参考
https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/connectivity/bluetooth-le
https://www.jianshu.com/p/3a372af38103
简介
最近公司有个连接设备商蓝牙的小功能,于是把蓝牙相关的api简单过了一下,基本可以开发了。
Android 4.3(api 18)引入了 蓝牙低功耗的支持,并提供了能够用来发现设备,查询service,传输信息的api。
当一个用户用他的设备 用ble和其他的设备配对时,两个设备间的数据传输是能被用户设备的所有app访问到的。因此,如果你的应用程序捕获敏感数据,你应该实现自己的应用层的协议来保护这些数据的隐私。
开发流程
权限声明
首先你需要声明bluetooth权限,这个权限是蓝牙的基础权限,其他的操作蓝牙都需要先声明此权限。
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH"/>
如果你要使用蓝牙扫描周围设备(BluetoothAdapter.startDiscovery,或BluetoothLeScanner.startScan),或者操作蓝牙的设置,你就需要此权限。
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH_ADMIN"/>
另外,如果你的app是运行在Android8.0以下的设备上时,因为可以被发现的设备可能会暴露其位置,你需要ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION权限,
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION" />
- 此权限是危险权限,所以需要运行时动态申请。
- 既然是访问定位,那么系统的定位功能必须的打开才行。
如果你的app是运行在Android8.0+的设备上时,你可以使用CompanionDeviceManager的api,CompanionDeviceManager将代表您的应用程序对附近设备执行蓝牙或Wi-Fi扫描,而无需访问ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION或BLUETOOTH_ADMIN权限。当然如果不使用CompanionDeviceManager的话就需要按上边的申请权限了。
如果你的app是需要支持ble的设备才能运行,就需要在清单文件中声明,
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.bluetooth_le" android:required="true"/>
但如果你也想让不支持ble的设备也能运行,也需要上边的声明,并把required设置为false,但你需要在代码中自行判断:
if (!getPackageManager().hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_BLUETOOTH_LE)) { Toast.makeText(this, R.string.ble_not_supported, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); return; }
启动蓝牙
1. 在Android4.3通过getSystemService获取
finaBluetoothManager bluetoothManager = (BluetoothManager) getSystemService(Context.BLUETOOTH_SERVICE); BluetoothAdapter bluetoothAdapter = bluetoothManager.getAdapter();
2. 然后启用蓝牙
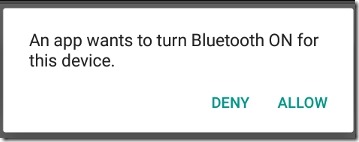
if (bluetoothAdapter == nul|| !bluetoothAdapter.isEnabled()) { Intent enableBtIntent = new Intent(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_REQUEST_ENABLE); startActivityForResult(enableBtIntent, REQUEST_ENABLE_BT); }
之后会启动一个系统弹窗,如下图:
REQUEST_ENABLE_BT是我们自定义的>=0,之后会在onActivityForResult中收到启动结果,RESULT_OK表示启动成功,RESULT_CANCELED表示取消。
获取当前已配对的外围设备
第一次和外部蓝牙设备连接时,配对请求就会自动的显示给用户,当配对成功后,设备的基本信息(如设备名,设备类型,mac地址等信息)就会被存储到手机中,可以通过getBondedDevices(需要先开启蓝牙)访问到。
之后再次连接时,就可以直接使用已配对的已知的mac地址直接和远程设备建立连接,而不需要先进行扫描(并不是真的不扫描,只是我们不用手动调用),当然前提时外围设备在我们能扫描到的范围内。
配对和连接的区别:
- 配对是两个设备之间互相存储了对方的设备信息,以及一个沟通的密钥。
- 连接是两个设备间共享同一个RFCOMM通道,可以进行互传数据。在Android api中,在连接之前会自动的先配对。
所以在扫描之前有必要先获取当前已配对的设备,看有没有我们想要进行连接的设备。
Set<BluetoothDevice> pairedDevices = bluetoothAdapter.getBondedDevices(); if (pairedDevices.size() > 0) { // There are paired devices. Get the name and address of each paired device. for (BluetoothDevice device : pairedDevices) { String deviceName = device.getName(); String deviceHardwareAddress = device.getAddress(); // MAC address } }
扫描ble设备
如果已配对的设备没有我们想要的,那么再进行扫描周围的蓝牙设备。
您只能扫描Bluetooth LE设备 或 传统蓝牙设备,如Bluetooth中所述。 您不能同时扫描Bluetooth LE和传统设备。
因为扫描是一个耗电的操作,所以您应该遵守以下准则:
- 一旦你找到期望的设备就应该停止扫描。
- 切勿循环扫描,并为扫描设置时间限制。 先前可用的设备可能已超出范围,并且继续扫描会耗尽电池电量。
private BluetoothLeScanner bluetoothLeScanner = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter().getBluetoothLeScanner(); private boolean mScanning; private Handler handler = new Handler(); // Stops scanning after 10 seconds. private static final long SCAN_PERIOD = 10000; private void scanLeDevice() { if (!mScanning) { // Stops scanning after a pre-defined scan period. handler.postDelayed(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { mScanning = false; bluetoothLeScanner.stopScan(leScanCallback); } }, SCAN_PERIOD); mScanning = true; bluetoothLeScanner.startScan(leScanCallback); } else { mScanning = false; bluetoothLeScanner.stopScan(leScanCallback); } }
- bluetoothLeScanner.startScan有几个重载方法,都是用来过滤扫描到的设备的。
startScan(ScanCallback)是不进行过滤,那么当屏幕关闭时为了省电会暂停扫描,屏幕再打开时恢复扫描,为了防止这样,请使用带有过滤的startScan。
- bluetoothLeScanner.stopScan时必须要传入和startScan传入的callback一样的callback才能停止。
ScanCallback:
private LeDeviceListAdapter leDeviceListAdapter; // Device scan callback. private ScanCallback leScanCallback = new ScanCallback() { @Override public void onScanResult(int callbackType, ScanResult result) { super.onScanResult(callbackType, result); leDeviceListAdapter.addDevice(result.getDevice()); leDeviceListAdapter.notifyDataSetChanged(); } };
- 此回调是在主线程的。
- callbackType:表示这个回调是如何触发的,它是在ScanSettings中配置的callbackType,
- ScanResult包含了下边几个重要数据:
- BluetoothDevice:扫描到的蓝牙设备的抽象,可以用此对象进行配对连接。
- int Rssi:received signastrength in dBm,接收到的此蓝牙设备的信号强度
- ScanRecord:表示扫描到的蓝牙设备的广播数据,
连接GATT server
和传统蓝牙的连接不同的是,我们可以使用已经封装好的Android api来进行连接ble设备,而不用再去创建通道,然后建立socket等操作。
与BLE设备交互的第一步是连接到它——更具体地说,连接到设备上的GATT服务器。
在第一次连接的时候会弹 一个系统弹窗 或 通知,让用户进行配对,
要连接到BLE设备上的GATT服务器,可以使用BluetoothDevice.connectGatt()方法。
public BluetoothGatt connectGatt(Context context, boolean autoConnect, BluetoothGattCallback callback)
- autoConnect:表示是否在BLE设备可用时自动连接。
关于autoConnect参数为true的意义?
在蓝牙核心文档Vol3: Core System Package[Host volume]->Part C: Generic Access Profile的Connection Modes and Procedures章节中有涉及到自动连接建立规程(Auto Connection Establishment Procedure)的定义。
自动连接建立规程用来向多个设备同时发起连接。一个中央设备的主机与多个外围设备绑定,只要它们开始广播,便立刻与其建立连接。跟多细节请参考蓝牙核心文档和协议栈源码。
- BluetoothGattCallback :是用来把一些信息返回给GATT client,比如连接状态的改变,GATT client的一些操作的结果。所有的回调都是后台线程上的。
当调用蓝牙的连接方法之后,蓝牙会异步执行蓝牙连接的操作,如果连接成功会回调 BluetoothGattCalbackl#onConnectionStateChange 方法。这个方法运行的线程是一个 Binder 线程,所以不建议直接在这个线程处理耗时的任务,因为这可能导致蓝牙相关的线程被阻塞。
public void onConnectionStateChange(BluetoothGatt gatt, int status, int newState)
- status:代表是否成功执行了连接操作,如果为 BluetoothGatt.GATT_SUCCESS 表示成功执行连接操作,第三个参数才有效,否则说明这次连接尝试不成功。有时候,我们会遇到 status == 133 的情况,根据网上大部分人的说法,这是因为 Android 最多支持连接 6 到 7 个左右的蓝牙设备,如果超出了这个数量就无法再连接了。所以当我们断开蓝牙设备的连接时,还必须调用 BluetoothGatt#close 方法释放连接资源。否则,在多次尝试连接蓝牙设备之后很快就会超出这一个限制,导致出现这一个错误再也无法连接蓝牙设备。
- newState:代表当前设备的连接状态,如果 newState == BluetoothProfile.STATE_CONNECTED 说明设备已经连接,可以进行下一步的操作了(发现蓝牙服务,也就是 Service)。当蓝牙设备断开连接时,这一个方法也会被回调,其中的 newState == BluetoothProfile.STATE_DISCONNECTED。
获取service
1. 在连接成功后,可以通过BluetoothGatt.discoverServices()来查找外围设备上支持的service,
2. 此操作是异步操作,之后会在 BluetoothGattCalbackl#onServicesDiscovered回调:
3. 然后我们可以通过BluetoothGatt.getService(UUID uuid)来获取我们期望的service。
private final BluetoothGattCallback gattCallback = new BluetoothGattCallback() { @Override public void onConnectionStateChange(BluetoothGatt bluetoothGatt, int status, int newState) { String intentAction; if (newState == BluetoothProfile.STATE_CONNECTED) { bluetoothGatt.discoverServices(); } else if (newState == BluetoothProfile.STATE_DISCONNECTED) { Log.i(TAG, "Disconnected from GATT server."); } } @Override // New services discovered public void onServicesDiscovered(BluetoothGatt bluetoothGatt, int status) { if (status == BluetoothGatt.GATT_SUCCESS) { bluetoothGatt.getService(uuid); } else { Log.w(TAG, "onServicesDiscovered received: " + status); } } @Override // Result of a characteristic read operation public void onCharacteristicRead(BluetoothGatt gatt, BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic, int status) { if (status == BluetoothGatt.GATT_SUCCESS) { } } };
获取Charactristic数据
接着通过 BluetoothGattService#getCharacteristic(UUID uuid)、getCharacteristics()获取 BluetoothGattCharacteristic。
此时获取的别没有Characteristic的value,只有uuid信息。调用BluetoothGatt.readCharacteristic来读取,之后会在BluetoothGattCallback.onCharacteristicRead回调:
@Override public void onCharacteristicRead(final BluetoothGatt gatt, final BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic, final int status) { Log.d(TAG, "callback characteristic read status " + status + " in thread " + Thread.currentThread()); if (status == BluetoothGatt.GATT_SUCCESS) { Log.d(TAG, "read value: " + characteristic.getValue()); } } BluetoothGattService service = gattt.getService(SERVICE_UUID); BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic = gatt.getCharacteristic(CHARACTER_UUID); gatt.readCharacteristic(characteristic);
向Charactristic写入数据
1. 调用 BluetoothGattCharactristic#setValue 传入需要写入的数据(蓝牙最多单次支持 20 个字节数据的传输,如果需要传输的数据大于这一个字节则需要分包传输)。
2. 调用 BluetoothGattCharactristic#writeCharacteristic 方法通知系统异步往设备写入数据。
3. 系统回调 BluetoothGattCallback#onCharacteristicWrite 方法通知数据已经完成写入。此时,我们需要执行 BluetoothGattCharactristic#getValue 方法检查一下写入的数据是否我们需要发送的数据,如果不是按照项目的需要判断是否需要重发。
@Override public void onCharacteristicWrite(final BluetoothGatt gatt, final BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic, final int status) { Log.d(TAG, "callback characteristic write in thread " + Thread.currentThread()); if(!characteristic.getValue().equal(sendValue)) { // 执行重发策略 gatt.writeCharacteristic(characteristic); } } //往蓝牙数据通道的写入数据 BluetoothGattService service = gattt.getService(SERVICE_UUID); BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic = gatt.getCharacteristic(CHARACTER_UUID); characteristic.setValue(sendValue); gatt.writeCharacteristic(characteristic);
超过20字节分包问题
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/24135682/android-sending-data-20-bytes-by-ble
做法是:
- 发送第一个20字节后,在onCharacteristicWrite接收到发送成功回调,
- 然后在接着发下一个20字节,然后再在onCharacteristicWrite接收到发送成功回调,循环如此直到发完为止。
另外可能和ble设备性能有关,有的ble设备在发送完上次20字节后需要等待几十毫秒(sleep),才能再发。
监听characteristic 的改变
private BluetoothGatt bluetoothGatt; BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic; boolean enabled; ... bluetoothGatt.setCharacteristicNotification(characteristic, enabled); ... BluetoothGattDescriptor descriptor = characteristic.getDescriptor( UUID.fromString(SampleGattAttributes.CLIENT_CHARACTERISTIC_CONFIG)); descriptor.setValue(BluetoothGattDescriptor.ENABLE_NOTIFICATION_VALUE); bluetoothGatt.writeDescriptor(descriptor);
值得注意的是,除了通过 BluetoothGatt#setCharacteristicNotification 开启 Android 端接收通知的开关,
还需要往 Characteristic 的 Descriptor 属性写入开启通知的数据开关使得当硬件的数据改变时,主动往手机发送数据。
之后如果监听的characteristic的值发生改变,就会在BluetoothGattCallback.onCharacteristicChanged(gatt, characteristic)接收到。
断开连接
当我们连接蓝牙设备完成一系列的蓝牙操作之后就可以断开蓝牙设备的连接了。
1. BluetoothGatt#disconnect
通过 BluetoothGatt#disconnect 可以断开正在连接的蓝牙设备。当这一个方法被调用之后,系统会异步回调 BluetoothGattCallback#onConnectionStateChange 方法。通过这个方法的 newState 参数可以判断是连接成功还是断开成功的回调。
2. BluetoothGatt#close
由于 Android 蓝牙连接设备的资源有限,当我们执行断开蓝牙操作之后必须执行 BluetoothGatt#close 方法释放资源。
需要注意的是通过 BluetoothGatt#close 方法也可以执行断开蓝牙的操作,不过 BluetoothGattCallback#onConnectionStateChange 将不会收到任何回调。此时如果执行 BluetoothGatt#connect 方法会得到一个蓝牙 API 的空指针异常。所以,我们推荐的写法是当蓝牙成功连接之后,通过 BluetoothGatt#disconnect 断开蓝牙的连接,紧接着在 BluetoothGattCallback#onConnectionStateChange 执行 BluetoothGatt#close 方法释放资源。
@Override public void onConnectionStateChange(final BluetoothGatt gatt, final int status, final int newState) { Log.d(TAG, "onConnectionStateChange: thread " + Thread.currentThread() + " status " + newState); if (status != BluetoothGatt.GATT_SUCCESS) { String err = "Cannot connect device with error status: " + status; // 当尝试连接失败的时候调用 disconnect 方法是不会引起这个方法回调的,所以这里 // 直接回调就可以了。 gatt.close(); Log.e(TAG, err); return; } if (newState == BluetoothProfile.STATE_CONNECTED) { gatt.discoverService(); } else if (newState == BluetoothProfile.STATE_DISCONNECTED) { gatt.close(); } }
监听蓝牙的状态的改变
你可以监听BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_STATE_CHANGED广播,当系统蓝牙的开关状态发生改变时会通知你,
广播包含两个int数据,
- BluetoothAdapter.EXTRA_STATE:现在的state
- BluetoothAdapter.EXTRA_PREVIOUS_STATE:表示之前的state
state的取值如下:
- BluetoothAdapter.STATE_TURNING_ON
- BluetoothAdapter.STATE_ON
- BluetoothAdapter.STATE_TURNING_OFF
- BluetoothAdapter.STATE_OFF
其他方法
获取已连接的蓝牙设备
直接通过bluetoothManager.getConnectedDevices是获取不到的,通过bluetoothManager.getConnectionState也不行- 通过反射获取,
List<BluetoothDevice> connectedDevices = new ArrayList<>(); Class<BluetoothAdapter> bluetoothAdapterClass = BluetoothAdapter.class;//得到BluetoothAdapter的Class对象 try { // getConnectionState方法是获取设备是否和任何一个蓝牙设备连接 Method method = bluetoothAdapterClass.getDeclaredMethod("getConnectionState", (Class[]) null); method.setAccessible(true); int state = (int) method.invoke(bluetoothAdapter, (Object[]) null); if (state == BluetoothAdapter.STATE_CONNECTED) { Log.i("BLUETOOTH", "BluetoothAdapter.STATE_CONNECTED"); // 已连接的设备肯定已经配对过了,所以从这里直接获取已配对的设备 Set<BluetoothDevice> devices = bluetoothAdapter.getBondedDevices(); for (BluetoothDevice device : devices) { Method isConnectedMethod = BluetoothDevice.class.getDeclaredMethod("isConnected", (Class[]) null); method.setAccessible(true); boolean isConnected = (boolean) isConnectedMethod.invoke(device, (Object[]) null); if (isConnected) { Log.i("BLUETOOTH", "connected:" + device.getName()); connectedDevices.add(device); } } } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
问题
startDiscovery、startScan的区别
android - BluetoothAdapter.startScan() vs BluetoothAdapter.startLeScan() - Stack Overflow
- startDiscovery()用来扫描 传统蓝牙设备,
- startLeScan()用来扫描 低功耗蓝牙设备。
对蓝牙适配器来说,执行设备发现是一个繁重的过程,将消耗大量资源。
Edit:
On LG Nexus 4 with Android 4.4.2 startDiscovery() finds Bluetooth LE devices.
On Samsung Galaxy S3 with Android 4.3 startDiscovery() doesn't find Bluetooth LE devices.
API常见错误码
https://www.cnblogs.com/Free-Thinker/p/11507349.html
android上层api并没有把所有的连接status都给公开(BluetoothGatt中),所以有时会收到api中没有的status,下边是几个可能会遇到的:
- GATT_ERROR 0x85 //133任何不惧名字的错误都出现这个错误码,出现了就认怂吧,重新连接吧。
- GATT_CONN_TIMEOUT 0x08 //8 连接超时,大多数情况是设备离开可连接范围,然后手机端连接超时断开返回此错误码。
- GATT_CONN_TERMINATE_PEER_USER 0x13 //19 连接被对端设备终止,直白点就是手机去连接外围设备,外围设备任性不让连接执行了断开。
- GATT_CONN_TERMINATE_LOCAL_HOST 0x16 //22 连接被本地主机终止,可以解释为手机连接外围设备,但是连接过程中出现一些比如鉴权等问题,无法继续保持连接,主动执行了断开操作。
- GATT_CONN_FAIL_ESTABLISH 03E //62 连接建立失败。
封装好的库
在做功能时顺便也做了个蓝牙工具库的module,之后上传到gayhub上再来更新地址。