继上一篇的 IO 多路复用之后,我们已经从操作系统的层面上,解决了 IO 不必要等待的问题
不用再写类似的代码了:
while (true) { if (socket.isReadable) { doRead(sockert); } sleep(); }
本质上是驱动程序通过中断通知我们,有数据来到了 IO 口,我们可以去接收了。
现在,需要在 select , poll 或者 epoll 之上进行抽象,套一层能和应用对接的代码。
这一层代码需要 下接 IO 多路复用,上接业务。也就是将 IO 设备传来的 数据交给业务代码。
一般的模式有 Reactor 和 Proactor
Reactor(反应堆模式):
本质做的事情是从 IO 多路复用器(select,poll, epoll)上 得知某些 IO 设备是否可读/写/accept,如果可以的话,就将相应的事件路由给对应的处理器(Handler)
Handler 完成业务逻辑后返回 结果,结果将在 写事件发生后传输给 可写的 IO 设备。
简单代码表示:

package reactor; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey; import java.nio.channels.Selector; import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel; import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel; import java.util.Date; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Set; public class Reactor implements Runnable{ private Selector selector; private ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel; public Reactor() throws IOException { selector = Selector.open(); serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); //TODO ? What is blocking? serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 5050), 1024); serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false); SelectionKey key = serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); key.attach(new Acceptor()); } @Override public void run() { while (true) { try { // select 阻塞,直到有 IO 事件发生 selector.select(); Set<SelectionKey> keys = selector.selectedKeys(); for (SelectionKey key : keys) { dispatch(key); } // 清空, 不清空的话,之前的 selectionKey 会积累(相同的不会积累) // 某个IO设备感兴趣的事件 就算不发生,只要之前发生过,也会在 set 中 // 加入这个 IO 设备注册的 selectionKey keys.clear(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } // 路由发生的事件到处理器 public void dispatch (SelectionKey key) { if (key.attachment() instanceof Runnable) { ((Runnable) key.attachment()).run(); } } // 接受器 public class Acceptor implements Handler { @Override public void run() { for (SelectionKey key : selector.keys()) { if (key.isAcceptable()) { SocketChannel socketChannel = null; try { socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept(); if (socketChannel == null) { return; } socketChannel.configureBlocking(false); SelectionKey key1 = socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); key1.attach(new BusinessHandler(socketChannel, key1)); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } } // 处理器 public interface Handler extends Runnable{} public class BusinessHandler implements Runnable { private SocketChannel socketChannel; private SelectionKey key; private String result; public BusinessHandler(SocketChannel socketChannel, SelectionKey key) { this.socketChannel = socketChannel; this.key = key; } @Override public void run() { ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); try { if (key.isReadable()) { socketChannel.read(byteBuffer); // 业务逻辑处理 result = processBusinessLogic(byteBuffer); // 必须使用 interestOps 改变在 select 上注册的监听事件 key.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_WRITE); } else if (key.isWritable()) { if (result != null) { // 默认 limit 一开始是数组最大值,position 是 0,每写入一个字节 position + 1,limit 不变 byteBuffer.put(result.getBytes()); // 读取需要令 position = 0, limit = put写入数据的最大边界(之前的 position),flip 做的就是这件事 byteBuffer.flip(); socketChannel.write(byteBuffer); // 必须使用 interestOps 改变在 select 上注册的监听事件 // 否则因为 select 是 LT (水平触发)模式,只要缓冲区可写就一直触发可写事件 key.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ); } } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } // 处理业务逻辑 public String processBusinessLogic(ByteBuffer byteBuffer) { // 读取需要令 position = 0 , limit = 写入数据的最大边界 byteBuffer.flip(); byte[] res = new byte[byteBuffer.limit() - byteBuffer.position()]; byteBuffer.get(res); String request = new String(res); if ("What is the time".equals(request)) { return new Date().toString(); } return "Unknown request"; } } }
Redis 也是使用类似的 Reactor 模型,而且采用单线程监听 IO 口,对业务的处理并没有使用线程池,所以对于所有用户的请求,Redis 只用一条线程处理
对此的解释是 Redis 是基于内存操作的,速度非常快,单线程减少了 锁互斥导致的 线程休眠问题,和安全问题,但是对于内存中的 大key 操作,还是有所不足
上述是单线程的 Reactor 模型,如果是在多核 CPU 环境,为了充分发挥 多 CPU 的优势,可以使用线程池处理业务逻辑,但是从 IO 口读取数据还是在 Reactor 的主线程
修改一下 Handler 的 run 方法,因为业务逻辑处理是最耗时的操作,可能设计文件IO 等复杂操作,所以应该发挥多核优势,让其他CPU核也参与到业务逻辑的处理过程中:
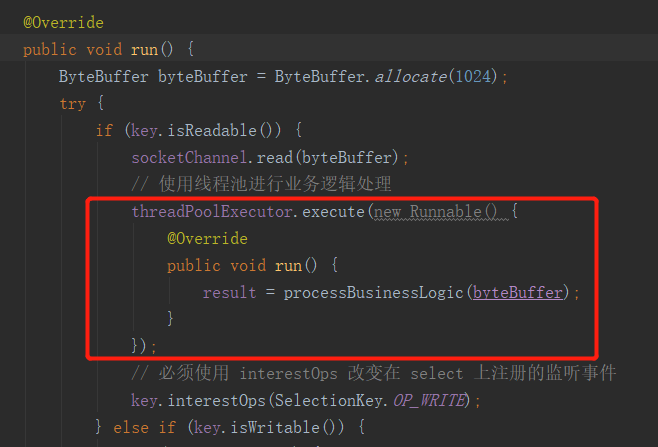
还有可以优化的地方,要直到,上面对 IO 设备的同步IO拷贝,是CPU在做拷贝。
如果并发量十分庞大,那么一个核心来接收连接请求,并且负责客户连接的 IO 就会使得单个核心的 压力大
优化想法很简单,使用两个 select 去跑 ,一个专门监听客户连接的到来事件,一个专门监听客户连接上的可读写事件
并且将两个 select 放在不同线程上跑,当有客户连接到来,监听客户连接的 select 将生成的 socketChannel 注册到 监听客户连接上读写请求的 select
如果还不够,还可以使用多个 select 监听客户连接上可读写事件,并且将他们放在线程池中跑,以应对大并发情况
Proactor,相对于 Reactor 不同的地方在于,Proactor 对 IO 设备的 IO操作是由操作系统完成的,也即是使用的 模型 是 AIO 的 模型,上述的 Java 的 select 在 windows 上是 轮询的 select, 不是 poll 或 epoll (Hotspot)。
目前不是全部操作系統都支持 AIO 模型,所以一般是 Reactor 模型更加常见。
