Netty服务启动源码
Server启动实例
public class Server {
private int port;
public Server(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public void run() {
NioEventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
NioEventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast("decoder", new StringDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("encoder", new StringEncoder());
pipeline.addLast(new ServerHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture ch = serverBootstrap.bind(port).sync();
ch.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Server(7000).run();
}
}
一、NioEventLoopGroup的创建
首先创建两个NioEventLoopGroup对象
NioEventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
NioEventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
- Boss Group:专门负责接受TCP请求,将请求转交给WorkerGroup;
- Worker Group:获得连接,进行通信,包括读写,编解码等;
EventLoopGroup本质是事件循环线程组;
执行流程
- 创建
NioEventLoopGroup对象
NioEventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
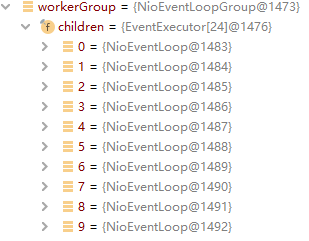
NioEventLoopGroup对象内有一个children数组对象:EventExecutor[] children
每一个EventExecutor都会创建一个NioEventLoop实例;也就是Netty模型中的处理每个连接读写的一个线程;
-
调用无参构造器:线程数为0
最终会调用父类
MultithreadEventLoopGroup的构造器
public NioEventLoopGroup() {
this(0);
}
// 传入线程数,默认Executor为null
public NioEventLoopGroup(int nThreads) {
this(nThreads, (Executor) null);
}
public NioEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor) {
this(nThreads, executor, SelectorProvider.provider());
}
public NioEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor, final SelectorProvider selectorProvider,
final SelectStrategyFactory selectStrategyFactory) {
super(nThreads, executor, selectorProvider, selectStrategyFactory, RejectedExecutionHandlers.reject());
}
-
MultithreadEventLoopGroup的构造器;如果nThreads=0,则赋值默认线程数为
DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS=CPU核数*2
protected MultithreadEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor, Object... args) {
super(nThreads == 0 ? DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS : nThreads, executor, args);
}
// 其中DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS = CPU处理器 * 2
// NettyRuntime.availableProcessors() * 2
static {
DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS = Math.max(1, SystemPropertyUtil.getInt(
"io.netty.eventLoopThreads", NettyRuntime.availableProcessors() * 2));
}
-
继续往下走,会再调用其父类
MultithreadEventExecutorGroup的构造方法:主要是:
(1)执行器
executor的初始化为ThreadPerTaskExecutor(2)
children初始化为线程数的EventExecutor数组:new EventExecutor[nThreads]每一个
children[i]传入一个executor执行器(ThreadPerTaskExecutor)这里每一个
children[i]都是Netty模型中的一个NioEventLoop(3)
chooser选择器:用于选择executor执行器,通过next方法;这里根据线程数是否为2的幂次方,来返回不同的
EventExecutorChooser,如果是2的幂次方,返回
PowerOfTwoEventExecutorChooser,使用&来调用next;(这里类似于HashMap的优化:在2的幂次方下&运算比%运算快)
(在自定义线程数的时候,最好是2的n次方)
如果不是,返回
GenericEventExecutorChooser,使用%来调用next;(4)为
children下的每个EventExecutor注册监听器terminationListener,监听终止事件;(5)最终,创建了
childrenSet本质是LinkedHashSet;将每个EventExecutor(每一个单例线程池)添加进去;
protected MultithreadEventExecutorGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor,
EventExecutorChooserFactory chooserFactory, Object... args) {
if (nThreads <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("nThreads: %d (expected: > 0)", nThreads));
}
// 执行器初始化为ThreadPerTaskExecutor
if (executor == null) {
executor = new ThreadPerTaskExecutor(newDefaultThreadFactory());
}
// 挨个初始化children,不成功shutdown
children = new EventExecutor[nThreads];
for (int i = 0; i < nThreads; i ++) {
boolean success = false;
try {
// 这里真正创建了Netty模型中的NioEventLoop
children[i] = newChild(executor, args);
success = true;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("failed to create a child event loop", e);
} finally {
if (!success) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j ++) {
children[j].shutdownGracefully();
}
for (int j = 0; j < i; j ++) {
EventExecutor e = children[j];
try {
while (!e.isTerminated()) {
e.awaitTermination(Integer.MAX_VALUE, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
} catch (InterruptedException interrupted) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
break;
}
}
}
}
}
// 选择器:根据线程数是否为2的幂次方,来决定next方法的不同
chooser = chooserFactory.newChooser(children);
// 创建监听器
final FutureListener<Object> terminationListener = new FutureListener<Object>() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(Future<Object> future) throws Exception {
if (terminatedChildren.incrementAndGet() == children.length) {
terminationFuture.setSuccess(null);
}
}
};
// 绑定监听器
for (EventExecutor e: children) {
e.terminationFuture().addListener(terminationListener);
}
Set<EventExecutor> childrenSet = new LinkedHashSet<EventExecutor>(children.length);
Collections.addAll(childrenSet, children);
readonlyChildren = Collections.unmodifiableSet(childrenSet);
}
-
单独说一下:
children[i] = newChild(executor, args);此方法最终调用了:NioEventLoop类下的构造函数:
NioEventLoop类就有
selector对象这个属性;在构造函数中,通过
selector = selectorTuple.selector;进行了初始化
// newChild方法,中args参数包含了多个对象
protected EventLoop newChild(Executor executor, Object... args) throws Exception {
return new NioEventLoop(this, executor, (SelectorProvider) args[0],
((SelectStrategyFactory) args[1]).newSelectStrategy(), (RejectedExecutionHandler) args[2]);
}
// 最终调用NioEventLoop构造函数
NioEventLoop(NioEventLoopGroup parent, Executor executor, SelectorProvider selectorProvider,
SelectStrategy strategy, RejectedExecutionHandler rejectedExecutionHandler) {
super(parent, executor, false, DEFAULT_MAX_PENDING_TASKS, rejectedExecutionHandler);
if (selectorProvider == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("selectorProvider");
}
if (strategy == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("selectStrategy");
}
provider = selectorProvider;
final SelectorTuple selectorTuple = openSelector();
// 初始化selector
selector = selectorTuple.selector;
unwrappedSelector = selectorTuple.unwrappedSelector;
selectStrategy = strategy;
}
- 至此,创建
NioEventLoopGroup对象成功;
二、ServerBootstrap的创建配置
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast("decoder", new StringDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("encoder", new StringEncoder());
pipeline.addLast(new ServerHandler());
}
});
这里主要有两个类:ServerBootstrap和其父类AbstractBootstrap,分工不同
- 所有针对
bossGroup的配置由其父类AbstractBootstrap完成; - 所有针对
workerGroup的配置由ServerBootstrap完成;
-
调用
ServerBootstrap的无参构造器,接着调用其父类AbstractBootstrap的无参构造器虽然是空构造器,但是会初始化,此类的多项属性,即下列属性;
private final Map<ChannelOption<?>, Object> childOptions = new LinkedHashMap<ChannelOption<?>, Object>(); private final Map<AttributeKey<?>, Object> childAttrs = new LinkedHashMap<AttributeKey<?>, Object>(); private final ServerBootstrapConfig config = new ServerBootstrapConfig(this); private volatile EventLoopGroup childGroup; private volatile ChannelHandler childHandler;主要初始化完成:
childOptions对象,是一个LinkedHashMap;options就是用来添加各项配置的对象;config对象,本质是ServerBootstrapConfig
public ServerBootstrap() { }
AbstractBootstrap() {}
-
初始化完成
ServerBootstrap后,就可以添加各项配置: -
.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)方法:主要:
(1)调用super在其父类中完成
bossgroup(parentGroup)的初始化(2)在本类中完成
workerGroup(childGroup)初始化
public ServerBootstrap group(EventLoopGroup parentGroup, EventLoopGroup childGroup) {
// 父类进行bossgroup的初始化
super.group(parentGroup);
// 当前类,进行workergroup的初始化
if (childGroup == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("childGroup");
}
if (this.childGroup != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("childGroup set already");
}
this.childGroup = childGroup;
return this;
}
-
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)方法:下面的参数:channelClass即
NioServerSocketChannelAbstractBootstrap父类,通过反射创建了channelFactory是一个ReflectiveChannelFactory实例;
public B channel(Class<? extends C> channelClass) {
if (channelClass == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("channelClass");
}
return channelFactory(new ReflectiveChannelFactory<C>(channelClass));
}
// 将NioServerSocketChannel传入,赋值
public ReflectiveChannelFactory(Class<? extends T> clazz) {
if (clazz == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("clazz");
}
this.clazz = clazz;
}
-
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)由
AbstractBootstrap初始化,主要通过options.put(option, value);完成添加配置;
public <T> B option(ChannelOption<T> option, T value) {
if (option == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("option");
}
if (value == null) {
synchronized (options) {
options.remove(option);
}
} else {
synchronized (options) {
options.put(option, value);
}
}
return self();
}
-
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>(){ })这里简单的,将传入的
ChannelInitializer对象,赋给本类的属性childHandler;
public ServerBootstrap childHandler(ChannelHandler childHandler) {
if (childHandler == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("childHandler");
}
this.childHandler = childHandler;
return this;
}
三、pipeline.addLast方法
pipeline.addLast(new ServerHandler());
向管道中添加自定义的Handler或者编解码器的流程;
流程:
-
通过接口
ChannelPipeline的addLast方法(此接口的注释中,描述了ChannelPipeline内部读写结构)由其实现类
DefaultChannelPipeline来完成;最终会来到一个addLast方法
public final ChannelPipeline addLast(EventExecutorGroup group, String name, ChannelHandler handler) {
// 新创建上下文对象ctx
final AbstractChannelHandlerContext newCtx;
// 同步
synchronized (this) {
checkMultiplicity(handler);
// 实例化ctx,
newCtx = newContext(group, filterName(name, handler), handler);
// 将新建的ctx,插入到pipeline的双向链表中
addLast0(newCtx);
if (!registered) {
newCtx.setAddPending();
callHandlerCallbackLater(newCtx, true);
return this;
}
EventExecutor executor = newCtx.executor();
if (!executor.inEventLoop()) {
newCtx.setAddPending();
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
callHandlerAdded0(newCtx);
}
});
return this;
}
}
callHandlerAdded0(newCtx);
return this;
}
addLast0(newCtx);在双向链表中的,尾部的前一个,插入上面新建的ctx;
private void addLast0(AbstractChannelHandlerContext newCtx) {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext prev = tail.prev;
newCtx.prev = prev;
newCtx.next = tail;
prev.next = newCtx;
tail.prev = newCtx;
}
四、端口绑定serverBootstrap.bind()
ChannelFuture ch = serverBootstrap.bind(port).sync();
最终就是要完成绑定,返回ChannelFuture(异步执行结果)
这个绑定的过程主要是在serverBootstrap的父类AbstractBootstrap内进行完成的;
主要是两个方法:doBind和initAndRegister
serverBootstrap.bind(port)的走向
// 首先调用此方法,将port封装进InetSocketAddress
public ChannelFuture bind(int inetPort) {
return bind(new InetSocketAddress(inetPort));
}
// 然后调用下面的方法,这里SocketAddress是InetSocketAddress的父类,没问题
public ChannelFuture bind(SocketAddress localAddress) {
// 验证方法,主要验证ServerBootstrap是否初始化完成
validate();
if (localAddress == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("localAddress");
}
// 最后调用doBind方法
return doBind(localAddress);
}
doBind方法
private ChannelFuture doBind(final SocketAddress localAddress) {
// 调用本类 initAndRegister方法
// 主要是初始化返回一个 ChannelFuture对象 并 向bossGroup注册
final ChannelFuture regFuture = initAndRegister();
final Channel channel = regFuture.channel();
if (regFuture.cause() != null) {
return regFuture;
}
// regFuture创建完成
if (regFuture.isDone()) {
ChannelPromise promise = channel.newPromise();
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
return promise;
} else {
// 这里是以防万一,regFuture没有创建完成
final PendingRegistrationPromise promise = new PendingRegistrationPromise(channel);
regFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
Throwable cause = future.cause();
if (cause != null) {
promise.setFailure(cause);
} else {
promise.registered();
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
}
}
});
return promise;
}
}
-
initAndRegister方法主要是:完成channel的创建 并 向bossGroup注册
channelFactory.newChannel():完成channel的封装,通过反射将JDK的channel进行封装;ChannelFuture regFuture = config().group().register(channel);上面这一段:
config().group()是拿到bossGroup对象,进行Channel注册;
final ChannelFuture initAndRegister() {
Channel channel = null;
try {
// 创建channel
channel = channelFactory.newChannel();
// 初始化channel
init(channel);
} catch (Throwable t) {
// 如果异常,强制关闭已经创建的channel
if (channel != null) {
channel.unsafe().closeForcibly();
return new DefaultChannelPromise(channel, GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE).setFailure(t);
}
return new DefaultChannelPromise(new FailedChannel(), GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE).setFailure(t);
}
// bossGroup注册channel
ChannelFuture regFuture = config().group().register(channel);
// 如果IO操作失败,也就是返回的cause存在,那么采取措施关闭Channel
if (regFuture.cause() != null) {
if (channel.isRegistered()) {
channel.close();
} else {
channel.unsafe().closeForcibly();
}
}
return regFuture;
}