ond需要指定一个Locker,通常是一个*Mutex或*RWMutex。
func (c *Cond) Broadcast() 和 func (c *Cond) Signal() 唤醒因wait condition而挂起goroutine,区别是Signal只唤醒一个,而Broadcast唤醒所有。允许调用者获取基础锁Locker之后再调用唤醒,但非必需。
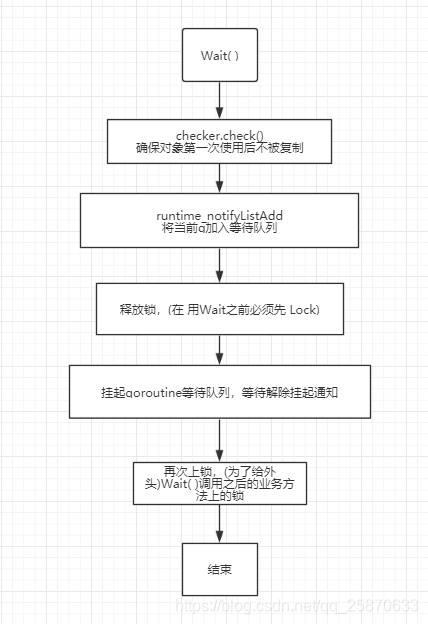
func (c *Cond) Wait()方法在调用时会释放底层锁Locker,并且将当前goroutine挂起,直到另一个goroutine执行Signal或者Broadcase,该goroutine才有机会重新唤醒,并尝试获取Locker,完成后续逻辑。
使用Wait 方法之前,我们必须先获取外部锁,原因是:先当前协程占有着锁,并挂起当前协程等待,其他协程的 通知唤醒,好走后续的业务逻辑,(占有着锁,是不想别人拿到锁,而自己走不到Wait这一步,而Wait是挂起了当前协程,等待别人通知,这样做,就知道只要通知一来,肯定是当前协程可以继续往下走了),这里自己通过对比 Wait的使用及Wait的源码自己就明白了,使用示例:
package main import ( "fmt" "math/rand" "sync" "time" ) var locker = new(sync.Mutex) var cond = sync.NewCond(locker) var capacity = 10 var consumerNum = 3 var producerNum = 5 func producer(out chan<- int) { for i := 0; i < producerNum; i++ { go func(nu int) { for { cond.L.Lock() for len(out) == capacity { fmt.Println("Capacity Full, stop Produce") cond.Wait() } num := rand.Intn(100) out <- num fmt.Printf("Produce %d produce: num %d ", nu, num) cond.L.Unlock() cond.Signal() time.Sleep(time.Second) } }(i) } } func consumer(in <-chan int) { for i := 0; i < consumerNum; i++ { go func(nu int) { for { cond.L.Lock() for len(in) == 0 { fmt.Println("Capacity Empty, stop Consume") cond.Wait() } num := <-in fmt.Printf("Goroutine %d: consume num %d ", nu, num) cond.L.Unlock() time.Sleep(time.Millisecond * 500) cond.Signal() } }(i) } } func main() { rand.Seed(time.Now().UnixNano()) quit := make(chan bool) product := make(chan int, capacity) producer(product) consumer(product) <-quit }
sync/Cond.go源码
package sync import ( "sync/atomic" "unsafe" ) // Cond implements a condition variable, a rendezvous point // for goroutines waiting for or announcing the occurrence // of an event. // // Each Cond has an associated Locker L (often a *Mutex or *RWMutex), // which must be held when changing the condition and // when calling the Wait method. // // A Cond must not be copied after first use. // Cond实现了一个条件变量,一个等待或宣布事件发生的goroutines的集合点。 // 每个Cond都有一个相关的Locker L(通常是* Mutex或* RWMutex) type Cond struct { // 不允许复制,一个结构体,有一个Lock()方法,嵌入别的结构体中,表示不允许复制 // noCopy对象,拥有一个Lock方法,使得Cond对象在进行go vet扫描的时候,能够被检测到是否被复制 noCopy noCopy // L is held while observing or changing the condition // 锁的具体实现,通常为 mutex 或者rwmutex L Locker // 通知列表,调用Wait()方法的goroutine会被放入list中,每次唤醒,从这里取出 // notifyList对象,维护等待唤醒的goroutine队列,使用链表实现 // 在 sync 包中被实现, src/sync/runtime.go notify notifyList // 复制检查,检查cond实例是否被复制 // copyChecker对象,实际上是uintptr对象,保存自身对象地址 checker copyChecker } // NewCond returns a new Cond with Locker l. // NewCond方法传入一个实现了Locker接口的对象,返回一个新的Cond对象指针, // 保证在多goroutine使用cond的时候,持有的是同一个实例 func NewCond(l Locker) *Cond { return &Cond{L: l} } // Wait atomically unlocks c.L and suspends execution // of the calling goroutine. After later resuming execution, // Wait locks c.L before returning. Unlike in other systems, // Wait cannot return unless awoken by Broadcast or Signal. // // Because c.L is not locked when Wait first resumes, the caller // typically cannot assume that the condition is true when // Wait returns. Instead, the caller should Wait in a loop: // 等待原子解锁c.L并暂停执行调用goroutine。 // 稍后恢复执行后,Wait会在返回之前锁定c.L. // 与其他系统不同,除非被广播或信号唤醒,否则等待无法返回。 // 因为等待第一次恢复时c.L没有被锁定, // 所以当Wait返回时,调用者通常不能认为条件为真。 // 相反,调用者应该循环等待: // // c.L.Lock() // for !condition() { // c.Wait() // } // ... make use of condition ... // c.L.Unlock() // //调用此方法会将此routine加入通知列表,并等待获取通知,调用此方法必须先Lock,不然方法里会调用Unlock(),报错 func (c *Cond) Wait() { // 检查是否被复制; 如果是就panic // check检查,保证cond在第一次使用后没有被复制 c.checker.check() // 将当前goroutine加入等待队列, 该方法在 runtime 包的 notifyListAdd 函数中实现 src/runtime/sema.go t := runtime_notifyListAdd(&c.notify) // 释放锁, 因此在调用Wait方法前,必须保证获取到了cond的锁,否则会报错 c.L.Unlock() // 等待队列中的所有的goroutine执行等待唤醒操作 // 将当前goroutine挂起,等待唤醒信号 // 该方法在 runtime 包的 notifyListWait 函数中实现 src/runtime/sema.go runtime_notifyListWait(&c.notify, t) c.L.Lock() } // Signal wakes one goroutine waiting on c, if there is any. // // It is allowed but not required for the caller to hold c.L // during the call. // 唤醒单个 等待的 goroutine func (c *Cond) Signal() { c.checker.check() // 通知等待列表中的一个, 顺序唤醒一个等待的gorountine // 在runtime 包的 notifyListNotifyOne 函数中被实现 src/runtime/sema.go runtime_notifyListNotifyOne(&c.notify) } // Broadcast wakes all goroutines waiting on c. // // It is allowed but not required for the caller to hold c.L // during the call. // 唤醒等待队列中的所有goroutine。 func (c *Cond) Broadcast() { c.checker.check() // 唤醒等待队列中所有的goroutine // 有runtime 包的 notifyListNotifyAll 函数实现 src untimesema.go runtime_notifyListNotifyAll(&c.notify) } // copyChecker holds back pointer to itself to detect object copying. // copyChecker保持指向自身的指针以检测对象复制。 type copyChecker uintptr // 检查c是否被复制,如果是则panic //check方法在第一次调用的时候,会将checker对象地址赋值给checker,也就是将自身内存地址赋值给自身 func (c *copyChecker) check() { /** 因为 copyChecker的底层类型为 uintptr 那么 这里的 *c其实就是 copyChecker类型本身,然后强转成uintptr 和拿着 c 也就是copyChecker的指针去求 uintptr,理论上要想等 即:内存地址为一样,则表示没有被复制 */ // 下述做法是: // 其实 copyChecker中存储的对象地址就是 copyChecker 对象自身的地址 // 先把 copyChecker 处存储的对象地址和自己通过 unsafe.Pointer求出来的对象地址作比较, // 如果发现不相等,那么就尝试的替换,由于使用的 old是0, // 则表示c还没有开辟内存空间,也就是说,只有是首次开辟地址才会替换成功 // 如果替换不成功,则表示 copyChecker出所存储的地址和 unsafe计算出来的不一致 // 则表示对象是被复制了 if uintptr(*c) != uintptr(unsafe.Pointer(c)) && !atomic.CompareAndSwapUintptr((*uintptr)(c), 0, uintptr(unsafe.Pointer(c))) && uintptr(*c) != uintptr(unsafe.Pointer(c)) { panic("sync.Cond is copied") } } // noCopy may be embedded into structs which must not be copied // after the first use. // // See https://golang.org/issues/8005#issuecomment-190753527 // for details. // noCopy可以嵌入到结构中,在第一次使用后不得复制。 type noCopy struct{} // Lock is a no-op used by -copylocks checker from `go vet`. func (*noCopy) Lock() {} func (*noCopy) Unlock() {} type notifyList struct { wait uint32 notify uint32 lock uintptr // key field of the mutex head unsafe.Pointer tail unsafe.Pointer }
我们可以看出,其中
-
Cond不能被复制:Cond在内部持有一个等待队列,这个队列维护所有等待在这个Cond的goroutine。因此若这个Cond允许值传递,则这个队列在值传递的过程中会进行复制,导致在唤醒goroutine的时候出现错误。
-
顺序唤醒: notifyList对象持有两个无限自增的字段wait和notify,wait字段在有新的goroutine等待的时候加1,notify字段在有新的唤醒信号的时候加1。在有新的goroutine加入队列的时候,会将当前wait赋值给goroutine的ticket,唤醒的时候会唤醒ticket等于notify的gourine。另外,当wait==notify时表示没有goroutine需要被唤醒,wait>notify时表示有goroutine需要被唤醒,waity恒大于等于notify
Wait: