1.进程


2.线程

例如记事本:我们在打开记事本的时候打开页面设置:


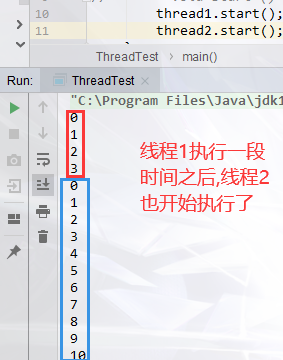
上面这种情况说明记事本整个执行流程只有一条执行路径,是单线程程序
再例如QQ:
上面QQ的聊天界面和好友搜索界面有各自的执行路径,说明QQ是多线程程序
3.多线程实现方式
方式1:

public class MyThread extends Thread { @Override public void run() { for (int i=0;i<=100;i++){ System.out.println(i); } } }
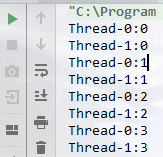
public class ThreadTest { public static void main(String[] args) { MyThread thread1 = new MyThread(); MyThread thread2 = new MyThread(); // thread1.run();//并没有启动线程,和普通方法调用一样 // thread2.run(); // void start() 导致此线程开始执行; Java虚拟机调用此线程的run方法。 thread1.start(); thread2.start(); } }
方式2:

//定义一个类实现Runnable接口 public class MyRunable implements Runnable{ // 重写run方法 @Override public void run() { for(int i=0;i<100;i++){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+i); } } }
public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建MyRunable对象 MyRunable myRunable = new MyRunable(); // 创建Thread对象并将myRunable对象作为Thread构造方法参数传递 Thread thread1 = new Thread(myRunable, "火车票"); Thread thread2 = new Thread(myRunable, "飞机票"); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); }
上面代码可以使用内部类方式优化:
public static void main(String[] args) { new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("匿名内部类的方式启动线程"); } }).start(); } }
4.设置和获取线程名称
获取默认线程名称
结果:Thread-n....
public class MyThread extends Thread { @Override public void run() { for (int i=0;i<=100;i++){ System.out.println(getName()+":"+i); } } /** * public class Thread implements Runnable { *private volatile String name; *public Thread() { * init(null, null, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0); * } *private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name,long stackSize) { * init(g, target, name, stackSize, null, true); * } *private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name,long stackSize, AccessControlContext acc, boolean inheritThreadLocals) { * this.name = name; * } * private static int threadInitNumber;0,1,2... *private static synchronized int nextThreadNum() { * return threadInitNumber++;//先return后++,所以依次返回0,1,2... * } * * public final String getName() { * return name; * } * } */ }
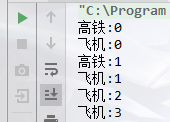
设置线程名称
thread1.setName("高铁");
thread2.setName("飞机");
帯参构造方法设置线程名称:
1.线程类要添加帯参构造方法,默认调用父类帯参构造方法
public class MyThread extends Thread { @Override public void run() { for (int i=0;i<=100;i++){ System.out.println(getName()+":"+i); } } public MyThread() { } public MyThread(String name) { super(name); } }
MyThread myThread = new MyThread("线程1");
获取当前类线程名称
//static Thread currentThread() 返回对当前正在执行的线程对象的引用。 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
5.线程调度(线程优先级)

// IllegalArgumentException - 如果优先级不在 MIN_PRIORITY到 MAX_PRIORITY范围内。 // thread1.setPriority(10000);//IllegalArgumentException:抛出表示一种方法已经通过了非法或不正确的参数。 // 从下面我们可以得知线程优先级的设置范围在1~10之间,并且默认值是5 System.out.println(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);//10 System.out.println(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);//1 System.out.println(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);//5 // 设置优先级 thread1.setPriority(1); thread2.setPriority(5); thread3.setPriority(10); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); thread3.start();
6.线程控制

sleep
public class MyThread extends Thread { @Override public void run() { for (int i=0;i<=100;i++){ System.out.println(getName()+":"+i); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
public static void main(String[] args) { MyThread t1 = new MyThread(); MyThread t2 = new MyThread(); MyThread t3 = new MyThread(); t1.setName("飞机"); t2.setName("火车"); t3.setName("汽车"); t1.start(); t2.start(); t3.start(); }
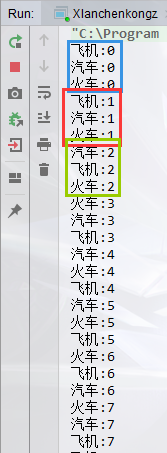
每个线程执行一下之后都会"等待"一秒钟,所以大家执行的很均匀
join
public class MyThread extends Thread { @Override public void run() { for (int i=0;i<=100;i++){ System.out.println(getName()+":"+i); } } }
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { MyThread t1 = new MyThread(); MyThread t2 = new MyThread(); MyThread t3 = new MyThread(); t1.setName("皇上"); t2.setName("三皇子"); t3.setName("六皇子"); //皇上死了之后三皇子和六皇子才 开始争夺"皇位(CPU)" t1.start(); t1.join(); t2.start(); t3.start(); }

SetDaemon()
public class MyThread extends Thread { @Override public void run() { for (int i=0;i<=100;i++){ System.out.println(getName()+":"+i); } } }
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { MyThread t1 = new MyThread(); MyThread t2 = new MyThread(); MyThread t3 = new MyThread(); t1.setName("悟空"); t2.setName("八戒"); t3.setName("老沙"); // 悟空,八戒,沙僧,都是守护师傅的,那么如果师傅"死掉了(线程结束)",他们三个也没有存在的必要了,也应该停止 // 这里我们将上面三个线程设置为守护线程,当运行的线程都是守护线程时.java虚拟机将退出: t1.setDaemon(true); t2.setDaemon(true); t3.setDaemon(true); t1.start(); t2.start(); t3.start(); Thread.currentThread().setName("师傅"); for (int i=0;i<5;i++){ System.out.println( Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+i); Thread.currentThread().sleep(1); } }

7.线程声明周期

8.线程同步
卖票案例

//定义一个类实现Runnable接口并重写run方法 public class SellTicket implements Runnable { // 定一个票数变量 private int tickets = 100; @Override public void run() { // 相同的票卖出了多次???卖负数票??? while (true) {//定义死循环,一直卖票 // 判断票数是否为0 // 假设thread1抢到了CPU执行权 if (tickets > 0) { try {//通过sleep模拟卖出每张票所需要的时间 Thread.sleep(100); // thread1休息100毫秒 // 此时thread2抢到了CPU执行权,thread2开始执行,执行到这里thread2也休息100毫秒 // 此时thread3抢到了CPU执行权,thread3开始执行,执行到这里thread3也休息100毫秒 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // 假设线程按照顺序醒过来 // thread1抢到了CPU执行权,在控制台输出:窗口1正在出售第100张票 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":正在卖第" + tickets + "张票"); // thread2抢到了CPU执行权,在控制台输出:窗口2正在出售第100张票 // thread3抢到了CPU执行权,在控制台输出:窗口3正在出售第100张票 tickets--; // 如果三个线程还是按照上面的顺序来,这次就执行了3次"--"的操作,tickets变成了97,,,最终同理就出现了卖"负数票" } } }
// 创建卖票窗口对象 SellTicket sellTicket = new SellTicket(); // 创建三个线程对应三个卖票窗口 Thread thread1 = new Thread(sellTicket, "窗口1"); Thread thread2 = new Thread(sellTicket, "窗口2"); Thread thread3 = new Thread(sellTicket, "窗口3"); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); thread3.start(); }
卖票结果:


卖票案例问题解决

同步代码块:

public class SellTicket implements Runnable { private int tickets = 100; private Object o=new Object();//这里定义一个任意Object对象,保证是同一把锁 @Override public void run() { while (true) { // thread1抢到了CPU执行权 synchronized (o){ if (tickets > 0) { try { // thread1进来之后就会把代码锁起来 Thread.sleep(100); // thread1休息100毫秒 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // thread1抢到了CPU执行权,在控制台输出:窗口1正在出售第100张票 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":正在卖第" + tickets + "张票"); tickets--; } // thread1出来之后解锁上面代码 } } } }
同步方法:

public class SellTicket implements Runnable { private static int tickets = 100; private Object o=new Object(); private int X=0; @Override public void run() { while (true) { if(X%2==0){ // synchronized (o){ // synchronized (this){ synchronized (SellTicket.class){ if (tickets > 0) { try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":正在卖第" + tickets + "张票"); tickets--; } } }else{ sellTicket(); } X++; } } // private synchronized void sellTicket() { // if (tickets > 0) { // try { // Thread.sleep(100); // } catch (InterruptedException e) { // e.printStackTrace(); // } // System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":正在卖第" + tickets + "张票"); // tickets--; // } // } private static synchronized void sellTicket() { if (tickets > 0) { try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":正在卖第" + tickets + "张票"); tickets--; } } }
9.线程安全的类

StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();//线程安全,多线程情况下使用 StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();//线程不安全,非多线程情况使用 Vector<Object> vector = new Vector<>();//线程安全,多线程情况下使用 ArrayList<Object> list = new ArrayList<>();//线程不安全,非多线程情况使用 Hashtable<Object, Object> hashtable = new Hashtable<>();//线程安全,多线程情况下使用 HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();//线程不安全,非多线程情况使用 // 集合的安全类被下面的方法替代了 // static <T> List<T> synchronizedList(List<T> list) 返回由指定列表支持的同步(线程安全)列表。 List<Object> synchronizedList = Collections.synchronizedList(list); Map<Object, Object> synchronizedMap = Collections.synchronizedMap(hashMap);
10.Lock

public class LockTest implements Runnable { private int tickets = 100; private Lock lock=new ReentrantLock(); @Override public void run() { while (true) { try { lock.lock(); if (tickets > 0) { try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":正在卖第" + tickets + "张票"); tickets--; } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //无论什么情况下都要释放锁 lock.unlock(); } } } }
11.生产者和消费者


但是有时候生产者还没有生产出数据,或者有了数据但是没有消费者来消费,于是就有了下面的方法:

生产者消费者案例

public class Box { private int milk; private boolean hasMilk=false; public synchronized void put(int milk){ // 如果有牛奶,等待消费而不是生产 if (hasMilk){ try { wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } // 如果没有牛奶就生产牛奶 this.milk=milk; System.out.println("送奶工将第"+milk+"瓶奶放入奶箱"); // 生产完之后,修改奶箱状态 hasMilk=true; // 唤醒其他等待的线程 notifyAll(); } public synchronized void get(){ // 如果没有牛奶,等待生产 if (!hasMilk){ try { wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } // 如果有牛奶,消费牛奶 System.out.println("消费者将第"+milk+"瓶奶取出"); // 消费完毕之后修改奶箱状态 hasMilk=false; // 唤醒其他等待的线程 notifyAll(); } }
public class Producter implements Runnable { private Box b; public Producter(Box box) { this.b=box; } @Override public void run() { for (int i=0;i<30;i++){ b.put(i); } } }
public class Customer implements Runnable { private Box b; public Customer(Box box) { this.b=box; } @Override public void run() { while (true){ b.get(); } } }
public class BoxDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Box box = new Box(); Producter producter = new Producter(box); Customer customer = new Customer(box); Thread thread1 = new Thread(producter); Thread thread2 = new Thread(customer); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); } }