Spring Boot提供了一种通过注解@Async实现异步的方式,可以在启动类上添加注解@EnableAsyn或者在线程池配置类上添加@EnableAsync两种方式实现。
下面重点说下线程池配置类的方式
package com.gy.doc.config; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync; import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor; import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor; /** * @author jyy * @description {异步线程池} * @date 2020/4/29 14:35 */ @EnableAsync @Configuration public class AsyncThreadPoolConfig { @Bean("asyncThreadPool") public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor simpleThreadPool() { ThreadPoolTaskExecutor asyncThreadPool = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor(); //设置线程池最小线程数量 asyncThreadPool.setCorePoolSize(5); //设置线程池最大线程数量 asyncThreadPool.setMaxPoolSize(15); //设置线程池缓冲队列大小 asyncThreadPool.setQueueCapacity(15); asyncThreadPool.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy()); //初始化线程池 asyncThreadPool.initialize(); return asyncThreadPool; } }
package com.gy.doc.service; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncResult; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import java.util.concurrent.Future; /** * @author jyy * @description {} * @date 2020/4/29 14:25 */ @Service public class TestService { @Async("asyncThreadPool") public Future<String> asyncMethod1() { try { Thread.sleep(5000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } return new AsyncResult("1"); } @Async("asyncThreadPool") public Future<String> asyncMethod2() { try { Thread.sleep(10000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } return new AsyncResult("2"); } @Async("asyncThreadPool") public void asyncMethod3() { try { Thread.sleep(5000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } System.out.println("1"); } @Async("asyncThreadPool") public void asyncMethod4() { try { Thread.sleep(10000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } System.out.println("2"); } }
有返回值的调用,返回类型Future<T>,当调用get()方法后,主线程等待,开始顺序执行。
public Result test() { try { System.out.println("start" + new Date()); Future<String> future1 = testService.asyncMethod1(); System.out.println("middle" + new Date()); Future<String> future2 = testService.asyncMethod2(); System.out.println("end" + new Date()); System.out.println(future1.get()); System.out.println(future2.get()); System.out.println("3"); System.out.println(new Date()); } catch (Exception e) { } return null; }
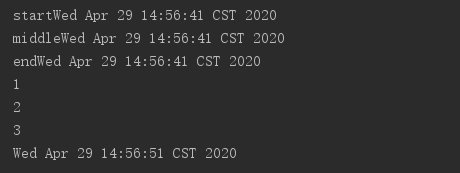
无返回值调用
public Result test() { try { System.out.println("start" + new Date()); testService.asyncMethod3(); testService.asyncMethod4(); System.out.println("end" + new Date()); } catch (Exception e) { } return null; }
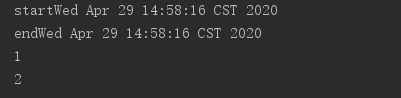
注意:切记不要在同一个类里面调用@Async声明的方法,会产生代理绕过问题,异步失效。