始化array0 28 eta0 = T.fscalar('eta0') 29 y = T.fvector(name='y') 30 X = T.fmatrix(name='X') 31 w = theano.shared(np.zeros( 32 shape=(X_train.shape[1] +1 ),dtype= theano.config.floatX), name = 'w') 33 34 #计算损失函数 35 net_input = T.dot(X, w[1:]) + w[0] # w[1:] 从第二个到最后一个数据 36 errors = y - net_input 37 cost = T.sum(T.pow(errors,2)) 38 39 #梯度更新 40 gradient = T.grad(cost,wrt=w) 41 update = [(w, w- eta0* gradient)] 42 43 #定义模型 44 train = theano .function(inputs=[eta0], 45 outputs=cost, 46 updates=update, 47 givens={X:X_train, 48 y: y_train}) 49 50 51 for i in range(epochs): 52 costs.append(train(eta)) 53 print w.get_value() 54 return costs, w 55 56 def predict_linreg(X,w): 57 Xt = T.matrix(name='X') 58 net_input = T.dot(Xt, w[1:])+w[0] 59 predict = theano.function(inputs=[Xt], 60 givens={w:w}, 61 outputs= net_input) 62 return predict(X) 63 64 65 costs,w= train_linreg(X_train,y_train,eta=0.001,epochs=10) 66 plt.plot(range(1,len(costs)+1),costs) 67 plt.tight_layout() 68 plt.xlabel("epoch") 69 plt.ylabel('cost') 70 plt.show() 71 # 72 #plt.scatter(X_train, y_train ,marker='s',s=50) 73 plt.plot(range(X_train.shape[0]),predict_linreg(X_train,w),color='gray',marker='o',markersize=4,linewidth=3) 74 plt.xlabel("x") 75 plt.ylabel('y') 76 plt.show()
结果图: