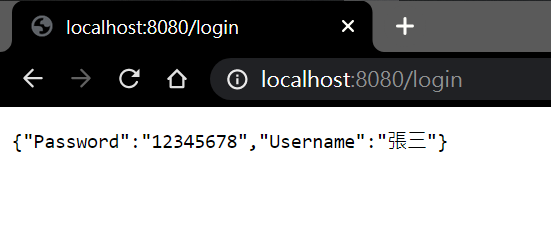
- 編寫一個簡單的提交form表單的
login.html頁面:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="./login" method="POST" novalidate autocomplete="off">
<!-- sction: 提交的對象
method: 提交的函數-->
<div>
<label for="username">username:</label>
<input type="text" name="username" id="username">
</div>
<div>
<label for="password">password:</label>
<input type="password" name="password", id="password">
</div>
<div>
<input type="submit" value="登錄">
</div>
</form>
</body>
</html>
展現出來的效果如下:
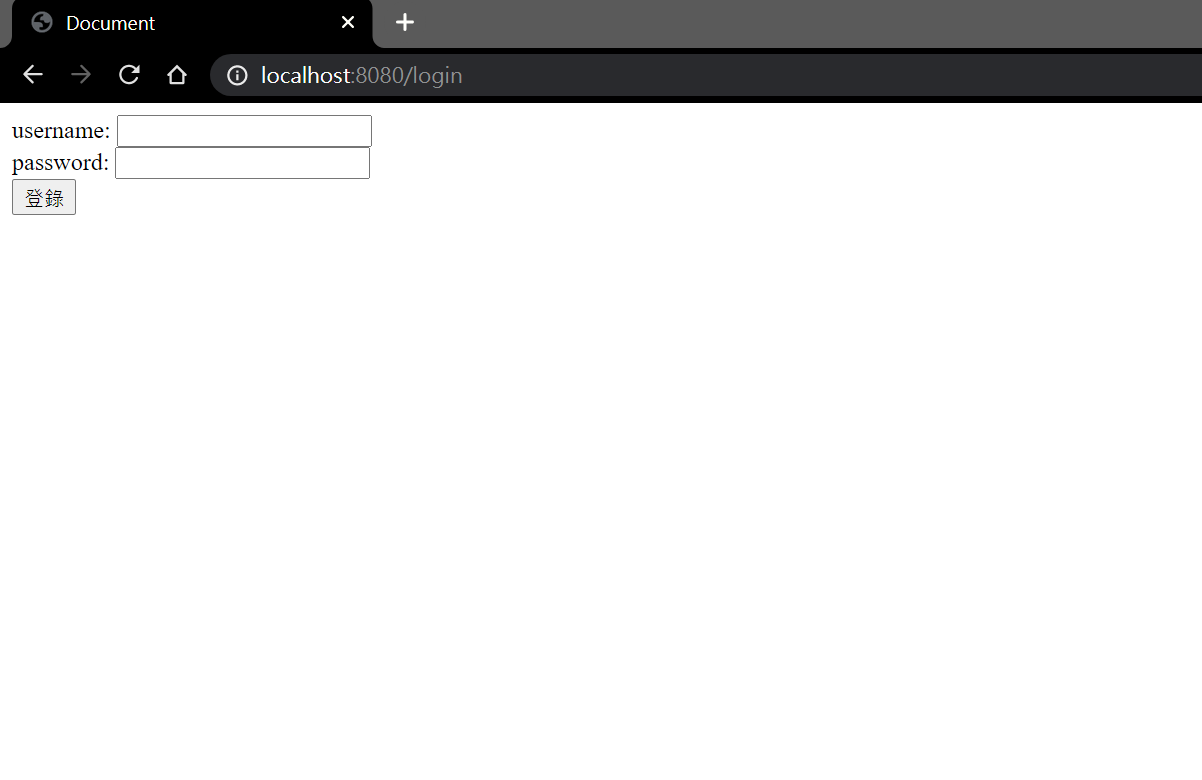
- 在主函數中顯示
login.html頁面.((也可以直接在postman中發起post請求,這樣就不用再編寫這個get請求頁面)
r.LoadHTMLFiles("./login.html")
// r.LoadHTMLGlob("./*")
r.GET("/login", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "login.html", nil)
})
- 在
main.go中獲取form提交的表單數據,并以json數據返回給前端(請不要在實際開發中這麼做,此處只是作為掩飾而這樣處理)
r.POST("/login", func(c *gin.Context) {
// DefaultPostForm取不到值时会返回指定的默认值
// username := c.DefaultPostForm("username", "小王子")
username := c.PostForm("username")
password := c.PostForm("password")
// 输出json结果给调用方
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"Password": password,
"Username": username,
})
})
**說明: **
1. 同一個login頁面有兩個函數那是因爲一個get函數是瀏覽器向服務端發起get請求,另一個是發起post請求,兩個請求不相同,所以需要使用不同的函數來完成--一次請求只能獲取一次響應,不同的請求獲得不同的響應。
2. 在main.go中PostForm中的參數對應的是html頁面中'name'屬性值,而前面的變量名並不影響結果.
儅點擊登錄之後看到的結果: