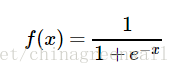1. 关于非线性转化方程(non-linear transformation function)
sigmoid函数(S 曲线)用来作为activation function:
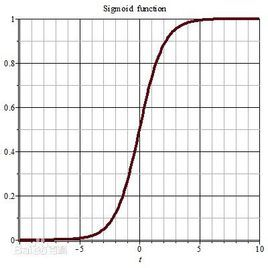
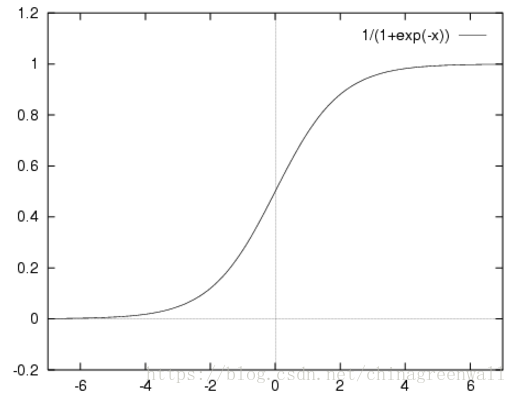
sigmoid函数是一个在生物学中常见的S型函数,也称为S型生长曲线。 在信息科学中,由于其单增以及反函数单增等性质,sigmoid函数常被用作神经网络的阈值函数,将变量映射到0,1之间。具有这种性质的S型函数统称为sigmoid函数。
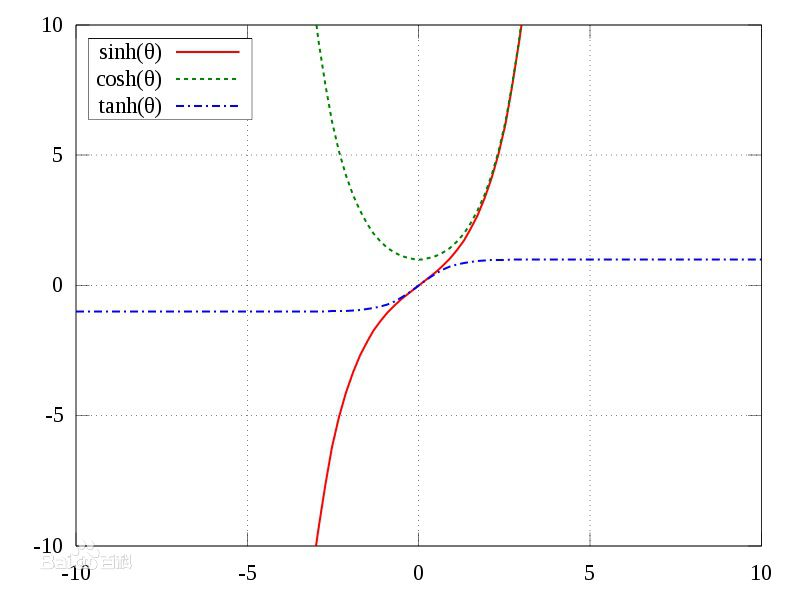
1.1 双曲函数(tanh)
1.2 逻辑函数(logistic function)
其实logistic函数也就是经常说的sigmoid函数,它的几何形状也就是一条sigmoid曲线(S型曲线)。
导数:
![]()
2. 手动实现一个简单的神经网络算法
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
def tanh(x):
return np.tanh(x)
def tanh_deriv(x):
return 1.0 - np.tanh(x) * np.tanh(x)
def logistic(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def logistic_deriv(x):
return logistic(x) * (1 - logistic(x))
class NeuralNetwork:
def __init__(self, layers, activation="tanh"): # layers=[10,10,3]
if activation == "logistic":
self.activation = logistic
self.activation_deriv = logistic_deriv
elif activation == "tanh":
self.activation = tanh
self.activation_deriv = tanh_deriv
# 随机产生权重[-0.25,+0.25]
self.weights = []
for i in range(1, len(layers) - 1): # 产生(layers[i-1]+1,layers[i]+1) 如(3,2) 3行2列的随机数矩阵
self.weights.append((2 * np.random.random((layers[i - 1] + 1, layers[i] + 1)) - 1) * 0.25)
self.weights.append((2 * np.random.random((layers[i] + 1, layers[i + 1])) - 1) * 0.25)
# print(str(self.weights))
def fit(self, x, y, learning_rate=0.2, epochs=10000):
x = np.atleast_2d(x)
temp = np.ones([x.shape[0], x.shape[1] + 1])
temp[:, 0:-1] = x
x = temp
y = np.array(y)
for k in range(epochs):
i = np.random.randint(x.shape[0]) # x.shape[0] is the number of the trainingset samples
a = [x[i]] # choose a sample randomly to train the model
# print(str(a))
for l in range(len(self.weights)):
# print("a["+str(l)+"]; "+str(a[l])+" WEIGHT "+str(self.weights[l])+str(len(self.weights)))
a.append(self.activation(np.dot(a[l], self.weights[l]))) # a每个结点output值
error = y[i] - a[-1] # 误差 实际值-每个结点output值
deltas = [error * self.activation_deriv(a[-1])] # 对应输出层
for l in range(len(a) - 2, 0, -1):
# dot()函数可以通过numpy库调用,也可以由数组实例对象进行调用。
# a.dot(b) 与 np.dot(a,b)效果相同。
# deltas[-1].dot(self.weights[l].T) 等价于 dot(deltas[-1],self.weights[l].T)
# deltas[-1] 对应上步的输出层
deltas.append(deltas[-1].dot(self.weights[l].T) * self.activation_deriv(a[l])) # 对于隐藏层
deltas.reverse()
for i in range(len(self.weights)):
layer = np.atleast_2d(a[i])
delta = np.atleast_2d(deltas[i])
self.weights[i] += learning_rate * layer.T.dot(delta) # layer.T.dot(delta)等价于dot(layer.T,delta)
def predict(self, x):
x = np.array(x)
temp = np.ones(x.shape[0] + 1)
temp[0:-1] = x
a = temp
for l in range(0, len(self.weights)):
a = self.activation(np.dot(a, self.weights[l]))
return a