(一)结论
-
在尾部插入数据,数据量较小时LinkedList比较快,因为ArrayList要频繁扩容,当数据量大时ArrayList比较快,因为ArrayList扩容是当前容量*1.5,大容量扩容一次就能提供很多空间,当ArrayList不需扩容时效率明显比LinkedList高,因为直接数组元素赋值不需new Node
-
在首部插入数据,LinkedList较快,因为LinkedList遍历插入位置花费时间很小,而ArrayList需要将原数组所有元素进行一次System.arraycopy
-
插入位置越往中间,LinkedList效率越低,因为它遍历获取插入位置是从两头往中间搜,index越往中间遍历越久,因此ArrayList的插入效率可能会比LinkedList高
-
插入位置越往后,ArrayList效率越高,因为数组需要复制后移的数据少了,那么System.arraycopy就快了,因此在首部插入数据LinkedList效率比ArrayList高,尾部插入数据ArrayList效率比LinkedList高
-
LinkedList可以实现队列,栈等数据结构,这是它的优势
(二)在尾部插入数据
结论:当数据量越来越大时,ArrayList比LinkedList快
原因:当数据量大时,ArrayList每次扩容都能得到很大的新空间,解决了前期频繁扩容的劣势,而LinkedList虽然有尾指针,但是每次add都要将对象new成一个Node(而ArrayList直接数组对应位置元素赋值)
末尾插入源码:
ArrayList:如果超出容量需要扩容,不需扩容时直接数组元素赋值
public boolean add(E e) { ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! elementData[size++] = e; return true; }
LinkedList:用传入的值new一个Node对象,然后尾指针指向该新的Node
public void addLast(E e) { linkLast(e); }
void linkLast(E e) { final Node<E> l = last; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); last = newNode; if (l == null) first = newNode; else l.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; }
实验对比:
public static void main(String[] argv) { LinkedList<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList<Integer>(); ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<Integer>(); Long start = System.nanoTime(); for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) { linkedList.addLast(i); } Long end = System.nanoTime(); System.out.println("LinkedList消耗时间:" + (end - start)); start = System.nanoTime(); for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) { arrayList.add(i); } end = System.nanoTime(); System.out.println("ArrayList消耗时间:" + (end - start)); }

(三)指定位置插入数据
(1)源码对比
ArrayList:性能主要在于扩容和数组复制,而当size很大时扩容影响就会减少
- 判断index是否合法
- 判断是否需要扩容
- 数组复制,从index开始把后面的数组元素全部复制到相对后一位的位置,该方法是native方法而且是连续内存复制问题,因此性能影响也没想象中的大
- 将element赋值给数组index元素
public void add(int index, E element) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, size - index); elementData[index] = element; size++; }
LinkedList:性能主要在于遍历链表查找index
- 判断是否超过链表长度,超过则抛错误
- 如果是插入最后的位置直接使用linkLast方法而不必去遍历查询对应位置
- node方法寻找index所指向的Node,首先判断index是否大于size/2,大于则从末尾往前找,小于则从0开始往后找
- 找到之后就是new一个node对象,设置指针的问题
public void add(int index, E element) { checkPositionIndex(index); if (index == size) linkLast(element); else linkBefore(element, node(index)); } Node<E> node(int index) { // assert isElementIndex(index); if (index < (size >> 1)) { Node<E> x = first; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x; } else { Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; } } void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) { // assert succ != null; final Node<E> pred = succ.prev; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ); succ.prev = newNode; if (pred == null) first = newNode; else pred.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; }
(2)首部插入实验对比


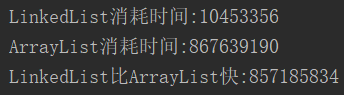
结论:开头插入,LinkedList比ArrayList快
(2)中间插入实验对比
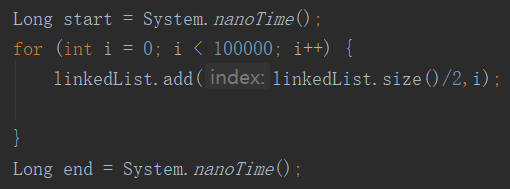


结论:中间插入LinkedList比ArrayList慢