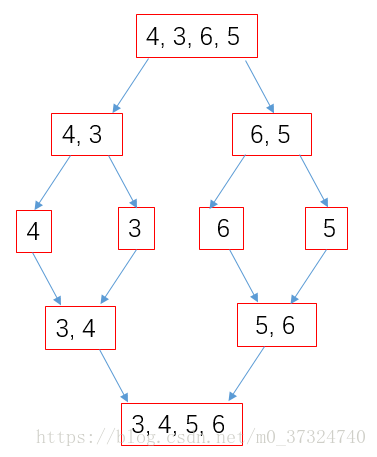
归并排序是一种稳定的排序,采用分而治之策略,可以用于顺序储存结构,也易于在链表上实现。其原理如下图:
算法时间复杂度为 O(nlogn),空间复杂度为 O(n)。
1 在数组上实现
def mergesort(seq):
if len(seq)<=1:
return seq
mid=int(len(seq)/2)
left=mergesort(seq[:mid])
right=mergesort(seq[mid:])
return merge(left,right)
def merge(left,right):
result=[]
i,j=0,0
while i<len(left) and j<len(right):
if left[i]<=right[j]:
result.append(left[i])
i+=1
else:
result.append(right[j])
j+=1
result+=left[i:]
result+=right[j:]
return result
if __name__=='__main__':
seq=[6,5,8,7]
print(mergesort(seq))输出:
[5, 6, 7, 8]2 在链表上实现
# Definition of ListNode
class ListNode(object):
def __init__(self, val, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution:
"""
@param: head: The head of linked list.
@return: You should return the head of the sorted linked list, using constant space complexity.
"""
# 归并法
def sortList(self, head):
# write your code here
if head is None or head.next is None:
return head
pre = head
slow = head # 使用快慢指针来确定中点
fast = head
while fast and fast.next:
pre = slow
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
left = head
right = pre.next
pre.next = None # 从中间打断链表
left = self.sortList(left)
right = self.sortList(right)
return self.merge(left,right)
def merge(self, left, right):
pre = ListNode(-1)
first = pre
while left and right:
if left.val < right.val:
pre.next = left
pre = left
left = left.next
else:
pre.next = right
pre = right
right = right.next
if left:
pre.next = left
else:
pre.next = right
return first.nextnode1 = ListNode(4)
node2 = ListNode(3)
node3 = ListNode(2)
node4 = ListNode(1)
node1.next = node2
node2.next = node3
node3.next = node4
s = Solution()
result = s.sortList(node1)
while (result != None):
print(result.val)
result = result.next 输出:
1
2
3
4