一、nfs存储卷
kubernetes的NFS存储卷用于将某实现存在的NFS服务器上导出export的存储空间挂在到pod中以供容器使用
与emptyDir不同的是、NFS存储卷在POD对象终止后仅是被卸载而非删除、另外NFS是文件系统级共享服务,它支持同时存在的多路关在请求
1、字段详解
[root@master ~]# kubectl explain pod.spec.volumes.nfs
KIND: Pod
VERSION: v1
RESOURCE: nfs <Object>
DESCRIPTION:
NFS represents an NFS mount on the host that shares a pod's lifetime More
info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/storage/volumes#nfs
Represents an NFS mount that lasts the lifetime of a pod. NFS volumes do
not support ownership management or SELinux relabeling.
FIELDS:
path <string> -required-
#NFS服务器导出共享的文件系统路径、必选字段
Path that is exported by the NFS server. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/storage/volumes#nfs
readOnly <boolean>
#是以只读方式挂在、默认为false
ReadOnly here will force the NFS export to be mounted with read-only
permissions. Defaults to false. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/storage/volumes#nfs
server <string> -required-
#NFS服务器的ip地址、默认是false
Server is the hostname or IP address of the NFS server. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/storage/volumes#nfs
2、配置清单
[root@master chapter7]# cat vol-nfs1.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: vol-nfs-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: myapp
image: ikubernetes/myapp:v1
volumeMounts:
- name: html
mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html
volumes:
- name: html
nfs:
path: /data/volumes
server: node2
3、nfs server搭建
yum install nfs-utils rpcbind -y #所有节点均安装 [root@node2 volumes]# cat /etc/exports /data/volumes 192.168.118.0/24 (rw,no_root_squash) # 启动rpcbind服务 systemctl restart rpcbind #启动 systemctl restart nfs-server [root@node2 volumes]# showmount -e Export list for node2: /data/volumes (everyone)
4、挂载主页
[root@node2 volumes]# ls index.html [root@node2 volumes]# pwd /data/volumes [root@node2 volumes]# cat index.html <h1>NFS node2</h1>
5、创建运行vol-nfs.yaml
[root@master chapter7]# kubectl get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod-example 1/1 Running 1 9d vol-emptydir-pod 2/2 Running 0 5d1h vol-hostpath-pod 1/1 Running 0 4d22h [root@master chapter7]# kubectl apply -f vol-nfs1.yaml pod/vol-nfs-pod created [root@master chapter7]# kubectl get pods -o wide NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES pod-example 1/1 Running 1 9d 10.244.2.9 node2 <none> <none> vol-emptydir-pod 2/2 Running 0 5d1h 10.244.2.68 node2 <none> <none> vol-hostpath-pod 1/1 Running 0 4d22h 10.244.1.43 node1 <none> <none> vol-nfs-pod 1/1 Running 0 4m24s 10.244.1.50 node1 <none> <none> [root@master chapter7]# curl 10.244.1.50 <h1>NFS node2</h1>
6、删除pod数据依然存在
为了测试其数据持久化效果,下面删除pod资源vol-nfs-pod、并重建后检测数据是否依然能访问
[root@master chapter7]# kubectl delete -f vol-nfs1.yaml pod "vol-nfs-pod" deleted [root@master chapter7]# kubectl get pods -o wide NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES pod-example 1/1 Running 1 9d 10.244.2.9 node2 <none> <none> vol-emptydir-pod 2/2 Running 0 5d1h 10.244.2.68 node2 <none> <none> vol-hostpath-pod 1/1 Running 0 4d22h 10.244.1.43 node1 <none> <none> [root@master chapter7]# kubectl apply -f vol-nfs1.yaml pod/vol-nfs-pod created [root@master chapter7]# kubectl get pods -o wide NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES pod-example 1/1 Running 1 9d 10.244.2.9 node2 <none> <none> vol-emptydir-pod 2/2 Running 0 5d1h 10.244.2.68 node2 <none> <none> vol-hostpath-pod 1/1 Running 0 4d22h 10.244.1.43 node1 <none> <none> vol-nfs-pod 1/1 Running 0 6s 10.244.1.51 node1 <none> <none> [root@master chapter7]# curl 10.244.1.51 <h1>NFS node2</h1>
这里应确保实现要存在一个名为nfs.ilinux.io的NFS服务器、其输出了/data/redis目录,并授权给了kubernetes集群中的节点访问、主机和目录都可以按需进行调整
从上面的命令中可以看出,此前创建的键mykey及其数据在pod资源重建后依然存在、这表明再删除pod资源时、其关联的外部存储卷并不会被一同删除、如果需要清除此类的数据、需要用户通过存储系统的管理接口手动进行
二、RBD存储卷
1、配置pod资源使用RBD存储卷、满足条件
- 存在某可用的Ceph RBD存储集群,否则就需要创建一个
- 在Ceph集群中创建一个能满足Pod资源数据存储需要的存储影响(images)
- 在kubernetes集群内的各节点上安装Ceph客户端程序包(ceph-common)
2、字段详解
在配置RBD类型的存储卷时、需要制定要连接的目标服务器和认证信息等、这一点通常使用一下嵌套字段进行定义
[root@master ~]# kubectl explain pod.spec.volumes.rbd
KIND: Pod
VERSION: v1
RESOURCE: rbd <Object>
DESCRIPTION:
RBD represents a Rados Block Device mount on the host that shares a pod's
lifetime. More info: https://examples.k8s.io/volumes/rbd/README.md
Represents a Rados Block Device mount that lasts the lifetime of a pod. RBD
volumes support ownership management and SELinux relabeling.
FIELDS:
fsType <string>
#要挂在的存储卷的文件系统类型,至少应该是节点操作系统支持的文件系统,如:ext4", "xfs", "ntfs".默认为"ext4"
Filesystem type of the volume that you want to mount. Tip: Ensure that the
filesystem type is supported by the host operating system. Examples:
"ext4", "xfs", "ntfs". Implicitly inferred to be "ext4" if unspecified.
More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/storage/volumes#rbd
image <string> -required-
#rados image的名称,必选字段
The rados image name. More info:
https://examples.k8s.io/volumes/rbd/README.md#how-to-use-it
keyring <string>
#RBD用户认证时的keyring文件路径,默认为/etc/ceph/keyring
Keyring is the path to key ring for RBDUser. Default is /etc/ceph/keyring.
More info: https://examples.k8s.io/volumes/rbd/README.md#how-to-use-it
monitors <[]string> -required-
#ceph存储见识其,逗号分隔的字符串列表;必选字段
A collection of Ceph monitors. More info:
https://examples.k8s.io/volumes/rbd/README.md#how-to-use-it
pool <string>
#rados 存储池名称,默认为RBD
The rados pool name. Default is rbd. More info:
https://examples.k8s.io/volumes/rbd/README.md#how-to-use-it
readOnly <boolean>
#是否以只读的方式进行访问
ReadOnly here will force the ReadOnly setting in VolumeMounts. Defaults to
false. More info:
https://examples.k8s.io/volumes/rbd/README.md#how-to-use-it
secretRef <Object>
#RBD用户认证时使用的保存有相应认真信息的secret对象,会覆盖由keyring字段提供的密钥信息
SecretRef is name of the authentication secret for RBDUser. If provided
overrides keyring. Default is nil. More info:
https://examples.k8s.io/volumes/rbd/README.md#how-to-use-it
user <string>
#rados 用户名,默认为admin
The rados user name. Default is admin. More info:
https://examples.k8s.io/volumes/rbd/README.md#how-to-use-it
3、实验架构图
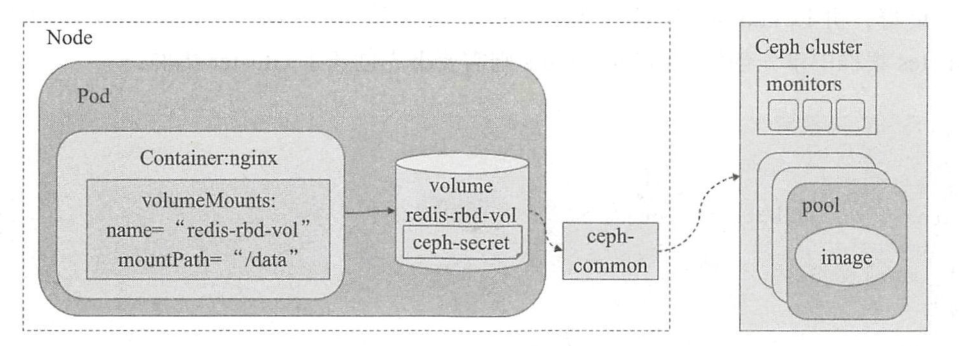
此示例依赖于实现存在的一个ceph存储集群
这里假设其监视器的地址为:172.16.0.56、172.16.0.57、172.16.0.58三个主机IP
并且集群上存储池kube中存在创建好的应先redis、此影响用油ext4文件系统
ceph客户端访问集群时需要实现完成认真之后才能进行后续的访问操作、此示例上、其认真信息保存于名为Ceph-secret的secret资源对象中
4、示例模板
[root@master chapter7]# cat vol-rbd.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: vol-rbd-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: redis
image: redis:4-alpine
ports:
- containerPort: 6379
name: redisport
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /data
name: redis-rbd-vol
volumes:
- name: redis-rbd-vol
rbd:
monitors:
- '172.16.0.56:6789'
- '172.16.0.57:6789'
- '172.16.0.58:6789'
pool: kube
image: redis
fsType: ext4
readOnly: false
user: admin
secretRef:
name: ceph-secret
三、GlusterFS存储卷
要配置pod资源使用GlusterFS存储卷、需要事先满足一下前提条件
1、前提条件
1、存储在某可用的GlusterFS存储集群、否则就要创建一个
2、在GlusterFS集群中创建一个能满足pod资源数据存储需要的卷
3、在kubernetes集群内的各节点上安装GlusterFS客户端程序包(glusterf和gluseterfs-fuse)
4、另外、若要基于GlusterFS是哦用存储卷的动态供给机制、还需要实现部署heketi,它用于为GlusterFS集群提供RESTFUL风格的管理接口
2、字段属性详解
[root@master ~]# kubectl explain pod.spec.volumes.glusterfs
KIND: Pod
VERSION: v1
RESOURCE: glusterfs <Object>
DESCRIPTION:
Glusterfs represents a Glusterfs mount on the host that shares a pod's
lifetime. More info: https://examples.k8s.io/volumes/glusterfs/README.md
Represents a Glusterfs mount that lasts the lifetime of a pod. Glusterfs
volumes do not support ownership management or SELinux relabeling.
FIELDS:
endpoints <string> -required-
#Endpoints 资源的名称、此资源需要实现存在,用于提供Cluster集群的部分节点信息作为其访问入口;必选字段
EndpointsName is the endpoint name that details Glusterfs topology. More
info: https://examples.k8s.io/volumes/glusterfs/README.md#create-a-pod
path <string> -required-
#用到的glusterfs集群的卷路径、如:kube-redis;必选字段
Path is the Glusterfs volume path. More info:
https://examples.k8s.io/volumes/glusterfs/README.md#create-a-pod
readOnly <boolean>
#是否为只读卷
ReadOnly here will force the Glusterfs volume to be mounted with read-only
permissions. Defaults to false. More info:
https://examples.k8s.io/volumes/glusterfs/README.md#create-a-pod
3、资源清单
[root@master chapter7]# cat vol-glusterfs.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: vol-glusterfs-pod
labels:
app: redis
spec:
containers:
- name: redis
image: redis:alpine
ports:
- containerPort: 6379
name: redisport
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /data
name: redisdata
volumes:
- name: redisdata
glusterfs:
endpoints: glusterfs-endpoints
path: kube-redis
readOnly: false
vol-glusterfs.yaml 它使用了glusterfs存储卷持久保存应用数据、它通过glusterfs-endpolints资源中定义的glusterfs集群节点信息接入集群
并以kube-redis卷作为pod资源的存储卷。glusterfs-endpolints资源需要在kubernetes集群中事先创建、而kube-redis则需要事先创建Gluster集群
4、创建运行
用于访问cluster集群的相关结点信息要实现保存于某特定的endpolints资源中、例如上面示例中调用的glusterfs-endpolints、此类的endpolints
资源可由用户根据实际需要手动创建、例如、下面的保存于glusterfs-endpolints.yaml文件中的资源示例中定义了三个接入相关的gluster存储集群
的节点gfs01.ilinux.io、gfs01.ilinux.io和gfs03.ilinux.io、期中的端口信息仅为满足endpolints资源必选字段要求、因此其值可以随意填写
[root@master chapter7]# cat glusterfs-endpoints.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Endpoints
metadata:
name: glusterfs-endpoints
subsets:
- addresses:
- ip: 172.16.2.36
ports:
- port: 24007
name: glusterd
- addresses:
- ip: 172.16.2.37
ports:
- port: 24007
name: glusterd
- addresses:
- ip: 172.16.2.38
ports:
- port: 24007
name: glusterd
首先创建endpolints资源glusterfs-endpoints,然后再创建pod资源vol-glusterfs即可测试其数据持久化存储的效果
四、cinder存储卷
1、字段详解
openstack构建的iaas环境中时、cinder的块存储功能可为pod资源提供外部持久存储的幼小方式
在pod资源上定义使用cinder存储卷时,其可用的嵌套字段包含如下几个
[root@master ~]# kubectl explain pod.spec.volumes.cinder
KIND: Pod
VERSION: v1
RESOURCE: cinder <Object>
DESCRIPTION:
Cinder represents a cinder volume attached and mounted on kubelets host
machine. More info: https://examples.k8s.io/mysql-cinder-pd/README.md
Represents a cinder volume resource in Openstack. A Cinder volume must
exist before mounting to a container. The volume must also be in the same
region as the kubelet. Cinder volumes support ownership management and
SELinux relabeling.
FIELDS:
fsType <string>
#要挂在的存储卷的问价那系统类型,至少应该是接待能操作系统支持的问价那系统
Filesystem type to mount. Must be a filesystem type supported by the host
operating system. Examples: "ext4", "xfs", "ntfs". Implicitly inferred to
be "ext4" if unspecified. More info:
https://examples.k8s.io/mysql-cinder-pd/README.md
readOnly <boolean>
#是否以只读方式访问
Optional: Defaults to false (read/write). ReadOnly here will force the
ReadOnly setting in VolumeMounts. More info:
https://examples.k8s.io/mysql-cinder-pd/README.md
secretRef <Object>
Optional: points to a secret object containing parameters used to connect
to OpenStack.
volumeID <string> -required-
#用于表示cinder中的存储卷的卷标识符、必选字段
volume id used to identify the volume in cinder. More info:
https://examples.k8s.io/mysql-cinder-pd/README.md
2、模板示例
下面的资源清单是定义在vol-cinder.yaml 文件中的使用示例、假设在openstack环境中有创建好的cinder卷可用
[root@master chapter7]# cat vol-cinder.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: vol-cinder-pod
spec:
containers:
- image: mysql
name: mysql
args:
- "--ignore-db-dir"
- "lost+found"
env:
- name: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD
value: YOUR_PASS
ports:
- containerPort: 3306
name: mysqlport
volumeMounts:
- name: mysqldata
mountPath: /var/lib/mysql
volumes:
- name: mysqldata
cinder:
volumeID: e2b8d2f7-wece-90d1-a505-4acf607a90bc
fsType: ext4