F maki和tree
思路:
用到并查集的思想

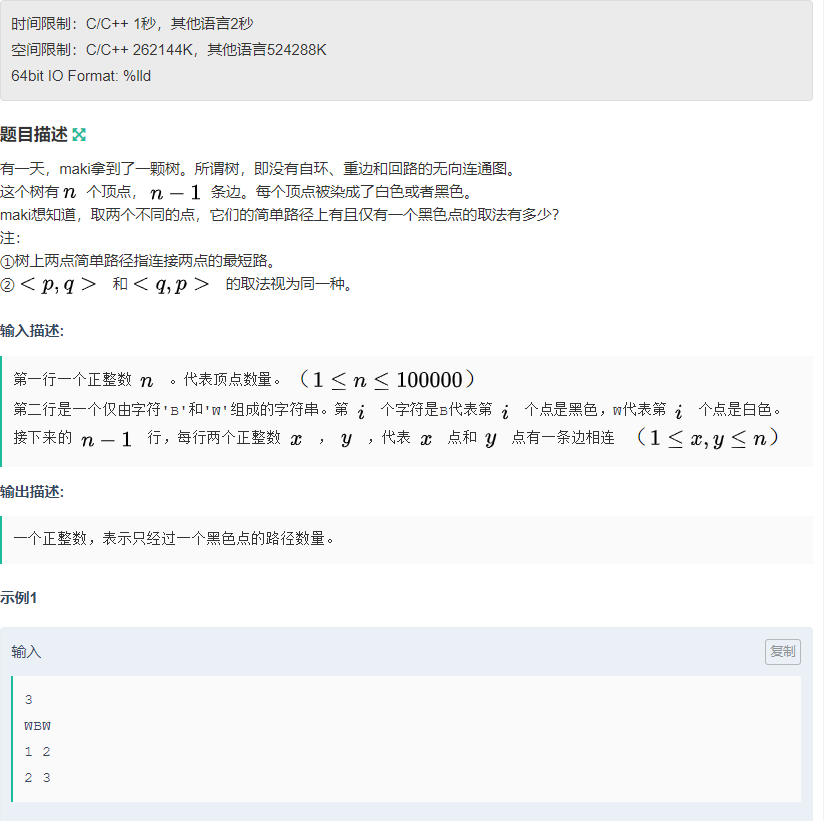
如图:
简单路径上只有一个黑色点的方案:第一种端点有一个为黑色点,第二种两端点均为白色点,端点连接的线路中有一个黑色点
ans = (1+2+3)+1*2+2*3+1*3 = (1+2+3)+1*(2+3)+2*3
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int maxn = 1e5+10;
vector<int>e[maxn];
int f[maxn],size[maxn];
char s[maxn];
int find(int x){
if(f[x]==x)
return x;
return f[x] = find(f[x]);
}
void merge(int x,int y){
int t1 = find(x);
int t2 = find(y);
if(t1!=t2){
f[t2] = t1;
size[t1]+=size[t2];
}
}
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
cin>>s+1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(s[i]=='W')
size[i]++;
f[i]=i;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n-1;i++){
int x,y;
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
e[x].push_back(y);
e[y].push_back(x);
if(s[x]==s[y]&&s[x]=='W'){
merge(x,y);
}
}
ll ans = 0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(s[i]=='B'){
ll sum=0;
for(auto v:e[i]){
sum+=size[find(v)];
}
ans+=sum;
for(auto v:e[i]){
sum-=size[find(v)];
ans+=sum*size[find(v)];
}
}
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
J u's的影响

思路:
f(1) = x;
f(2)= y;
f(3)=x*y*(a^b);
f(4)=x*(y^2)*(a^b)^2;
f(5) = (x^2)*(y^3)*(a^b)^4;
f(6) = (x^3)*(y^5)*(a^b)^7;
f: f(1) f(2) f(3) f(4) f(5) f(6) f(7) f(8)
x的系数 : 1 0 1 1 2 3 5 8
y的系数 : 0 1 1 2 3 5 8 13
a^b的系数:0 0 1 2 4 7 12 20
红色数字:斐波拉契数列
a^b的系数 = x的系数+y的系数-1
这道题用到了费马小定理:例子 (3^100)%13 = (3^(12*8+4))%13 = (3^4)%13
p为质数 a,b均为非负 (a^b)%p = (a%p)^(b%(p-1))%p

代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const ll mod = 1e9+7;
struct mat{
ll a[2][2];
};
mat mat_mul(mat x,mat y){
mat res;
memset(res.a,0,sizeof(res.a));
for(ll i=0;i<2;i++){
for(ll j=0;j<2;j++){
for(ll k=0;k<2;k++){
res.a[i][j] = (res.a[i][j]+(x.a[i][k]*y.a[k][j])%(mod-1))%(mod-1);
}
}
}
return res;
}
mat quM(mat t,ll b){
mat ans;
memset(ans.a,0,sizeof(ans.a));
ans.a[0][0]=1;
ans.a[1][1]=1;
while(b){
if(b&1) ans = mat_mul(t,ans);
t = mat_mul(t,t);
b>>=1;
}
return ans;
}
ll qui(ll a,ll b){
a=a%mod;
ll t = 1;
while(b){
if(b&1) t = t*a%mod;
a = a*a%mod;
b>>=1;
}
return t;
}
int main(){
ll n,x,y,a,b;
cin>>n>>x>>y>>a>>b;
mat ans;
ans.a[0][0]=1;
ans.a[0][1]=1;
ans.a[1][0]=1;
ans.a[1][1]=0;
ll cx=0,cy=0,c=0;
if(n==1){
cx=1;cy=0;c=0;
}
else{
ans = quM(ans,n-1);
cx = ans.a[1][1]%(mod-1)+mod-1;
cy = ans.a[1][0]%(mod-1)+mod-1;
c = cx+cy-1;//避免c为mod 貌似是这样
}
cout<<((qui(x,cx)%mod*qui(y,cy))%mod*qui(qui(a,b),c%(mod-1)))%mod<<endl;
return 0;
}