一、11-20
11、ord(c)
功能:根据字符,找到对应的ascii值
|
1
2
|
>>> ord('a')97 |
12、classmethod(function)
功能:类方法,这个到后续谈到类的时候再说。
13、compile(source, filename, mode, flags=0, dont_inherit=False, optimize=-1)
功能:用于把代码编译的一个过程,这个基本用不到
|
1
2
3
4
|
>>> code = """1+3/2*6""" >>> py_object = compile(code,'','eval') #把代码转换为字符串>>> eval(py_object) #执行10.0 |
14、complex([real[, imag]])
功能:返回一个复数,我们几乎用不到。
|
1
2
|
>>> complex('1+2j')(1+2j) |
15、delattr(object, name)
功能:类那边使用的,先不care。
16、dict(**kwarg)、dict(mapping, **kwarg)、dict(iterable, **kwarg)
功能:返回一个字典
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
>>> dict() #定义一个字典{}>>> dict(name='zhangqigao',age=18) #传入非固定关键字参数{'name': 'zhangqigao', 'age': 18}>>> dict([('name','zhangqigao'),('age',18)]) #传入一个列表{'name': 'zhangqigao', 'age': 18}>>> dict([['name','zhangqigao'],['age',18]]) #传入一个列表{'name': 'zhangqigao', 'age': 18} |
17、dir([object])
功能:看一个对象有哪些方法
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
>>> name = []>>> dir(name) #显示name下的所有的方法['__add__', '__class__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__delitem__', '__dir__', '__doc__','__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__gt__', '__hash__','__iadd__', '__imul__', '__init__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__mul__', '__ne__','__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__reversed__', '__rmul__','__setattr__', '__setitem__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', 'append', 'clear','copy', 'count', 'extend', 'index', 'insert', 'pop', 'remove', 'reverse', 'sort'] |
18、divmod(a,b)
功能:地板除,获得一个元组,元组第一个元素是商,第二个元素是余数。
|
1
2
|
>>> divmod(5,2)(2, 1) #2是商,1是余数 |
19、enumerate(iterable,start=0)
功能:获取一个列表,列表中的每个元素都是一个元组,元组的第一个数是iterable的索引,第二个数是iterable的元素。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
>>> seasons = ['Spring', 'Summer', 'Fall', 'Winter']>>> list(enumerate(seasons))[(0, 'Spring'), (1, 'Summer'), (2, 'Fall'), (3, 'Winter')]>>> list(enumerate(seasons, start=1))[(1, 'Spring'), (2, 'Summer'), (3, 'Fall'), (4, 'Winter')] |
20、eval(expression, globals=None, locals=None)
功能:把字典类型的字符串变成字典,把一个整数类型的字符变成int类型,或者加减乘除这种简单转换成表达式。
|
1
2
3
4
|
>>> eval('1') #字符类型转换成int类型1>>> eval("1+3/2*6") #字符串转换为表达式10.0 |
二、21-25
21、exec(object[, globals[, locals]])
功能:有语句的和复杂的语句的字符串转换成表达式
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
code = '''def timmer(func): #timmer(test1) func=test1 def deco(*args,**kwargs): res = func(*args,**kwargs) #run test1() return res return deco@timmerdef test1(): print("in the test1") return "from the test1"res = test1()print(res)'''exec(code) #输出in the test1from the test1 |
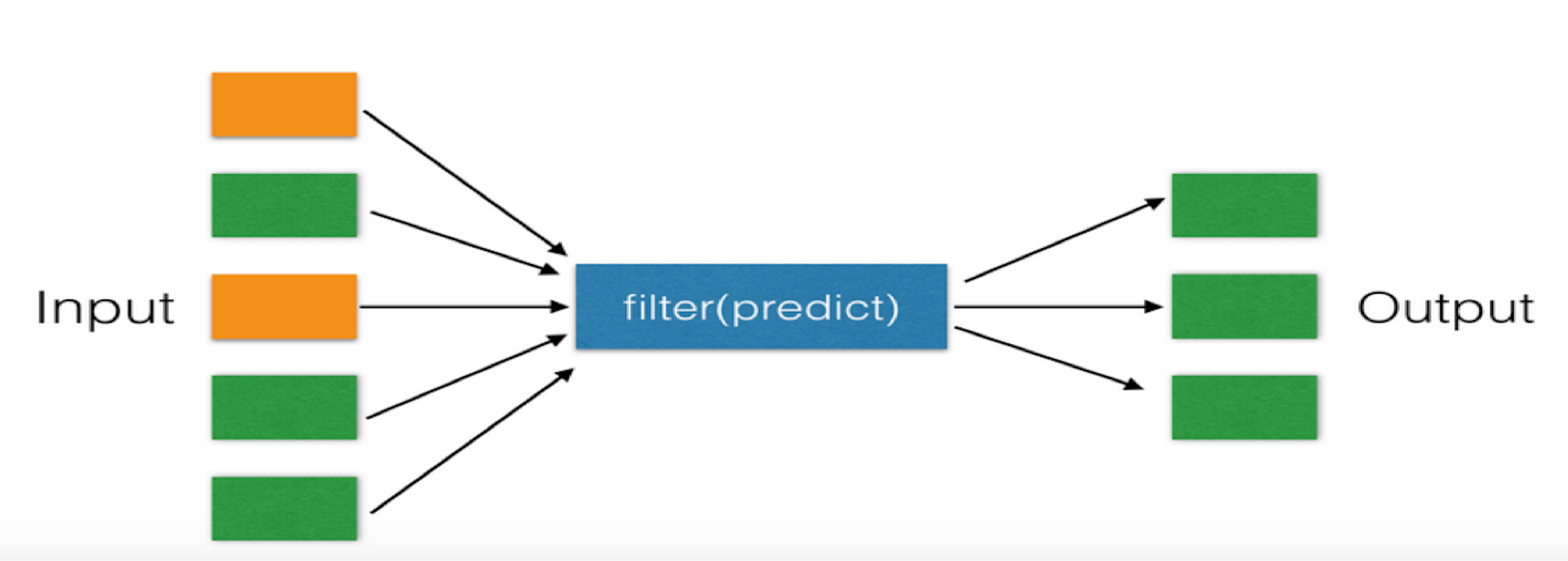
22、filter(function, iterable)
功能:对于序列中的元素进行筛选,最终获取符合条件的序列
def f1(args):
result = []
for item in args:
if item > 22:
result.append(item)
return result
li = [11, 22, 33, 44, 55]
ret = f1(li)
print(ret)
filter(函数,可迭代的对象)
def f2(a):
if a>22:
return True
li = [11, 22, 33, 44, 55]
filter内部,循环第二个参数
result = []
for item in 第二个参数:
r = 第一个参数(item)
if r :
result(item)
return result
filter ,循环循环第二个参数,让每个循环元素执行 函数,如果函数返回值True,表示元素合法
ret = filter(f2, li)
print(list(ret))
filter,内部循环,参数比较
自动return
f1 = lambda a: a > 30
ret = f1(10)
print(ret)
li = [11, 22, 33, 44, 55]
result = filter(lambda a: a > 33, li)
print(list(result))
23、map(function, iterable)
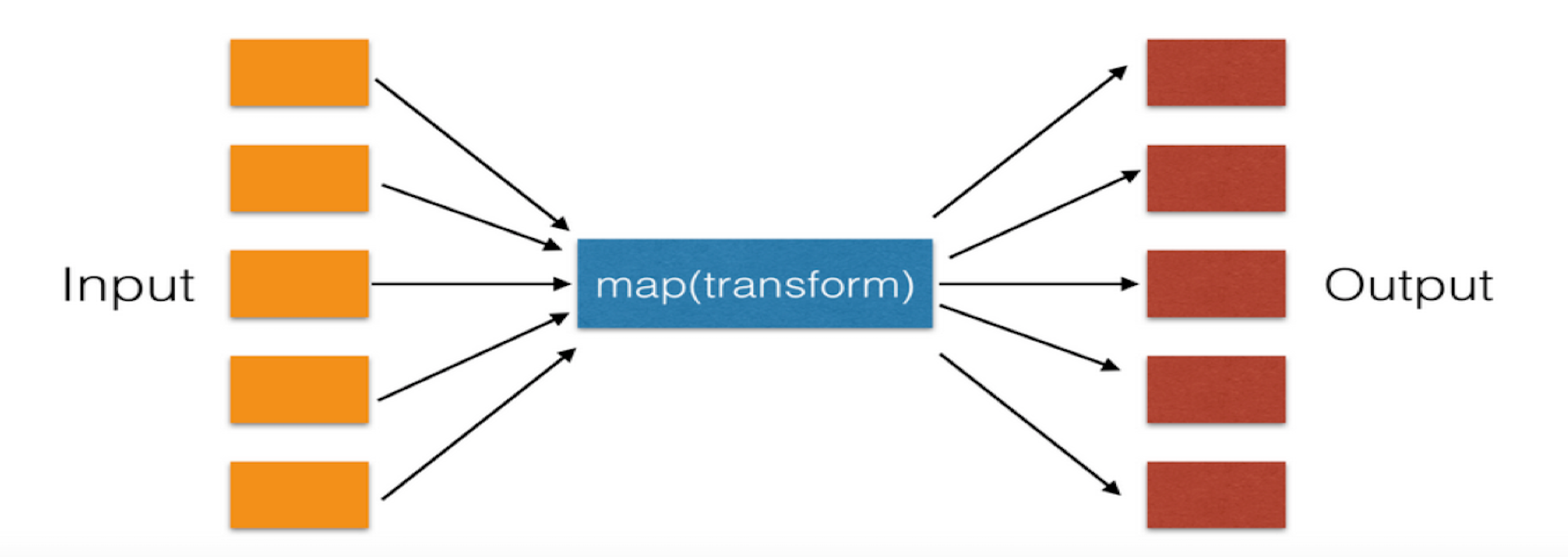
功能:遍历序列,对序列中每个元素进行操作,最终获取新的序列。
i = [11, 22, 33, 44, 55]
map(函数,可迭代的对象(可以for循环的东西))
def f2(a):
return a + 100
result = map(f2, li)
result = map(lambda a: a + 200, li)
print(list(result))
filter # 函数返回True,将元素添加到结果中
map # 将函数返回值添加到结果中
def f1(args):
result = []
for i in args:
result.append(100+i)
return result
r = f1(li)
print(list(r))
24、reduce(function,iterable)
功能:把一组可迭代序列通过function函数操作,元素之间相加或者相乘操作。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
>>> from functools import reduce>>> res = reduce(lambda x,y:x+y,range(10)) #x+y的值赋给x,rang(10)中的每个元素赋给y>>> res45>>> res = reduce(lambda x,y:x*y,range(1,10)) #x*y的值赋给x,rang(10)中的每个元素赋给y>>> res362880 |
25、float([x])
功能:把一个浮点类型的字符串转换为浮点类型的数据。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
>>> float('+1.23')1.23>>> float(' -12345
')-12345.0>>> float('1e-003')0.001>>> float('+1E6')1000000.0>>> float('-Infinity')-inf |
三、26-35
26、format(value[, format_spec])
27、frozenset([iterable])
功能:把集合变成一个不可变的集合
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
>>> res = frozenset([1,2,3,4,3])>>> resfrozenset({1, 2, 3, 4}) #去重的,不可变的集合>>> dir(res) #没有可变的方法['__and__', '__class__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__','__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__or__', '__rand__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__','__repr__', '__ror__', '__rsub__', '__rxor__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__sub__','__subclasshook__', '__xor__', 'copy', 'difference', 'intersection', 'isdisjoint', 'issubset','issuperset', 'symmetric_difference', 'union'] |
注:set()是可变的
28、getattr(object, name[, default])
功能:这边是类那边的,后续再讲。
29、globals()
功能:返回当前这个python文件中的所有变量的key-value,变量是key,值是value
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
print(globals())#输出{'__spec__': None, '__name__': '__main__', '__file__': 'D:/PycharmProjects/pyhomework/day4/内置函数/内置函数.py', '__doc__': None, '__package__': None, '__loader__':<_frozen_importlib_external.SourceFileLoader object at 0x0000000000695B00>,'__cached__': None, '__builtins__': <module 'built |
注:可以判断一个文件中的变量是否存在,而globals()只能打印全局变量
30、hash(object)
功能:反射出一个对象的对应的hash值。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
>>> hash('zhangqigao')2313972277536963491>>> hash(255)255>>> hash('a')6806508886604307842 |
这个有什么用呐?
先看下面的图:
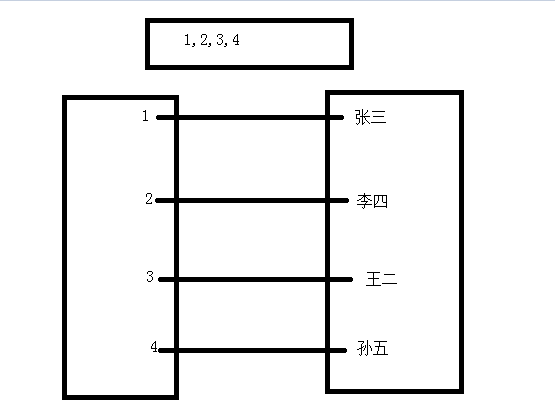
看上面的图我们知道,如果一张表中5百万个用户信息,以我们现在的知识,只能用for循环去查找,那样的话,效率会很低。那我们怎么办呢?我们可以这样,就是把每一个姓名对应有一对应的值,然后通过对应的key值去定位,key值是放在一个列表中,当我们去查找某个key值时,可以折半查找,这样大大减少了查找时间,提高效率,这种也叫二分法查找,后面会有对应的博客专门写这一块的。
内置函数三
31、help([object])
功能:显示对象的帮助信息
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
>>> res = [] #定义一个列表>>> help(res) #打印帮助信息Help on list object:class list(object) | list() -> new empty list | list(iterable) -> new list initialized from iterable's items | | Methods defined here: | ..... |
32、hex(x)
功能:把一个数字转成16进制
|
1
2
3
4
|
>>> hex(255)'0xff'>>> hex(10)'0xa' |
33、id(object)
功能:返回对象的内存地址
|
1
2
|
>>> id('zhangqigao')50993136 #'zhangqigao'这个字符串的内存地址 |
34、input([prompt])
功能:输入字符串
|
1
2
3
4
|
>>> s = input('--> ') --> Monty Python's Flying Circus #输入的内容>>> s "Monty Python's Flying Circus" |
35、int(x)
功能:把其他数据类型强制转换成int类型
|
1
2
|
>>> int('10')10 |