设计模式--代理模式
1.概述
1.1 定义
"Provide a surrogate or placeholder for another object to control access to it"(提供一种代理以控制对这个对象的访问)
代理模式分为动态代理、静态代理,从本质上两者都是产生一个新的类(可以加入一些行为)来代理之前的类。
1.2 分类
静态代理模式:自己手写一个代理类,该代理类会在编译期就生成。这种代理由于不需要再运行期重新生成一个代理类,所以性能较好。但是由于我们需要在代理类中加入一些行为时,需要写的代理较多,且与委托类耦合性较差,代码复用性较差。
动态代理模式:代理类是在运行期生成。相比静态代理,动态代理可以方便的对委托类进行统一处理,代码复用性较好。分为jdk动态代理和cglib动态代理(不懂)。
1.3 应用
代理可以通过延迟实例化(lazily-instantiating),如Hibrenate中的表的连接查询中就有延迟加载;AOP的核心就是使用的动态代理,通过AOP我们可以进行事务处理、日志处理等,
2.详解
2.1 静态代理
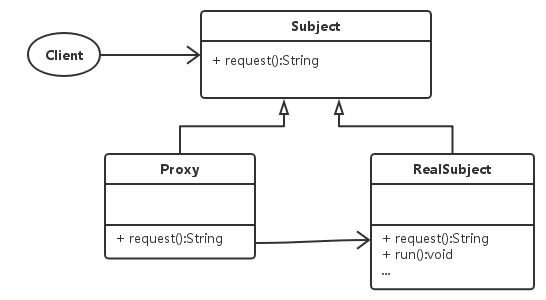
代码如下:
1 public interface Subject { 2 void method(); 3 } 4 5 public class RealSubject implements Subject { 6 @Override 7 public void method() { 8 System.out.println("RealSubject.method()"); 9 } 10 } 11 12 public class Proxy implements Subject { 13 private Subject realSubject; 14 15 // 通过构造函数传递被代理者 16 Proxy(Subject realSubject){ 17 this.realSubject = realSubject; 18 } 19 20 // 真正实现代理,在这里我们可以加入一些行为。 21 public void method() { 22 System.out.println("Proxy do something"); 23 realSubject.method(); 24 } 25 } 26 27 public class Client { 28 public static void main(String[] args) { 29 Subject realSubject = new RealSubject(); 30 Subject proxy = new Proxy(realSubject); 31 proxy.method(); 32 } 33 }output: 34 Proxy do something 35 RealSubject.method()
2.2 动态代理
代码如下:
1 public interface Subject { 2 void method(); 3 } 4 5 public class RealSubject implements Subject { 6 @Override 7 public void method() { 8 System.out.println("RealSubject.method()"); 9 } 10 }
JDK自带的动态代理实现:
利用java.lang.reflect.Proxy类和java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler接口定义代理类的实现
public class SubjectInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler { private Object target; SubjectInvocationHandler(Object target) { this.target = target; } // 在这里实现代理,我们可以通过反射机制加入我们想到的行为 public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { if(Objects.equals(method.getName(), "method")) { System.out.println("Proxy do something"); } return method.invoke(target, args); } // 通过JDK自带的动态代理方法生成代理对象 public Object getProxy() { ClassLoader loader = target.getClass().getClassLoader(); Class<?>[] interfaces = target.getClass().getInterfaces(); return Proxy.newProxyInstance(loader, interfaces, this); } } public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { Subject realSuject = new RealSubject(); SubjectInvocationHandler handler = new SubjectInvocationHandler(realSuject); Subject subject = (Subject) handler.getProxy(); subject.method(); } }outpu: Proxy do something RealSubject.method()
上面动态代理具体实现还不是很清楚,以后再写。
3. 应用
通过动态代理实现了非常简单的事务处理
Entity类

1 public class User { 2 private long id; 3 4 private String email; 5 6 private String password; 7 8 private int sex; 9 10 private int age; 11 12 public User() { 13 14 } 15 16 public long getId() { 17 return id; 18 } 19 20 public void setId(long id) { 21 this.id = id; 22 } 23 24 public String getEmail() { 25 return email; 26 } 27 28 public void setEmail(String email) { 29 this.email = email; 30 } 31 32 public String getPassword() { 33 return password; 34 } 35 36 public void setPassword(String password) { 37 this.password = password; 38 } 39 40 public int getSex() { 41 return sex; 42 } 43 44 public void setSex(int sex) { 45 this.sex = sex; 46 } 47 48 public int getAge() { 49 return age; 50 } 51 52 public void setAge(int age) { 53 this.age = age; 54 } 55 56 public User(String email, String password, int sex, int age) { 57 this.email = email; 58 this.password = password; 59 this.sex = sex; 60 this.age = age; 61 } 62 }
JDBC工具类

1 public class JDBCUtil { 2 /** 3 * 返回一个Connection 4 */ 5 public static Connection getConnection() { 6 Connection connection = null; 7 String driverClass = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"; 8 String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hibernate?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8"; 9 String user = "root"; 10 String password = ""; 11 try { 12 // 加载mysql驱动 13 Class.forName(driverClass); 14 // 获得Connection 15 connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); 16 } catch (Exception e) { 17 e.printStackTrace(); 18 } 19 return connection; 20 } 21 }
用户DAO类

1 public class UserDao { 2 private Connection connection; 3 4 // 注入其需要的Connection 5 UserDao(Connection connection) { 6 this.connection = connection; 7 } 8 9 // DAO中saveUser方法:抛出异常表明出现错误,需要Rollback。在这里我们就抛出异常,让Service处理。 10 public int saveUser(User user) throws Exception{ 11 String sql = "INSERT INTO USER(email, password, sex, age) VALUES (?,?,?,?)"; 12 // 获得PreparedStatement 13 PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql, Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS); 14 // 预编译 15 preparedStatement.setString(1, user.getEmail()); 16 preparedStatement.setString(2, user.getPassword()); 17 preparedStatement.setInt(3, user.getSex()); 18 preparedStatement.setInt(4, user.getAge()); 19 // 插入数据库 20 return preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); 21 } 22 }
代理逻辑相关类

1 /** 2 * 被代理接口:用户业务类 3 */ 4 public interface UserService { 5 boolean saveUser(User user) throws Exception; 6 } 7 8 /** 9 * 实际被代理类 10 */ 11 public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { 12 private UserDao userDao; 13 14 // 注入UserDao 15 UserServiceImpl(UserDao userDao) { 16 this.userDao = userDao; 17 } 18 19 // Service中saveUser方法:抛出异常表明出现错误,需要Rollback。在这里我们就抛出异常,让代理类处理。 20 public boolean saveUser(User user) throws Exception { 21 int countNum = userDao.saveUser(user); 22 return countNum == 1; 23 } 24 } 25 26 /** 27 * 代理类 28 */ 29 public class UserServiceProxy implements InvocationHandler { 30 // 被代理类 31 private UserService userService; 32 33 // 该数据库Connection,因为只有Conenction才能开启事务 34 private Connection connection; 35 36 // 注入被代理类及其使用的Connection 37 UserServiceProxy(UserService userService, Connection connection) { 38 this.userService = userService; 39 this.connection = connection; 40 } 41 42 @Override 43 // 实际代理逻辑 44 public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { 45 // 如果方法名是savaUser,则需要开启事务 46 if(method.getName().equalsIgnoreCase("saveUser")) { 47 // 设置Connection不能自动提交 48 connection.setAutoCommit(false); 49 // 调用真正的saveUser方法:若抛出异常就Rollback, 否则Commit 50 try { 51 Object object = method.invoke(userService, args); 52 connection.commit(); 53 return object; 54 } catch (Exception e) { 55 connection.rollback(); 56 throw new Exception("出现错误, 错误信息是:" + e); 57 } 58 } 59 return method.invoke(userService, args); 60 } 61 62 // 实现代理: 通过JDK自带的动态代理方法生成代理对象 63 public UserService getProxy() { 64 ClassLoader classLoader = userService.getClass().getClassLoader(); 65 Class<?>[] interfaces = userService.getClass().getInterfaces(); 66 return (UserService) Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, interfaces, this); 67 } 68 }
测试类:

1 public class Client { 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 3 Connection connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection(); 4 User user = new User("kanyuxia@outlook.com", "123456", 0, 21); 5 6 UserDao userDao = new UserDao(connection); 7 // 被代理类 8 UserService userService = new UserServiceImpl(userDao); 9 // 代理类 10 UserService proxy = new UserServiceProxy(userService, connection).getProxy(); 11 // 执行saveUser方法 12 proxy.saveUser(user); 13 } 14 }
