在Spring中容器在初始化某个bean的时候会有相应的生命周期,类似于Servlet,有相应的init,destory等方法
例如:如下service
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | public class UserService { public void init(){ System.out.println("UserService init ....."); } public void execute(){ System.out.println("UserService execute..."); } public void distory(){ System.out.println("UserService distory..."); }} |
想让容器在初始化该bean之前调用init方法,容器销毁之后执行distory方法,可以这样配置
1 2 3 | <bean id="userService" class="com.fz.service.UserService" init-method="init" destroy-method="distory"></bean> |
测试代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | @Testpublic void getProperties(){ ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); UserService user = (UserService) ctx.getBean("userService"); System.out.println(user); ctx.destroy();} |
注意:这里是直接使用的applicationContext接口的实现类ClassPathXmlApplicationContext,因为下面要用到ctx.destroy()方法,这个方法
在ApplicationContext接口里是没有的。
打印结果:

假如现在我们再获取一次userService对象呢?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | @Testpublic void getProperties(){ ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); UserService user = (UserService) ctx.getBean("userService"); UserService user1 = (UserService) ctx.getBean("userService"); System.out.println(user); System.out.println(user1); ctx.destroy();} |
此时,结果如下:
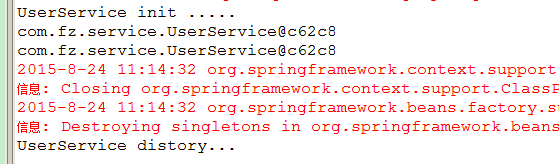
从上图可以看出,此时对象是获取了两次,并且这两个对象是同一个对象(因为默认的scope属性是singleton),但是init和distory都是只执行了一次。
假如现在我们再配置上scope=prototype之后呢?
1 2 3 | <bean id="userService" class="com.fz.service.UserService" init-method="init" destroy-method="distory" scope="prototype"></bean> |
同样的测试代码,结果如下:

此时发现,现在是init了两次,也获取到两个不同的bean。但是distory却没有执行。
可以看出在配置了prototype之后,ClassPathXmlApplicationContext是监控不到bean的生存和销毁的。
总结:
1、在bean初始化之前执行某个方法:init-method="init"
2、在容器销毁之后执行某个方法: destroy-method="distory"
3、如果同一个bean获取多次,此时init-method和destroy-method都只执行一次(没有使用prototype情况下)
4、init-method、destroy-method不要和scope=prototype一起使用
5、init-method和destroy-method一般情况下我们开发人员很少使用,但是spring自己却需要使用。
比如:在Spring的连接池中就用到了destroy-method方法,不用该数据源的时候则把它关闭。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | <bean id="myDataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close"><!-- results in a setDriverClassName(String) call --><property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/><property name="username" value="root"/><property name="password" value="masterkaoli"/></bean> |