Table of Contents
简介
如果要使一个网络设备可用,它就必须能被内核正确识别并且与正确的设备驱动关联起来。首先,设备驱动既可以做为内核模块动态加载,也可以是内核的一个静态组件。
其次,设备可以在启动时识别,也可以在运行时加载识别(热插拔设备 USB PCI IEEE…)。
系统初始化概论
下图为系统初始化流程
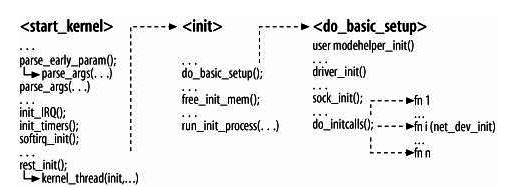
图5-1:内核初始化
引导期间选项
调用两次parse_args(一次是直接调用, 而另外一次是通过parse_early_param间接调用)以处理引导加载程序(bootloader, 如LILO或GRUB)
在引导期间传给内核的配置参数。
中断和定时器
硬中断和软中断分别由init_IRQ和softirq_init做初始化。
初始化函数
内核子系统及内建的设备驱动程序由do_initcall初始化。
设备注册和初始化
注册和初始化的任务的一部分的内核负责,而其他部分由设备驱动程序负责。
硬件初始化
由设备驱动在总线(pci,usb)的协调下完成,主要分配中断号和i/o地址。
软件初始化
在设备可用前需要配置一些参数,如ip地址
功能初始化
与设备相关,如流量控制
NIC初始化的基本目标
IRQ线
NIC必须被分派一个IRQ。
I/O端口和内存注册
I/O端口和内存f分别使用request_region和release_region注册及释放。
硬件中断
注册中断
1: static inline int __must_check 2: request_irq(unsigned int irq, irq_handler_t handler, unsigned long flags, 3: const char *name, void *dev) 4: { 5: return request_threaded_irq(irq, handler, NULL, flags, name, dev); 6: }
解除中断
1: extern void free_irq(unsigned int, void *);
模块选项
每个模块都在/sys/modules中分派一个目录。子目录/sys/modules/module/parameters中的每个文件就是
改模块所输出的每个参数。
设备处理层初始化
[注] net/core/dev.c
1: /* 2: * Initialize the DEV module. At boot time this walks the device list and 3: * unhooks any devices that fail to initialise (normally hardware not 4: * present) and leaves us with a valid list of present and active devices. 5: * 6: */ 7: 8: /* 9: * This is called single threaded during boot, so no need 10: * to take the rtnl semaphore. 11: */ 12: static int __init net_dev_init(void) 13: { 14: int i, rc = -ENOMEM; 15: 16: BUG_ON(!dev_boot_phase); 17: 18: if (dev_proc_init()) 19: goto out; 20: 21: if (netdev_kobject_init()) 22: goto out; 23: 24: INIT_LIST_HEAD(&ptype_all); 25: for (i = 0; i < PTYPE_HASH_SIZE; i++) 26: INIT_LIST_HEAD(&ptype_base[i]); 27: 28: if (register_pernet_subsys(&netdev_net_ops)) 29: goto out; 30: 31: /* 32: * Initialise the packet receive queues. 33: */ 34: 35: for_each_possible_cpu(i) { 36: struct softnet_data *sd = &per_cpu(softnet_data, i); 37: 38: memset(sd, 0, sizeof(*sd)); 39: skb_queue_head_init(&sd->input_pkt_queue); 40: skb_queue_head_init(&sd->process_queue); 41: sd->completion_queue = NULL; 42: INIT_LIST_HEAD(&sd->poll_list); 43: sd->output_queue = NULL; 44: sd->output_queue_tailp = &sd->output_queue; 45: #ifdef CONFIG_RPS 46: sd->csd.func = rps_trigger_softirq; 47: sd->csd.info = sd; 48: sd->csd.flags = 0; 49: sd->cpu = i; 50: #endif 51: 52: sd->backlog.poll = process_backlog; 53: sd->backlog.weight = weight_p; 54: sd->backlog.gro_list = NULL; 55: sd->backlog.gro_count = 0; 56: } 57: 58: dev_boot_phase = 0; 59: 60: /* The loopback device is special if any other network devices 61: * is present in a network namespace the loopback device must 62: * be present. Since we now dynamically allocate and free the 63: * loopback device ensure this invariant is maintained by 64: * keeping the loopback device as the first device on the 65: * list of network devices. Ensuring the loopback devices 66: * is the first device that appears and the last network device 67: * that disappears. 68: */ 69: if (register_pernet_device(&loopback_net_ops)) 70: goto out; 71: 72: if (register_pernet_device(&default_device_ops)) 73: goto out; 74: 75: open_softirq(NET_TX_SOFTIRQ, net_tx_action); 76: open_softirq(NET_RX_SOFTIRQ, net_rx_action); 77: 78: hotcpu_notifier(dev_cpu_callback, 0); 79: dst_init(); 80: dev_mcast_init(); 81: rc = 0; 82: out: 83: return rc; 84: } 85: 86: subsys_initcall(net_dev_init);
- 初始化cpu相关数据结构,用于网络软中断
- 调用dev_proc_init,dev_mcast_init在/proc下增加相应的文件
- 调用netdev_sysfs在/sys下增加相应配置文件
- 调用net_random_init初始化cpu种子数组,这些数组用于在net_random中生成随机数
- 调用dst_init初始化dst
- 初始化网络处理函数数组ptype_base,这些函数用来多路分解接收到的包
- 在通知链表上注册回调函数用于接收cpu热插拔事件
除了上述初始化,对于网络设备来说更重要的是 初始化它的net_device结构,这个会在第8章详细讲
动态加载设备/设备驱动
讲动态加载之前先介绍2个用户空间程序和1个内核函数
- /sbin/modprobe 在内核需要加载某个模块时调用,判断内核传递的模块是不是/etc/modprobe.conf文件中定义的别名
- /sbin/hotplug 在内核检测到一个新设备插入或拔出系统时调用,它的任务是根据设备标识加载正确的驱动
内核函数call_usermodehelper 上面两个用户进程统一由这个函数调用,其中参数arg1指示call_usermodehelper调用哪个用户进程,arg2指示call..使用哪个配
置脚本,流程详见下图;
实际上看懂了上面所说的,动态加载的概念应该很清楚了,最后再说说使用场景
- 以模块方式加载
kmod模块加载器允许内核组件通过调用request_module请求加载某个模块
举个例子;如果系统管理员使用ifconfig配置某个网卡,但这个网卡驱动还没有加载,如eth0,内核就会给/sbin/modprobe发送一个请求,让它加载名称为
eth0的模块。如果/etc/modprobe.conf中包含“alias eth0 xxx”的字符,/sbin/modprobe就会尝试加载xxx.ko模块。
module_param 宏定义在引入sysfs后可以通过文件来访问得到模块参数
模块选项有三项 , 第一项参数名称,第二项参数类型,第三项表示参数作为文件在sys文件系统中所有的权限。
每个模块都会在sys/modules下生成对应的目录,通过目录下的文件可以获取模块参数。
- pnp热插拔
hotplug允许内核检测热插拔设备的插入和拔出并通知用户进程(/sbin/hotplug),用户进程根据这些通知来加载相应的驱动
在编译内核时,会在kernel目录下生成modules.pcimap和modules.usbmap两个文件,这两个文件分别包含了内核所支持设备的pci id和usb id,文件中还包
含于每个设备的id相对应的内核模块名称,当用户进程收到内核关于pnp的通知后,会使用这个文件来查找正确的设备驱动