@
博客说明
| 撰写日期 | 2018.12.08 |
|---|---|
| 完稿日期 | 2019.10.06 |
| 最近维护 | 暂无 |
| 本文作者 | multimicro |
| 联系方式 | multimicro@qq.com |
| GitHub | https://github.com/wifialan |
| 本文地址 | https://blog.csdn.net/multimicro/article/details/84898135 |
开发环境
| 环境说明 | 详细信息 | 备注信息 |
|---|---|---|
| 操作系统 | Ubunut 18.04.3 LTS | |
| 开发板 | S3C2440(JZ2440-V3) | |
| kernel版本 | linux-3.4.2 | 官网地址 |
| busybox版本 | busybox-1.22.1 | 官网地址 |
| 编译器 | arm-linux-gcc-4.4.3 | 下载地址 |
| 编译器路径 | /opt/FriendlyARM/toolschain/4.4.3/bin | 绝对路径 |
1. Linux字符设备驱动的组成
引自宋宝华《Linux设备驱动开发详解--基于最新的Linux 4.0内核》P138内容:
在Linux中,字符设备驱动由如下几个部分组成。
1. 字符设备驱动模块加载与卸载函数
2. 字符设备驱动的file_operations 结构体中的成员函数
这里先介绍一下字符设备的开发流程:字符设备驱动是通过设备号 与上位机程序连接。而上位机程序对驱动的控制则是通过文件操作,即read、write、ioctl等完成。
- ps.(对于Linux系统而言,一切皆文件,驱动加载成功后,会在
/proc/devices里面添加驱动节点号信息)
因此一个字符设备驱动应包含1. 设备号的注册、卸载和2. 文件操作两个功能,注册的设备号用于提供接口,而文件操作用于对驱动的操作。
字符设备驱动的结构如下图所示:
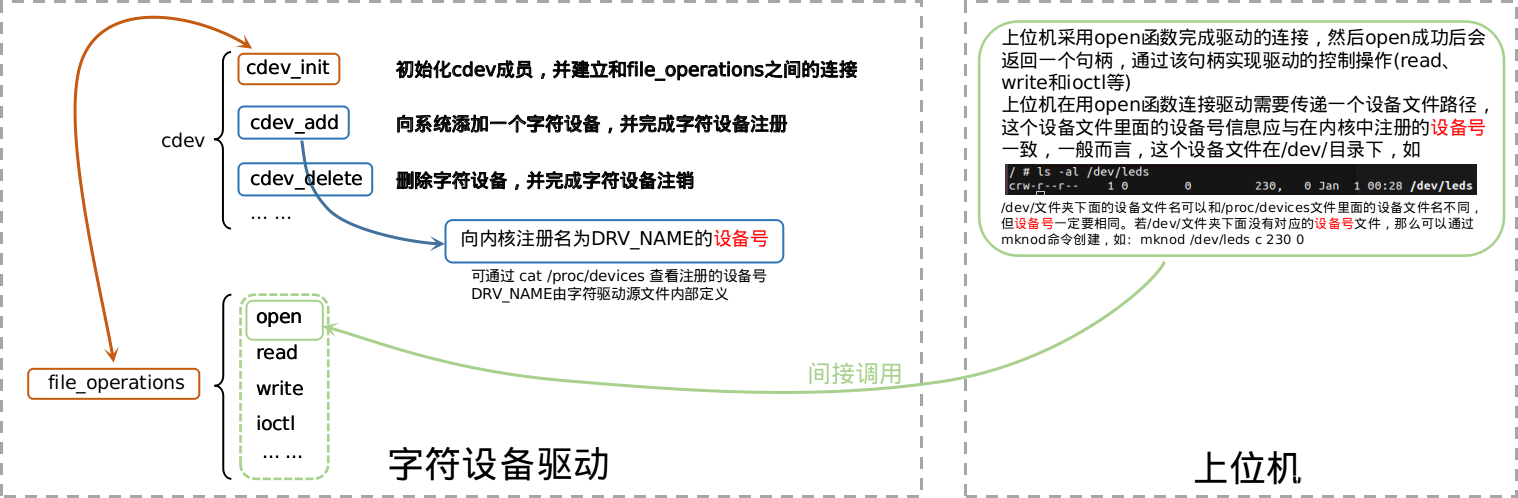
对于cdev_init函数中,建立file_operations之间的连接的疑问,看一下cdev_init的实现
void cdev_init(struct cdev *cdev, const struct file_operations *fops)
{
memset(cdev, 0, sizeof *cdev);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&cdev->list);
kobject_init(&cdev->kobj, &ktype_cdev_default);
cdev->ops = fops;
}
可以看出,最后的一个语句cdev->ops = fops;完成了在cdev中的file_operations的绑定
下面从程序语言角度感性的认识一下设备号的注册、卸载函数原型,和文件操作函数原型。
1.1 字符设备驱动模块加载与卸载函数
//加载函数
static int __init xxx_init(void)
{
... ...
}
//卸载函数
static int __exit xxx_exit(void)
{
... ...
}
1.2 字符设备驱动的file_operations 结构体中的成员函数
static const struct file_operations xxx_fileops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.write = xxx_write,
.read = xxx_read,
.open = xxx_open,
.unlocked_ioctl = xxx_ioctl,
... ...
};
static int xxx_open( struct inode *inodes, struct file *filp )
{
... ...
}
static long xxx_ioctl( struct file *file, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg )
{
... ...
}
static ssize_t xxx_write( struct file *filp, const char __user *buffer, size_t size, loff_t *f_pos )
{
... ...
}
static ssize_t xxx_read( struct file *filp, const char __user *buffer, size_t size, loff_t *f_pos )
{
... ...
}
2. 字符设备驱动——设备号注册卸载
以我写的字符设备驱动源代码为例,路径为linux-3.4.2driverschars3c2440_leds.c,文章后附有完整的代码
设备号的注册由static int __init s3c2440_leds_init(void)完成
设备号的卸载由static int __init s3c2440_leds_exit(void)完成
首先分析设备号的注册,然后分析卸载
2.1 设备号注册
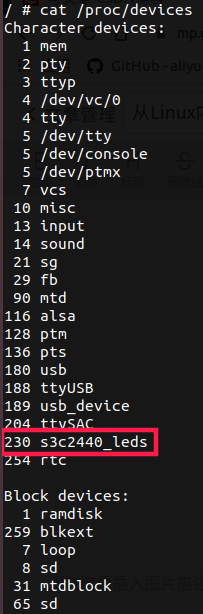
设备号分为主设备号和次设备号,若源代码中定义了主设备号(次设备号一般为0),那么可以直接完成设备号的注册,其流程为

注册成功后,可通过cat /proc/devices命令查看设备号
2.2 设备号注销
相比设备号的注册,注销流程就十分简单:

3. 字符设备驱动——文件操作
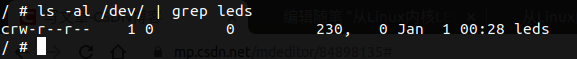
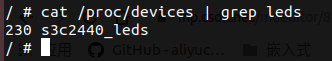
上位机程序首先要调用open函数打开此驱动,具体方法就是,打开该设备号对应的文件,一般而言,该设备号文件在/dev/文件夹下,驱动在内核中注册成功后会在/proc/devices中包含设备号信息,但/dev/文件夹内并没有创建该设备号对应的文件,因此需要手动创建该设备号文件,命令为:
mknod /dev/leds c 230 0
表示在/dev文件夹下创建名为leds的字符设备文件,其主设备号为230,次设备号为0。
字符设备文件名可以另取,但设备号一定要对应/proc/devices里面的设备号。
然后通过fd = open("/dev/leds",0);完成设备驱动的打开
当上位机程序通过调用open函数打开(链接上)相应的驱动程序后,open函数会返回一个文件描述符暂且记为fd,然后对该驱动的read、write、ioctl等操作都可以通过使用fd完成。简单的字符设备驱动程序大多采用ioctl函数控制驱动程序,而这个ioctl函数本身也不难,其实现为:
static long s3c2440_leds_ioctl( struct file *file, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg )
函数中
第一个参数:表示要操作的文件描述符
第二个参数:表示传递的命令字
第三个参数:表示传递的变量字
第二个参数和第三个参数的含义没有硬性规定,传递的参数符合对应的关键字限定类型即可
下面的给出示例参考
static long s3c2440_leds_ioctl( struct file *file, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg )
{
printk(DRV_NAME " Recv cmd: %u
", cmd);
printk(DRV_NAME " Recv arg: %lu
", arg);
//IO operations function.
if(arg > 4) {
return -EINVAL;
}
switch (cmd) {
case IOCTL_LED_ON: //#define IOCTL_LED_ON 1
s3c2410_gpio_setpin(S3C2410_GPF(arg+3), 0);//Set pin
printk("Open LED %lu ",arg);
return 0;
case IOCTL_LED_OFF: //#define IOCTL_LED_OFF 0
s3c2410_gpio_setpin(S3C2410_GPF(arg+3), 1);
printk("Close LED %lu ",arg);
return 0;
default:
return -EINVAL;
}
}
参考资料
1. 宋宝华《Linux设备驱动开发详解–基于最新的Linux 4.0内核》 第6章 字符设备驱动
2. Jonathan Corbet《linux设备驱动程序第三版》 P50-P51
示例代码
/*
* Driver for S3C2440 base board.
*
* Copyright (C) 2019 Alan NWPU <alantian.at@gmail.com>
*
* This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
* the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
* (at your option) any later version.
*
* This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
* GNU General Public License for more details.
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
* along with this program; if not, write to the Free Software
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
* MULTIBEANS, NPU Youyi West Ave, Beilin District, Xi'an, China.
*/
#include <linux/module.h> /* Every Linux kernel module must include this head */
#include <linux/init.h> /* Every Linux kernel module must include this head */
#include <linux/kernel.h> /* printk() */
#include <linux/fs.h> /* struct fops */
#include <linux/errno.h> /* error codes */
#include <linux/cdev.h> /* cdev_alloc() */
#include <linux/ioport.h> /* request_mem_region() */
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/moduleparam.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/gpio.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>
#include <asm/irq.h>
#include <mach/gpio-nrs.h>
#include <mach/gpio.h>
#include <mach/hardware.h>
#include <plat/gpio-cfg.h>
#define DRV_NAME "s3c2440_leds"
#define DRV_AUTHOR "Alan Tian <alantian.at@gmail.com>"
#define DRV_DESC "S3C2440 LED Pin Driver"
#define S3C2440_LED_SIZE 0x1000
#define S3C2440_LED_MAJOR 230
#define S3C2440_LED_MINOR 0
static int major = S3C2440_LED_MAJOR;
static int minor = S3C2440_LED_MINOR;
/* 应用程序执行ioctl(fd, cmd, arg)时的第2个参数 */
#define IOCTL_LED_ON 0
#define IOCTL_LED_OFF 1
static int s3c2440_leds_open( struct inode *inodes, struct file *filp );
static long s3c2440_leds_ioctl( struct file *file, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg );
static ssize_t s3c2440_leds_write( struct file *filp, const char __user *buffer,
size_t size, loff_t *f_pos );
static ssize_t s3c2440_leds_read( struct file *filp, const char __user *buffer,
size_t size, loff_t *f_pos );
struct s3c2440_leds_dev_t
{
struct cdev cdev;
unsigned char mem[S3C2440_LED_SIZE];
} *s3c2440_leds_dev;
//Step 2: Add file operations
static const struct file_operations s3c2440_leds_fileops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.write = s3c2440_leds_write,
.read = s3c2440_leds_read,
.open = s3c2440_leds_open,
.unlocked_ioctl = s3c2440_leds_ioctl,
};
static int s3c2440_leds_open( struct inode *inodes, struct file *filp )
{
//int ret;
filp->private_data = s3c2440_leds_dev;
printk(DRV_NAME" S3C2440 open function...
");
return 0;
}
static long s3c2440_leds_ioctl( struct file *file, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg )
{
printk(DRV_NAME " Recv cmd: %u
", cmd);
printk(DRV_NAME " Recv arg: %lu
", arg);
//IO operations function.
if(arg > 4) {
return -EINVAL;
}
switch (cmd) {
case IOCTL_LED_ON:
s3c2410_gpio_setpin(S3C2410_GPF(arg+3), 0);//Set pin
printk("Open LED %lu ",arg);
return 0;
case IOCTL_LED_OFF:
s3c2410_gpio_setpin(S3C2410_GPF(arg+3), 1);
printk("Close LED %lu ",arg);
return 0;
default:
return -EINVAL;
}
}
static ssize_t s3c2440_leds_write( struct file *filp, const char __user *buffer,
size_t size, loff_t *f_pos )
{
unsigned long p = *f_pos;
unsigned int count = size;
int ret = 0;
struct s3c2440_leds_dev_t *dev = filp->private_data;
if(p >= S3C2440_LED_SIZE)
return 0;
if(count > S3C2440_LED_SIZE - p)
count = S3C2440_LED_SIZE - p;
memset(dev->mem, 0, S3C2440_LED_SIZE);
if(copy_from_user(dev->mem + p, buffer, count)) {
ret = -EFAULT;
} else {
*f_pos += count;
ret = count;
printk(KERN_INFO "writter %u bytes(s) from %lu
", count, p);
}
return ret;
}
static ssize_t s3c2440_leds_read( struct file *filp, const char __user *buffer,
size_t size, loff_t *f_pos )
{
unsigned long p = *f_pos;
unsigned int count = size;
int ret = 0;
struct s3c2440_leds_dev_t *dev = filp->private_data;
if(p >= S3C2440_LED_SIZE)
return 0;
if(count > S3C2440_LED_SIZE - p)
count = S3C2440_LED_SIZE - p;
if(copy_to_user(buffer, dev->mem + p, count)) {
ret = -EFAULT;
} else {
*f_pos += count;
ret = count;
printk(KERN_INFO "read %u bytes(s) from %lu
", count, p);
}
return ret;
}
static int __init s3c2440_leds_init(void)
{
int ret,err;
dev_t devid;
if(major) {
devid = MKDEV(major, 0);
ret = register_chrdev_region(devid, 1, DRV_NAME);
printk("Origin Creat node %d
",major);
} else {
ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&devid, 0, 1, DRV_NAME);
major = MAJOR(devid);
printk("Arrage1 Creat node %d
",major);
}
if(ret < 0) {
printk(DRV_NAME " s3c2440 new device failed
");
//goto fail_malloc;
return ret;
}
s3c2440_leds_dev = kzalloc(sizeof(struct s3c2440_leds_dev_t), GFP_KERNEL);
if(!s3c2440_leds_dev) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto fail_malloc;
}
printk("success init leds
");
cdev_init(&s3c2440_leds_dev->cdev, &s3c2440_leds_fileops);
err = cdev_add(&s3c2440_leds_dev->cdev, devid, 1);
if(err)
printk(KERN_NOTICE "Error %d adding s2c2440_leds %d",err, 1);
return 0;
fail_malloc:
unregister_chrdev_region(devid, 1);
return ret;
}
static void __exit s3c2440_leds_exit(void)
{
printk("Starting delet node %d
",major);
cdev_del(&s3c2440_leds_dev->cdev);
kfree(s3c2440_leds_dev);
unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(major, minor), 1);
printk("Delete node %d
",major);
}
module_init(s3c2440_leds_init);
module_exit(s3c2440_leds_exit);
MODULE_AUTHOR(DRV_AUTHOR);
MODULE_DESCRIPTION(DRV_DESC);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");