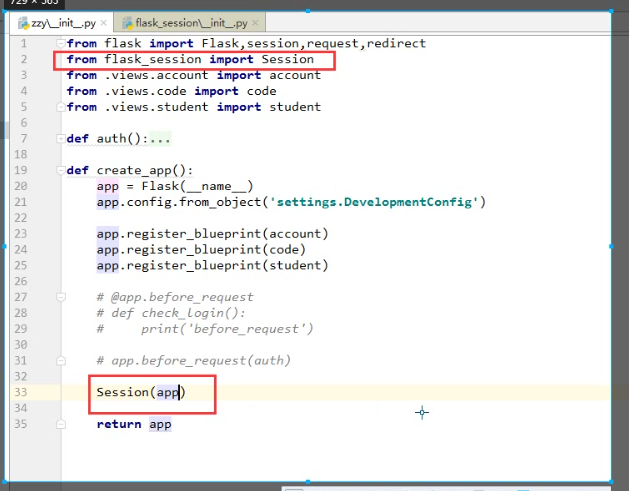
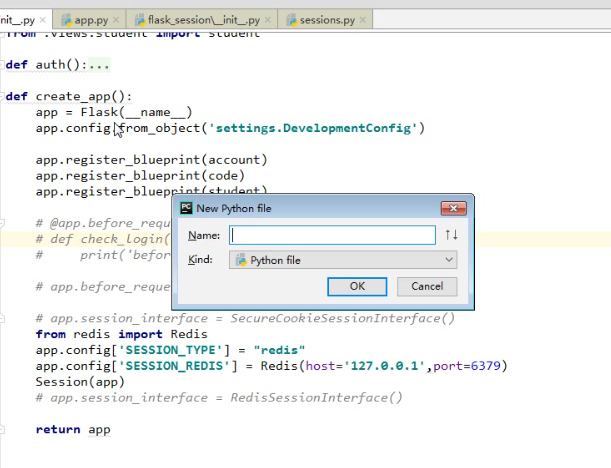
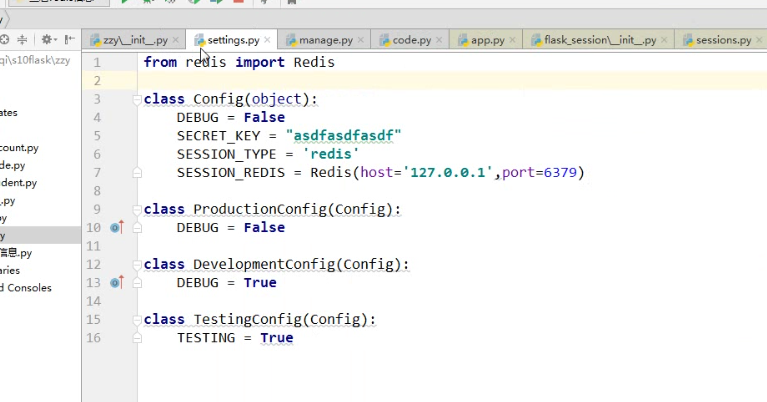
一,配置文件
flask中的配置文件是一个flask.config.Config对象(继承字典),默认配置为: { 'DEBUG': get_debug_flag(default=False), 是否开启Debug模式 'TESTING': False, 是否开启测试模式 'PROPAGATE_EXCEPTIONS': None, 'PRESERVE_CONTEXT_ON_EXCEPTION': None, 'SECRET_KEY': None, 'PERMANENT_SESSION_LIFETIME': timedelta(days=31), 'USE_X_SENDFILE': False, 'LOGGER_NAME': None, 'LOGGER_HANDLER_POLICY': 'always', 'SERVER_NAME': None, 'APPLICATION_ROOT': None, 'SESSION_COOKIE_NAME': 'session', 'SESSION_COOKIE_DOMAIN': None, 'SESSION_COOKIE_PATH': None, 'SESSION_COOKIE_HTTPONLY': True, 'SESSION_COOKIE_SECURE': False, 'SESSION_REFRESH_EACH_REQUEST': True, 'MAX_CONTENT_LENGTH': None, 'SEND_FILE_MAX_AGE_DEFAULT': timedelta(hours=12), 'TRAP_BAD_REQUEST_ERRORS': False, 'TRAP_HTTP_EXCEPTIONS': False, 'EXPLAIN_TEMPLATE_LOADING': False, 'PREFERRED_URL_SCHEME': 'http', 'JSON_AS_ASCII': True, 'JSON_SORT_KEYS': True, 'JSONIFY_PRETTYPRINT_REGULAR': True, 'JSONIFY_MIMETYPE': 'application/json', 'TEMPLATES_AUTO_RELOAD': None, }
方式一: app.config['DEBUG'] = True PS: 由于Config对象本质上是字典,所以还可以使用app.config.update(...) 方式二: app.config.from_pyfile("python文件名称") 如: settings.py DEBUG = True app.config.from_pyfile("settings.py") app.config.from_envvar("环境变量名称") 环境变量的值为python文件名称名称,内部调用from_pyfile方法 app.config.from_json("json文件名称") JSON文件名称,必须是json格式,因为内部会执行json.loads app.config.from_mapping({'DEBUG':True}) 字典格式 app.config.from_object("python类或类的路径") app.config.from_object('pro_flask.settings.TestingConfig') settings.py class Config(object): DEBUG = False TESTING = False DATABASE_URI = 'sqlite://:memory:' class ProductionConfig(Config): DATABASE_URI = 'mysql://user@localhost/foo' class DevelopmentConfig(Config): DEBUG = True class TestingConfig(Config): TESTING = True PS: 从sys.path中已经存在路径开始写 PS: settings.py文件默认路径要放在程序root_path目录,如果instance_relative_config为True,则就是instance_path目录
案例1
from flask import Flask app = Flask(__name__) app.config.from_object("settings.DevelopmentConfig") @app.route('/') def hello_world(): return 'Hello World!' if __name__ == '__main__': app.run()
class Config(object): DEBUG = False TESTING = False DATABASE_URI = 'sqlite://:memory:' class ProductionConfig(Config): DATABASE_URI = 'mysql://user@localhost/foo' class DevelopmentConfig(Config): DEBUG = False class TestingConfig(Config): TESTING = True
2. URL 反向解析
from flask import Flask,url_for app = Flask(__name__) app.config.from_object("settings.DevelopmentConfig") # @app.route('/') # def hello_world(): # return 'Hello World!' # 1. index函数路由 @app.route("/index",endpoint="n1") #<string:xx><default:xx> <xxx> 都表示字符串 def index(): print(id) return "hello" #2. order 函数路由 @app.route("/order",endpoint="n2") def order(): print("order") return "hello" #3. user 函数路由 @app.route("/user") def user(): print(url_for("n1")) #打印结果 /index print(url_for("n2")) #打印结果 /order #endport ,为url起别名,根据别名可以反向生成url return 'hello11' if __name__ == '__main__': app.run()
3.路由系统
三、路由系统 @app.route('/user/<username>') @app.route('/post/<int:post_id>') @app.route('/post/<float:post_id>') @app.route('/post/<path:path>') @app.route('/login', methods=['GET', 'POST']) 常用路由系统有以上五种,所有的路由系统都是基于一下对应关系来处理: DEFAULT_CONVERTERS = { 'default': UnicodeConverter, 'string': UnicodeConverter, 'any': AnyConverter, 'path': PathConverter, 'int': IntegerConverter, 'float': FloatConverter, 'uuid': UUIDConverter, }

def auth(func): def inner(*args, **kwargs): print('before') result = func(*args, **kwargs) print('after') return result return inner @app.route('/index.html',methods=['GET','POST'],endpoint='index') @auth def index(): return 'Index' 或 def index(): return "Index" self.add_url_rule(rule='/index.html', endpoint="index", view_func=index, methods=["GET","POST"]) or app.add_url_rule(rule='/index.html', endpoint="index", view_func=index, methods=["GET","POST"]) app.view_functions['index'] = index 或 def auth(func): def inner(*args, **kwargs): print('before') result = func(*args, **kwargs) print('after') return result return inner class IndexView(views.View): methods = ['GET'] decorators = [auth, ] def dispatch_request(self): print('Index') return 'Index!' app.add_url_rule('/index', view_func=IndexView.as_view(name='index')) # name=endpoint 或 class IndexView(views.MethodView): methods = ['GET'] decorators = [auth, ] def get(self): return 'Index.GET' def post(self): return 'Index.POST' app.add_url_rule('/index', view_func=IndexView.as_view(name='index')) # name=endpoint @app.route和app.add_url_rule参数: rule, URL规则 view_func, 视图函数名称 defaults=None, 默认值,当URL中无参数,函数需要参数时,使用defaults={'k':'v'}为函数提供参数 endpoint=None, 名称,用于反向生成URL,即: url_for('名称') methods=None, 允许的请求方式,如:["GET","POST"] strict_slashes=None, 对URL最后的 / 符号是否严格要求, 如: @app.route('/index',strict_slashes=False), 访问 http://www.xx.com/index/ 或 http://www.xx.com/index均可 @app.route('/index',strict_slashes=True) 仅访问 http://www.xx.com/index redirect_to=None, 重定向到指定地址 如: @app.route('/index/<int:nid>', redirect_to='/home/<nid>') 或 def func(adapter, nid): return "/home/888" @app.route('/index/<int:nid>', redirect_to=func) subdomain=None, 子域名访问 from flask import Flask, views, url_for app = Flask(import_name=__name__) app.config['SERVER_NAME'] = 'wupeiqi.com:5000' @app.route("/", subdomain="admin") def static_index(): """Flask supports static subdomains This is available at static.your-domain.tld""" return "static.your-domain.tld" @app.route("/dynamic", subdomain="<username>") def username_index(username): """Dynamic subdomains are also supported Try going to user1.your-domain.tld/dynamic""" return username + ".your-domain.tld" if __name__ == '__main__': app.run()
4 .文件上传
@app.route("/upload",methods=["GET","POST"]) def upload(): if request.method =="GET": return render_template("upload.html") from werkzeug.datastructures import FileStorage file =request.files.get("ff") print("file是什么:",file,"file类型:",type(file)) print("file_name:",file.filename) print("file_stream:",file.stream)
#方法一、
file_path =os.path.join('upload',file.filename) print(file_path) with open(file_path,"wb") as f: file.save(f)
#方法二、
file.save(file_path) 直接保存文件路径.
return "上传成功" if __name__ == '__main__': app.run()
输出结果:

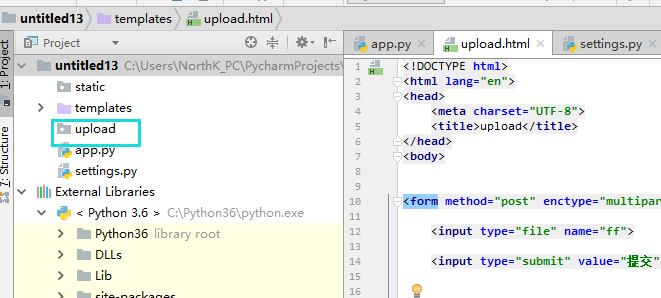
html页面
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>upload</title>
</head>
<body>
<form method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<input type="file" name="ff">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>
5、 请求和相应.
复制代码
from flask import Flask
from flask import request
from flask import render_template
from flask import redirect
from flask import make_response
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/login.html', methods=['GET', "POST"])
def login():
# 请求相关信息
# request.method
# request.args
# request.form
# request.values
# request.cookies
# request.headers
# request.path
# request.full_path
# request.script_root
# request.url
# request.base_url
# request.url_root
# request.host_url
# request.host
# request.files
# obj = request.files['the_file_name']
# obj.save('/var/www/uploads/' + secure_filename(f.filename))
# 响应相关信息
# return "字符串"
# return render_template('html模板路径',**{})
# return redirect('/index.html')
# response = make_response(render_template('index.html'))
# response是flask.wrappers.Response类型
# response.delete_cookie('key')
# response.set_cookie('key', 'value')
# response.headers['X-Something'] = 'A value'
# return response
return "内容"
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()
6. flask-session