线程池相关类
ExecutorService , 线程池接口
Executors 线程池工具类,可以生成不同类型的线程池,
Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3); //固定数量的线程池 corePoolSize=maximumPoolSize=3 Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); //缓存线程池corePoolSize =0,maximumPoolSize=Integer.MAX_VALUE, Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();//单线程池 corePoolSize=maximumPoolSize=1 Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(3); //支持定时或者周期性任务执行 Executors.newWorkStealingPool(); //支持并行执行任务
Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);调用的是new ThreadPoolExecutor

所以ThreadPoolExecutor线程池的真正实现类
线程池状态
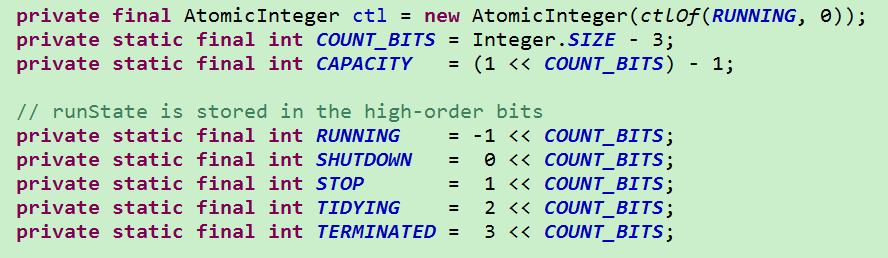
线程池状态和当前线程池线程数量是封装在ctl原子变量里的
RUNNING:接受新任务并处理队列中的任务
SHUTDOWN :不接受新任务,但处理队列中的任务
STOP :不接受新任务,不处理队列中的任务,并中断正在进行的任务(只是向当前线程发送中断信息,是否中断取决于Runnable 的实现逻辑)
TIDYING :所有任务都已终止,workerCount为0时,线程池会过度到该状态,并即将调用 terminate()
TERMINATED :terminated()调用完成;线程池中止
向线程池提交任务
带返回值

不带返回值
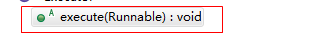
execute(Runnable) 内部的逻辑

1.如果当前线程池内线程数量小于corePoolSize 数量,会创建一个新的线程,去执行该任务
2.如果线程池内线程数量大于corePoolSize,则会将任务提交到 workQueue(阻塞队列)。通过offer方法添加,会立即返回是否添加成功
3.如果workQueued队列已经满了,而当前线程池内线程数量小于maximumPoolSize ,
则创建一个新的线程执行该任务,如果当前线程池内线程数量大于maximumPoolSize数量,则执行拒绝策略
测试execute方法
public class TestExecute { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable> queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(5); ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5, 10, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS, queue); // 默认直接抛出异常 for (int i = 1; i <= 17; i++) { Thread.sleep(10); threadPool.execute(new Thread(new MyRunnable(), "Thread—Pool-".concat(i + ""))); System.out.println(" index = "+ i+" , 线程池的线程数量: " + threadPool.getPoolSize()); if (queue.size() > 0) { System.out.println("----------------任务队列大小" + queue.size()); } } threadPool.shutdown(); System.out.println("*********"); } public static class MyRunnable implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { try { //休眠300毫秒 Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
测试结果

============================================================================================================
线程池的状态

关闭线程池
ThreadPoolExecutro#shutdown()方法,其实做了三件事:1、 将线程池的状态修改为shutdown,使得不能再往线程池添加新的任务。2 、中断所有的空闲线程。3、试着终止线程池(只有当线程池的状态是Tyding时,才调用子类重写的terminated方法)

调用shutdown方法
(1)线程池状态被修改为shutdown了,不能继续向线程池添加新任务了,如果继续调用execute方法添加新任务的话,就会抛出RejectedExecutionException异常。
(2)会中断所有的空闲线程,但是已经提交的任务会继续执行完。
(3)该方法是立即返回的,不阻塞当前线程。
/** * 测试shutdown方法,创建固定数量的线程池,线程大小为4,执行executorService.shutdown();后,线程池的状态被修改为shutdown了, * 3个idle线程会中断,即线程运行结束了,然后有1个正在运行的线程在1秒后也运行结束了,由线程池状态转化关系可知,线程池会变为terminated状态 * 应用结束 */ public class ExecutorSeviceTest { public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4); executorService.submit(() -> { try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("=========="); }); executorService.shutdown(); // try { // executorService.submit(()->{}); // }catch (Exception e){ // e.printStackTrace(); // } System.out.println("#####################"); } }
ThreadPoolExecutor#shutdownNow()该方法会将线程池状态修改为stop,会中断所有启动的线程

调动shutdownNow()方法
(1)线程池状态被修改为stop了,不能继续向线程池添加新任务了,如果继续调用execute方法添加新任务的话,就会抛出RejectedExecutionException异常。
(2) 会中断所有的线程
(3)该方法不会阻塞,会返回在任务队列中还没有执行的任务
/** * 测试shutdownNow()方法,创建固定数量的线程池,线程大小为4,执行executorService.shutdownNow();后,线程池的状态被修改为stop了, * 会中断所有的线程,由线程池状态转化关系可知,线程池会变为terminated状态 * 应用结束 */ public class ExecutorSeviceTest { public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4); executorService.submit(() -> { try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println(" --------------- interruped ----------------"); e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("=========="); }); executorService.shutdownNow(); // try { // executorService.submit(()->{}); // }catch (Exception e){ // e.printStackTrace(); // } System.out.println("#####################"); } }
ThreadPoolExecutor#awaitTerminated() , 传入一个超时时间,在指定的时间范围内,所有的任务都结束返回true,假如超时则返回false
/** * 测试awaitTermination()方法, * 该方法会阻塞当前线程,一般是在调用shutdown方法后调用该方法, * 返回true, 当线程池所有任务都执行完了,线程池状态变为terminated了,并且没有超时 * 返回false, 超时 */ public class ExecutorSeviceTest { public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4); executorService.submit(() -> { try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println(" --------------- interruped ----------------"); e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("=========="); }); executorService.shutdown(); // try { // executorService.submit(()->{}); // }catch (Exception e){ // e.printStackTrace(); // } try { boolean flag = executorService.awaitTermination(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS); if(flag){ System.out.println("线程池所有的任务都执行完了"); }else{ System.out.println("线程池还有任务没有执行完,等待超时了"); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
默认的线程池拒绝策略
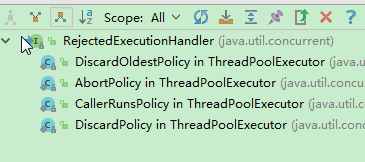
DiscardOldestPolicy 丢弃时间最久还没有执行的任务,然后添加当前的任务
AbortPolicy 抛出异常
DiscardPolicy 直接丢弃当前任务
CallerRunsPolicy main线程去执行当前任务