转载请声明出处哦~,本篇文章发布于luozhiyun的博客:https://www.luozhiyun.com
本文使用的Istio源码是 release 1.5。
Config Controller用于管理各种配置数据,包括用户创建的流量管理规则和策略。Istio目前支持三种类型的Config Controller:
- MCP:是一种网络配置协议,用于隔离Pilot和底层平台(文件系统、K8s),使得Pilot无须感知底层平台的差异,从而达到解耦的目的。
- File:通过监视器周期性地读取本地配置文件,将配置规则缓存在内存中,并维护配置的增加、更新、删除事件,当缓存由变化的时候,异步通知执行事件回调。
- Kubernetes:基于k8s的Config发现利用了k8s Informer的监听能力。在k8s集群中,Config以CustomResource的形式存在。通过监听apiserver配置规则资源,维护所有资源的缓存Store,并触发事件处理回调函数。
ConfigController初始化
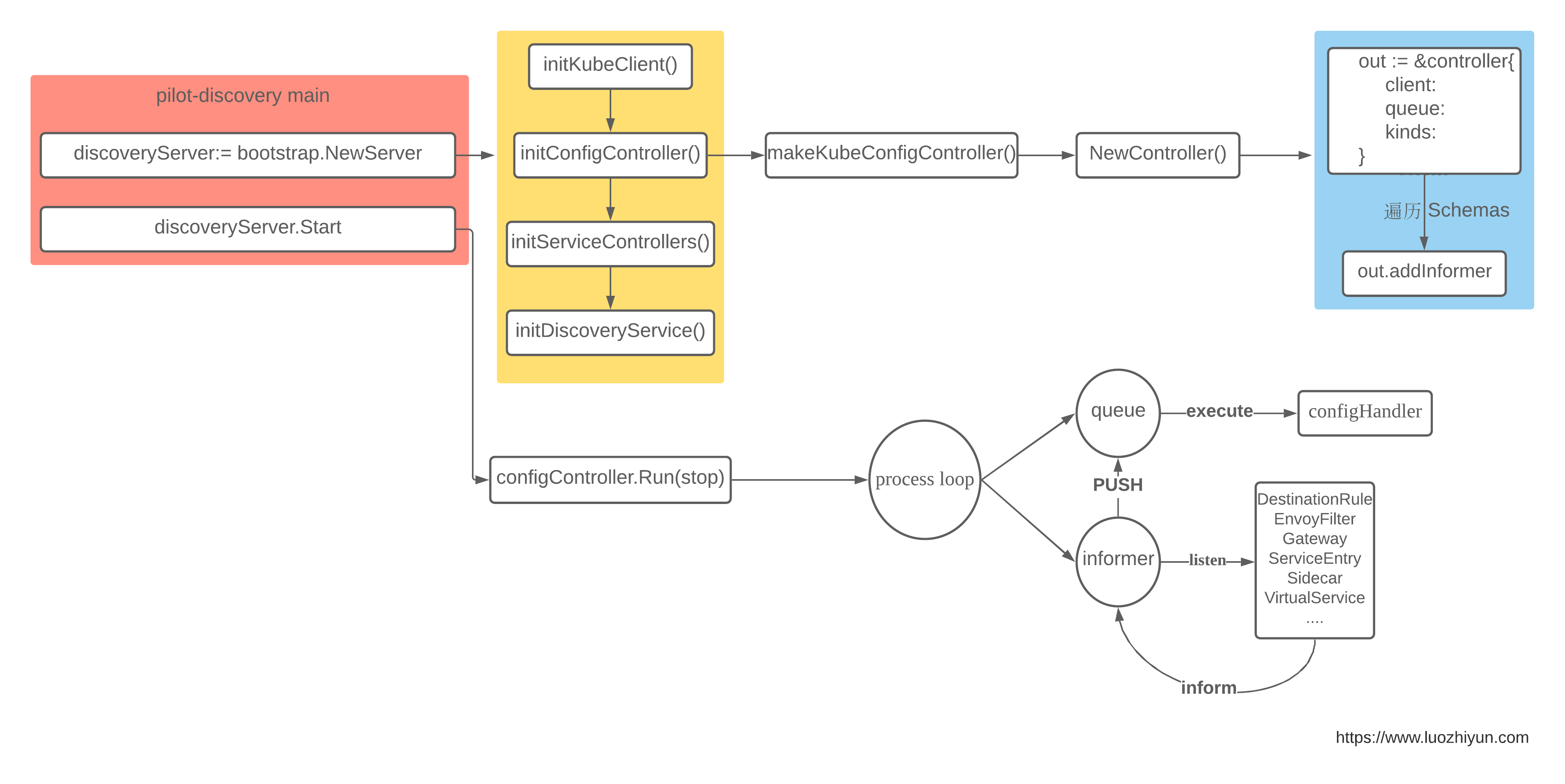
ConfigController是在initConfigController中被初始化的,在initConfigController方法中会调用makeKubeConfigController进行controller的初始化。
func (s *Server) makeKubeConfigController(args *PilotArgs) (model.ConfigStoreCache, error) {
//创建configClient
configClient, err := controller.NewClient(args.Config.KubeConfig, "", collections.Pilot,
args.Config.ControllerOptions.DomainSuffix, buildLedger(args.Config), args.Revision)
if err != nil {
return nil, multierror.Prefix(err, "failed to open a config client.")
}
//创建controller,并为config资源设置监听
return controller.NewController(configClient, args.Config.ControllerOptions), nil
}
func NewController(client *Client, options controller2.Options) model.ConfigStoreCache {
log.Infof("CRD controller watching namespaces %q", options.WatchedNamespace)
// The queue requires a time duration for a retry delay after a handler error
out := &controller{
client: client,
queue: queue.NewQueue(1 * time.Second),
kinds: make(map[resource.GroupVersionKind]*cacheHandler),
}
// add stores for CRD kinds
//获取所有的CRD类型
for _, s := range client.Schemas().All() {
//为每一种Config资源都创建一个informer,监听所有的Config资源
out.addInformer(s, options.WatchedNamespace, options.ResyncPeriod)
}
return out
}
初始化完controller之后会获取所有的CRD类型,为每一种Config资源都创建一个informer,监听所有的Config资源。
Pilot = collection.NewSchemasBuilder().
//MeshPolicy
MustAdd(IstioAuthenticationV1Alpha1Meshpolicies).
MustAdd(IstioAuthenticationV1Alpha1Policies).
MustAdd(IstioConfigV1Alpha2Httpapispecbindings).
MustAdd(IstioConfigV1Alpha2Httpapispecs).
MustAdd(IstioMixerV1ConfigClientQuotaspecbindings).
MustAdd(IstioMixerV1ConfigClientQuotaspecs).
//DestinationRule
MustAdd(IstioNetworkingV1Alpha3Destinationrules).
//EnvoyFilter
MustAdd(IstioNetworkingV1Alpha3Envoyfilters).
//Gateway
MustAdd(IstioNetworkingV1Alpha3Gateways).
//ServiceEntry
MustAdd(IstioNetworkingV1Alpha3Serviceentries).
//Sidecar
MustAdd(IstioNetworkingV1Alpha3Sidecars).
//VirtualService
MustAdd(IstioNetworkingV1Alpha3Virtualservices).
MustAdd(IstioRbacV1Alpha1Clusterrbacconfigs).
MustAdd(IstioRbacV1Alpha1Rbacconfigs).
MustAdd(IstioRbacV1Alpha1Servicerolebindings).
MustAdd(IstioRbacV1Alpha1Serviceroles).
MustAdd(IstioSecurityV1Beta1Authorizationpolicies).
MustAdd(IstioSecurityV1Beta1Peerauthentications).
MustAdd(IstioSecurityV1Beta1Requestauthentications).
Build()
这里定义好了所有要用到的Config资源类型,主要涉及网络配置、认证、鉴权、策略管理等。
ConfigController事件处理
下面我们看一下controller定义:
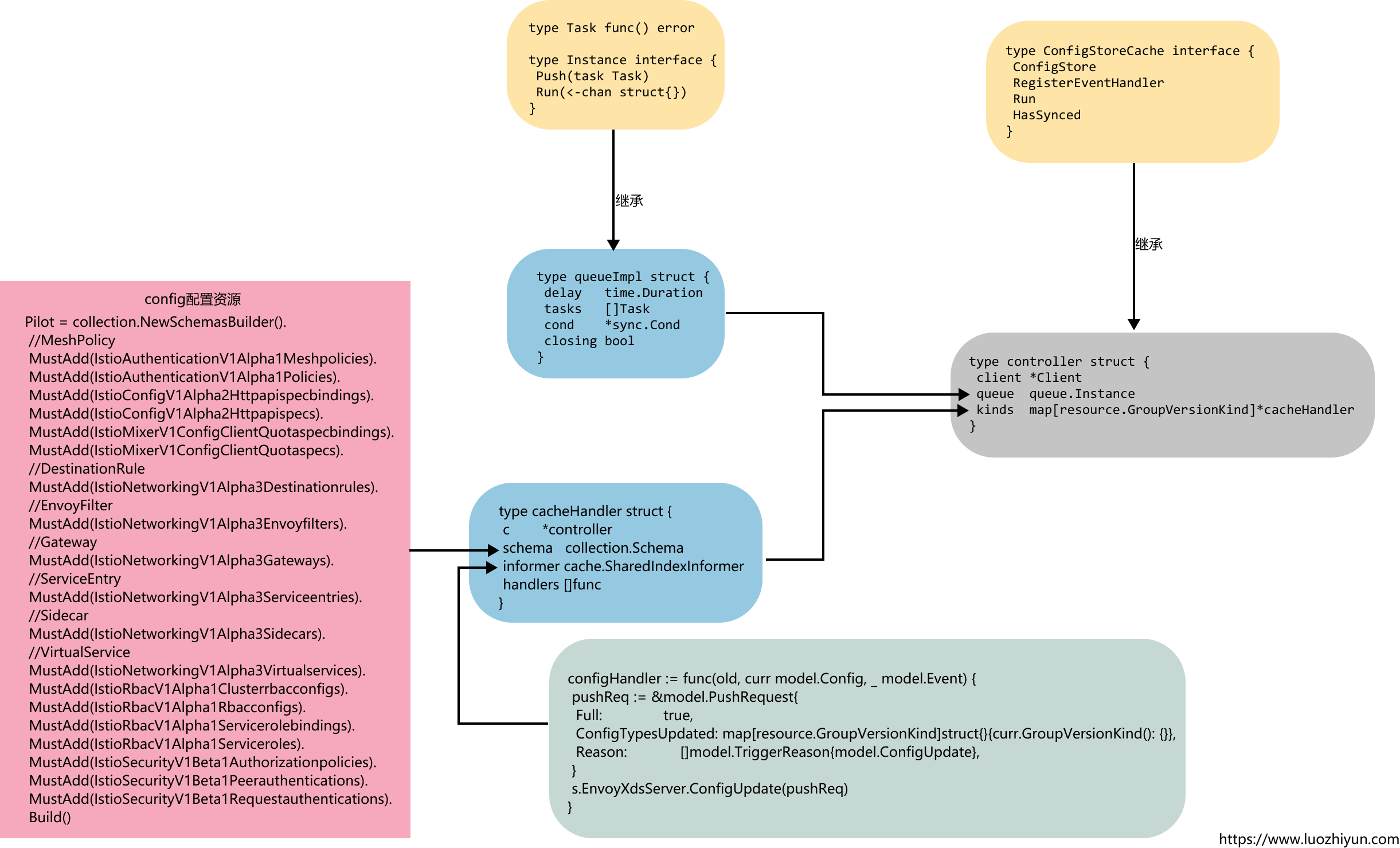
type controller struct {
client *Client
queue queue.Instance
kinds map[resource.GroupVersionKind]*cacheHandler
}
client是调用controller.NewClient初始化的client;queue会在Informer监听到资源的变动的时候将数据push到队列中,controller在调用run方法的时候单独运行一个线程运行queue中的函数;kinds在调用addInformer方法的时候初始化进去。
queue.Instance的定义如下:
type Task func() error
type Instance interface {
Push(task Task)
Run(<-chan struct{})
}
type queueImpl struct {
delay time.Duration
tasks []Task
cond *sync.Cond
closing bool
}
queueImpl继承了Instance接口,在调用push方法的时候,会将Task放入到tasks数组中,并在调用Run方法的时候消费数组中的数据。
controller继承了ConfigStoreCache接口:
type ConfigStoreCache interface {
ConfigStore
// 注册规则事件处理函数
RegisterEventHandler(kind resource.GroupVersionKind, handler func(Config, Config, Event))
// 运行
Run(stop <-chan struct{})
// 配置缓存是否已同步
HasSynced() bool
}
ConfigStoreCache通过RegisterEventHandler接口为上面提到的配置资源都注册事件处理函数,通过Run方法启动控制器。
func (c *controller) Run(stop <-chan struct{}) {
log.Infoa("Starting Pilot K8S CRD controller")
go func() {
cache.WaitForCacheSync(stop, c.HasSynced)
//单独启动一个线程运行queue里面的函数
c.queue.Run(stop)
}()
for _, ctl := range c.kinds {
go ctl.informer.Run(stop)
}
<-stop
log.Info("controller terminated")
}
在调用Run方法的时候会单独的启动一个线程调用queue的Run方法消费队列中的数据,并遍历所有的配置信息,调用informer的Run方法开启监听。
监听器的EventHandler通过如下代码注册:
func (c *controller) newCacheHandler(
schema collection.Schema,
o runtime.Object,
otype string,
resyncPeriod time.Duration,
lf cache.ListFunc,
wf cache.WatchFunc) *cacheHandler {
informer := cache.NewSharedIndexInformer(
&cache.ListWatch{ListFunc: lf, WatchFunc: wf}, o,
resyncPeriod, cache.Indexers{})
h := &cacheHandler{
c: c,
schema: schema,
informer: informer,
}
informer.AddEventHandler(
cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: func(obj interface{}) {
incrementEvent(otype, "add")
//将ADD事件发送至队列
c.queue.Push(func() error {
return h.onEvent(nil, obj, model.EventAdd)
})
},
UpdateFunc: func(old, cur interface{}) {
if !reflect.DeepEqual(old, cur) {
incrementEvent(otype, "update")
//将Update事件发送至队列
c.queue.Push(func() error {
return h.onEvent(old, cur, model.EventUpdate)
})
} else {
incrementEvent(otype, "updatesame")
}
},
DeleteFunc: func(obj interface{}) {
incrementEvent(otype, "delete")
//将Delete事件发送至队列
c.queue.Push(func() error {
return h.onEvent(nil, obj, model.EventDelete)
})
},
})
return h
}
当Config资源创建、更新、删除时,EventHandler创建任务对象并将其发送到任务队列中,然后由任务处理线程处理。当对应的事件被调用的时候会触发onEvent方法,会调用到cacheHandler的onEvent方法,最后设置完毕后将cacheHandler返回,controller会将此cacheHandler设置到kinds数组中存下来。
下面我们看一下cacheHandler的定义:
type cacheHandler struct {
c *controller
schema collection.Schema
informer cache.SharedIndexInformer
handlers []func(model.Config, model.Config, model.Event)
}
cacheHandler在上面初始化的时候,会传入对应的controller、Schema、informer,然后在调用configController的RegisterEventHandler方法的时候会初始化对应的configHandler。
configController的RegisterEventHandler方法会在初始化DiscoveryService的时候调用initEventHandlers方法进行初始化:
func (s *Server) initEventHandlers() error {
...
if s.configController != nil {
configHandler := func(old, curr model.Config, _ model.Event) {
pushReq := &model.PushRequest{
Full: true,
ConfigTypesUpdated: map[resource.GroupVersionKind]struct{}{curr.GroupVersionKind(): {}},
Reason: []model.TriggerReason{model.ConfigUpdate},
}
s.EnvoyXdsServer.ConfigUpdate(pushReq)
}
//遍历所有的资源
for _, schema := range collections.Pilot.All() {
// This resource type was handled in external/servicediscovery.go, no need to rehandle here.
//ServiceEntry 这个资源不在这里注册,感兴趣的朋友可以自己找一下
if schema.Resource().GroupVersionKind() == collections.IstioNetworkingV1Alpha3Serviceentries.
Resource().GroupVersionKind() {
continue
}
//注册configHandler到configController中
s.configController.RegisterEventHandler(schema.Resource().GroupVersionKind(), configHandler)
}
}
return nil
}
initEventHandlers会调用collections.Pilot.All方法获取所有的资源配置,然后遍历调用RegisterEventHandler方法将configHandler函数注册到cacheHandler的handlers中,至于configHandler函数做了什么,我们到下一篇讲XdsServer的时候再讲。
这一部分的代码是比较绕的,这里画个图理解一下吧。
整个执行流程为:
总结
至此,ConfigController的核心原理及工作流程就介绍完毕了。本篇主要讲解了我们常用的Istio的Gateway、DestinationRule及VirtualService等配置是如何被Istio监听到并作出相应改变的。希望大家能有所收获。
Reference
https://ruofeng.me/2018/11/08/how-does-istio-pilot-push-eds-config/
https://zhaohuabing.com/post/2019-10-21-pilot-discovery-code-analysi
https://www.servicemesher.com/blog/envoy-proxy-config-deep-dive/