我们在前面分析客户端引用的时候会看到如下这段代码:
// 产生开始调用事件
if (EventBus.isEnable(ClientStartInvokeEvent.class)) {
EventBus.post(new ClientStartInvokeEvent(request));
}
这里用EventBus调用了一下post方法之后就什么也没做了,就方法名来看是发送了一个post请求,也不知道发给谁,到底有什么用。
所以这一节我们来分析一下EventBus这个类的作用。
首先我们来看一下这个类的方法

从EventBus的方法中我们是不是应该想到了这是使用了什么设计模式?
没错,这里用到的是订阅发布模式(Subscribe/Publish)。订阅发布模式定义了一种一对多的依赖关系,让多个订阅者对象同时监听某一个主题对象。这个主题对象在自身状态变化时,会通知所有订阅者对象,使它们能够自动更新自己的状态。
我们先分析源码,分析完源码之后再来总结一下。
EventBus发送事件
根据上面的示例,我们先看EventBus#post是里面是怎么做的。
EventBus#post
private final static ConcurrentMap<Class<? extends Event>, CopyOnWriteArraySet<Subscriber>> SUBSCRIBER_MAP = new ConcurrentHashMap<Class<? extends Event>, CopyOnWriteArraySet<Subscriber>>();
public static void post(final Event event) {
//是否开启总线
if (!isEnable()) {
return;
}
//根据传入得event获取到相应的Subscriber
CopyOnWriteArraySet<Subscriber> subscribers = SUBSCRIBER_MAP.get(event.getClass());
if (CommonUtils.isNotEmpty(subscribers)) {
for (final Subscriber subscriber : subscribers) {
//如果事件订阅者是同步的,那么直接调用
if (subscriber.isSync()) {
handleEvent(subscriber, event);
} else { // 异步
final RpcInternalContext context = RpcInternalContext.peekContext();
//使用线程池启动一个线程一部执行任务
final ThreadPoolExecutor asyncThreadPool = AsyncRuntime.getAsyncThreadPool();
try {
asyncThreadPool.execute(
new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
RpcInternalContext.setContext(context);
//调用订阅者的event事件
handleEvent(subscriber, event);
} finally {
RpcInternalContext.removeContext();
}
}
});
} catch (RejectedExecutionException e) {
LOGGER
.warn("This queue is full when post event to async execute, queue size is " +
asyncThreadPool.getQueue().size() +
", please optimize this async thread pool of eventbus.");
}
}
}
}
}
private static void handleEvent(final Subscriber subscriber, final Event event) {
try {
subscriber.onEvent(event);
} catch (Throwable e) {
if (LOGGER.isWarnEnabled()) {
LOGGER.warn("Handle " + event.getClass() + " error", e);
}
}
}
这个post方法主要做了这么几件事:
- 根据传入的Event获取对应的订阅列表subscribers
- 遍历subscribers
- 如果订阅者是异步的,那么就使用线程池启动执行任务
4, 如果是同步的那么就调用handleEvent方法向订阅者发布消息
我们再来看看订阅者是怎样的:
Subscriber
public abstract class Subscriber {
/**
* 接到事件是否同步执行
*/
protected boolean sync = true;
/**
* 事件订阅者
*/
protected Subscriber() {
}
/**
* 事件订阅者
*
* @param sync 是否同步
*/
protected Subscriber(boolean sync) {
this.sync = sync;
}
/**
* 是否同步
*
* @return 是否同步
*/
public boolean isSync() {
return sync;
}
/**
* 事件处理,请处理异常
*
* @param event 事件
*/
public abstract void onEvent(Event event);
}
Subscriber是一个抽象类,默认是同步的方式进行订阅。总共有下面四个实现类:
LookoutSubscriber
FaultToleranceSubscriber
RestTracerSubscriber
SofaTracerSubscriber
这里我不打算每个都进行分析,到时候打算用到了再详细说明,这样不会那么抽象。
由于我们前面讲到了,在客户端引用的时候会发送一个产生开始调用事件给总线,那一定要有订阅者这个发送事件才有意义。所以我们接下来看看是在哪里进行事件的注册的。
订阅者注册到EventBus
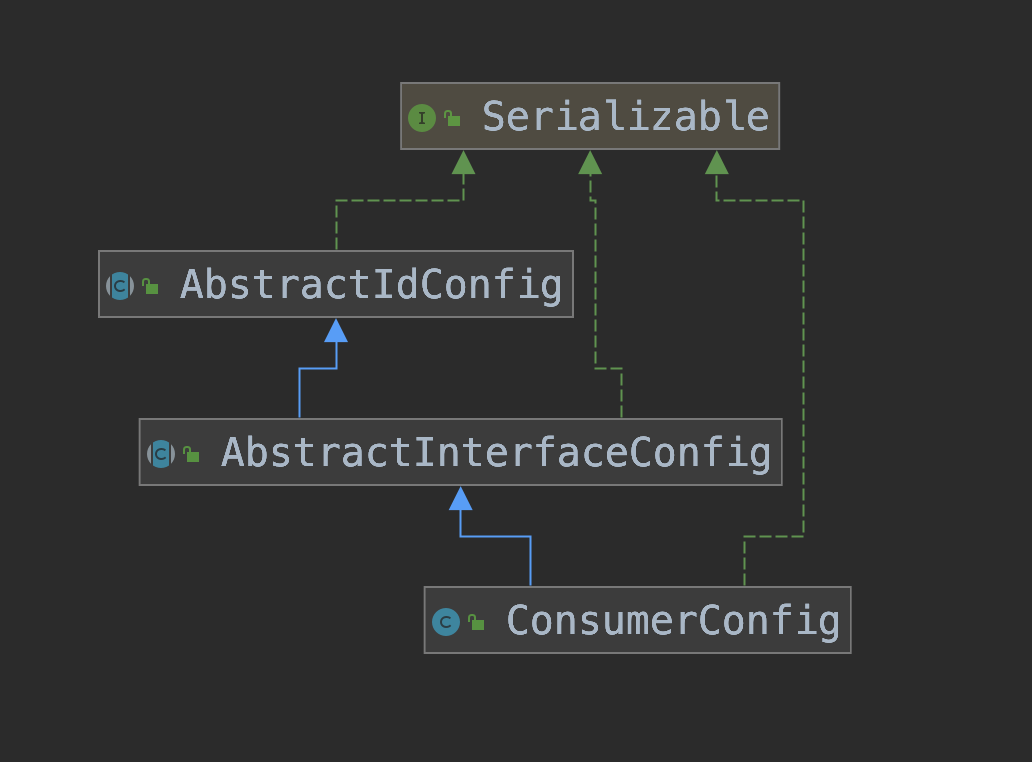
通过上面的继承关系图可以看到,在ConsumerConfig是AbstractIdConfig的子类,所以在初始化ConsumerConfig的时候AbstractIdConfig静态代码块也会被初始化。
public abstract class AbstractIdConfig<S extends AbstractIdConfig> implements Serializable {
static {
RpcRuntimeContext.now();
}
}
在调用RpcRuntimeContext#now方法的时候,会调用到RpcRuntimeContext的静态代码块
RpcRuntimeContext
public class RpcRuntimeContext {
static {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Welcome! Loading SOFA RPC Framework : {}, PID is:{}", Version.BUILD_VERSION, PID);
}
put(RpcConstants.CONFIG_KEY_RPC_VERSION, Version.RPC_VERSION);
// 初始化一些上下文
initContext();
// 初始化其它模块
ModuleFactory.installModules();
// 增加jvm关闭事件
if (RpcConfigs.getOrDefaultValue(RpcOptions.JVM_SHUTDOWN_HOOK, true)) {
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (LOGGER.isWarnEnabled()) {
LOGGER.warn("SOFA RPC Framework catch JVM shutdown event, Run shutdown hook now.");
}
destroy(false);
}
}, "SOFA-RPC-ShutdownHook"));
}
}
public static long now() {
return System.currentTimeMillis();
}
}
在RpcRuntimeContext静态代码块里主要做了以下几件事:
- 初始化一些上下文的东西,例如:应用Id,应用名称,当前所在文件夹地址等
- 初始化一些模块,等下分析
- 增加jvm关闭时的钩子
我们直接看installModules方法就好了,其他的方法和主流程无关。
ModuleFactory#installModules
public static void installModules() {
//通过SPI加载Module模块
ExtensionLoader<Module> loader = ExtensionLoaderFactory.getExtensionLoader(Module.class);
//moduleLoadList 默认是 *
String moduleLoadList = RpcConfigs.getStringValue(RpcOptions.MODULE_LOAD_LIST);
for (Map.Entry<String, ExtensionClass<Module>> o : loader.getAllExtensions().entrySet()) {
String moduleName = o.getKey();
Module module = o.getValue().getExtInstance();
// judge need load from rpc option
if (needLoad(moduleLoadList, moduleName)) {
// judge need load from implement
if (module.needLoad()) {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Install Module: {}", moduleName);
}
//安装模板
module.install();
INSTALLED_MODULES.put(moduleName, module);
} else {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("The module " + moduleName + " does not need to be loaded.");
}
}
} else {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("The module " + moduleName + " is not in the module load list.");
}
}
}
}
-
这个方法里面一开始获取Module的扩展类,Module的扩展类有如下几个:
FaultToleranceModule
LookoutModule
RestTracerModule
SofaTracerModule -
然后会去获取MODULE_LOAD_LIST配置类,多个配置用“;”分割。
-
调用loader.getAllExtensions()获取所有的扩展类。遍历扩展类。
-
接着调用needLoad方法:
static boolean needLoad(String moduleLoadList, String moduleName) {
//用;拆分
String[] activatedModules = StringUtils.splitWithCommaOrSemicolon(moduleLoadList);
boolean match = false;
for (String activatedModule : activatedModules) {
//ALL 就是 *
if (StringUtils.ALL.equals(activatedModule)) {
match = true;
} else if (activatedModule.equals(moduleName)) {
match = true;
} else if (match && (activatedModule.equals("!" + moduleName)
|| activatedModule.equals("-" + moduleName))) {
match = false;
break;
}
}
return match;
}
这个方法会传入配置的moduleLoadList和当前遍历到的moduleName,moduleLoadList默认是*所以会返回true,如果配置了moduleLoadList不为*的话,如果moduleName是配置中的之一便会返回true。
- 调用module的install进行模板的装配
这里我们进入到SofaTracerModule#install中
SofaTracerModule#install
public void install() {
Tracer tracer = TracerFactory.getTracer("sofaTracer");
if (tracer != null) {
subscriber = new SofaTracerSubscriber();
EventBus.register(ClientStartInvokeEvent.class, subscriber);
EventBus.register(ClientBeforeSendEvent.class, subscriber);
EventBus.register(ClientAfterSendEvent.class, subscriber);
EventBus.register(ServerReceiveEvent.class, subscriber);
EventBus.register(ServerSendEvent.class, subscriber);
EventBus.register(ServerEndHandleEvent.class, subscriber);
EventBus.register(ClientSyncReceiveEvent.class, subscriber);
EventBus.register(ClientAsyncReceiveEvent.class, subscriber);
EventBus.register(ClientEndInvokeEvent.class, subscriber);
}
}
这里我们可以看到文章一开始被发送的ClientStartInvokeEvent在这里被注册了。订阅者的实现类是SofaTracerSubscriber。
订阅者被调用
在上面我们分析到在注册到EventBus之后,会发送一个post请求,然后EventBus会遍历所有的Subscriber,调用符合条件的Subscriber的onEvent方法。
SofaTracerSubscriber#onEvent
public void onEvent(Event originEvent) {
if (!Tracers.isEnable()) {
return;
}
Class eventClass = originEvent.getClass();
if (eventClass == ClientStartInvokeEvent.class) {
ClientStartInvokeEvent event = (ClientStartInvokeEvent) originEvent;
Tracers.startRpc(event.getRequest());
}
else if (eventClass == ClientBeforeSendEvent.class) {
ClientBeforeSendEvent event = (ClientBeforeSendEvent) originEvent;
Tracers.clientBeforeSend(event.getRequest());
}
.....
}
这个方法里面主要就是对不同的event做出不同的反应。ClientStartInvokeEvent所做的请求就是调用一下Tracers#startRpc,Tracers是用来做链路追踪的,这篇文章不涉及。
总结
我们首先上一张图,来说明一下订阅发布模式整体的结构。
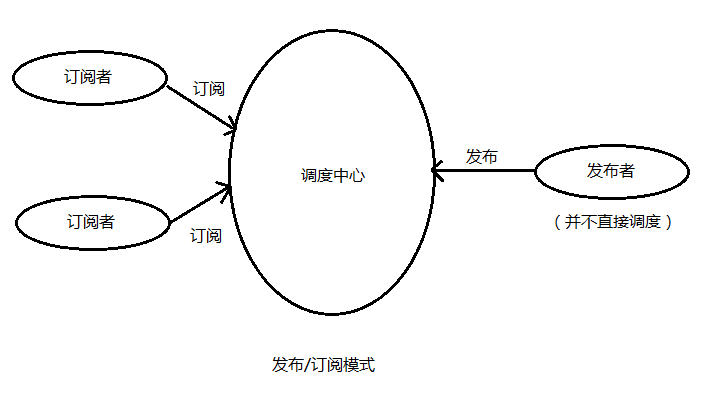
在我们这个例子里EventBus的职责就是调度中心,subscriber的具体实现注册到EventBus中后,会保存到EventBus的SUBSCRIBER_MAP集合中。
发布者在发布消息的时候会调用EventBus的post方法传入一个具体的event来调用订阅者的事件。一个事件有多个订阅者,消息的发布者不会直接的去调用订阅者来发布消息,而是通过EventBus来进行触发。
通过EventBus来触发不同的订阅者的事件可以在触发事件之前同一的为其做一些操作,比如是同步还是异步,要不要过滤部分订阅者等。
SOFARPC源码解析系列: