在“队列”(Queue)这种数据结构中,数据项是先进先出(FIFO:first in first out)。队列的容量可以有限,也可以是无限的。
一、基于数组的Queue实现
一般情况下,对于Queue而言,最核心的操作是:插入队列(enqueue)、移出队列(dequeue)。因为在队列中,插入操作是插入到队列的最后,而移出操作是移出队列的头部元素。因此我们通常会使用两个变量front(队头指针)和rear(队尾指针)记录当前元素的位置。
假设我们有一个容量有限队列,用于存放字母,如下图所示:
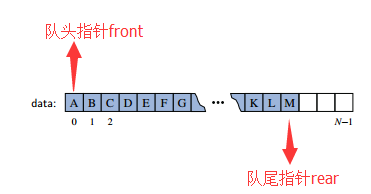
当我们要插入一个元素时,因为总是插入到队列的最尾部,所以插入的位置是rear+1的位置。
当我们要移出一个元素时,是从队头指针front的位置开始移除(因为Queue头部的元素是最先加入进来的,根据FIFO原则,应该最先移除)。当移除一个元素之后,front应该加1,因为移出一个元素之后,下一个元素就变成了第一个元素。例如现在我们移出了5个元素:
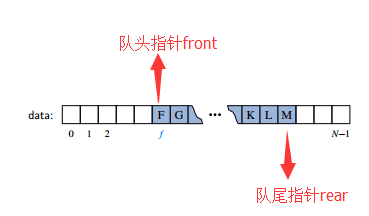
当移出5个元素之后,队头指针就移动到了字母F的位置,前五个位置空下来了。队尾指针rear不变。
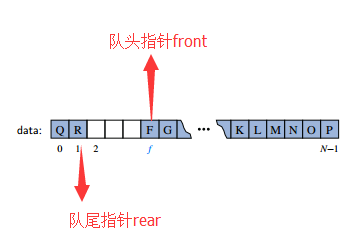
现在问题来了:队列头部移出的几个元素,位置空下来了。当我们添加元素的时候,从队尾开始加,当添加到最后一个位置时,怎么办?不让添加时不合理的,毕竟前几个位置已经空下来了。我们的期望是,当一个位置上的元素被移出之后,这个位置是可以被重复使用的。而我们这里讨论的是有限容量的数据,如果我们还继续添加元素,那么就要往队列头部来添加。
这实际上就涉及到了循环队列的概念。也就是当队尾指针到了数组的最后一个下标时,下一个位置应该就是数组的首部。
因此,当队尾指针指向数组顶端的时候,我们要将队尾指针(rear)重置为-1,此时再加1,就是0,也就是数组顶端例。如我们又添加了5个字母,那么结果应该如下图:
代码实现:
- package com.tianshouzhi.algrithm.queue;
- import java.util.Arrays;
- /**
- * 队列满足的条件是FIFO先进先出,本例是基于数组完成的Queue
- *
- * @author Administrator
- *
- */
- public class ArrayQueue<T> {
- Object[] data = null;
- // 对头指针
- private int front;
- // 队尾指针
- private int rear;
- // 队列中当前的元素
- private int itemNums;
- private int maxSize;
- public ArrayQueue(Integer maxSize) {
- this.maxSize = maxSize;
- data = new Object[maxSize];
- front = 0;
- rear = -1;
- itemNums = 0;
- }
- /**
- * 插入元素:
- * 1、一般情况下,插入操作是在队列不满的情况下,才调用。因此在插入前,应该先调用isFull
- * 2、在队列中插入元素,正常情况下是在队尾指针(rear)+1的位置上插入,因为我们编写的是循环队列
- * 因此,当队尾指针指向数组顶端的时候,我们要将队尾指针(rear)重置为-1,此时再加1,就是0,也就是数组顶端
- * @param element
- */
- public void enqueue(T element) {
- if (isFull()) {
- throw new IllegalStateException("queue is full!");
- }
- needCycle();
- data[++rear] = element;
- itemNums++;
- }
- /**
- * 让队列支持循环的核心代码:
- * 如果rear= maxSize - 1,说明下一个元素因该是的数组的首部,将rear置为-1
- * 因为插入操作是队尾指针rear+1的位置,因此下一个位置就是0,即数组第一个元素下标
- */
- private void needCycle() {
- if (rear == maxSize - 1) {
- rear = -1;
- }
- }
- /**
- * 移除元素,返回队头指针front所指向的数据项的值
- * 正常情况下,在remove之前,应该调用isEmpty,如果为空,则不能输入
- * @return
- */
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
- public T dequeue() {
- if (isEmpty()) {
- throw new IllegalStateException("no elements in the queue");
- }
- T t = (T) data[front];
- data[front]=null;
- front=front+1;
- if (front == maxSize) {
- front = 0;
- }
- itemNums--;
- return t;
- }
- /**
- * 查看队列首部元素,不移除
- *
- * @return
- */
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
- public T peekFront() {
- if (isEmpty()) {
- throw new IllegalStateException("no elements in the queue");
- }
- return (T) data[front];
- }
- public boolean isEmpty() {
- return itemNums == 0;
- }
- public boolean isFull() {
- return itemNums == maxSize;
- }
- public int size() {
- return itemNums;
- }
- public int getMaxSize() {
- return maxSize;
- }
- public void setMaxSize(int maxSize) {
- this.maxSize = maxSize;
- }
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- return "ArrayQueue [container=" + Arrays.toString(data)
- + ", front=" + front + ", rear=" + rear + ", size="
- + itemNums + ", maxSize=" + maxSize + "]";
- }
- }
测试:
- package com.tianshouzhi.algrithm.queue;
- import org.junit.Test;
- /**
- * 本测试演示上述分析插入字母案例,因为A-P共有16个字母。而16个字母插满之后,还有3个空余位置,说明队列大小为19
- * 因此在每个测试方法中,我们都设置队列初始大小为16
- * @author Administrator
- *
- */
- public class ArrayQueueTest {
- private char begin='A';
- private char end='P';
- /**
- * 队列中插入16个元素A-P,观察front、rear指针的位置
- * 一般情况下,插入操作是在队列不满的情况下,才调用。因此在插入前,应该先调用isFull()
- * 如果队列中元素已经满了,就不应该继续插入
- */
- @Test
- public void testInsertA_P() {
- ArrayQueue<Character> queue=new ArrayQueue<Character>(19);
- for (char i = begin; i <= end; i++) {
- if(!queue.isFull()){
- queue.enqueue(i);
- }
- }
- System.out.println(queue);
- }
- /**
- * 测试添加之后,再删除
- */
- @Test
- public void testInsertRemoveInsert() {
- //初始数据,队列中有5个元素
- char current=0;
- ArrayQueue<Character> queue=new ArrayQueue<Character>(19);
- for (char i = begin; i <= end; i++) {
- if(!queue.isFull()){
- queue.enqueue(i);
- current=i;
- }
- }
- System.out.println(queue);
- System.out.println("初始数据: "+queue);
- //移除3个元素
- System.out.println("移除队列首部的5个元素:");
- for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
- if(!queue.isEmpty()){
- queue.dequeue();
- }
- }
- System.out.println(queue);
- System.out.println("添加元素5个元素,数组尾部只剩3个位置,因此有个元素要添加到队列首部:");
- int endChar = current+5;
- for (; current <= endChar; current++) {
- if(!queue.isFull()){
- queue.enqueue(current);
- }
- }
- System.out.println(queue);
- }
- }
二、Java中的Queue
java中定义了一个java.util.Queue接口,定义了如下方法:
- public interface Queue<E> extends Collection<E> {
- //增加一个元索到队尾,如果队列已满,则抛出一个IIIegaISlabEepeplian异常
- boolean add(E e);
- //移除并返回队列头部的元素,如果队列为空,则抛出一个NoSuchElementException异常
- E remove();
- //添加一个元素到队尾,如果队列已满,则返回false
- boolean offer(E e);
- //移除并返问队列头部的元素,如果队列为空,则返回null
- E poll();
- //返回队列头部的元素,如果队列为空,则返回null
- E peek();
- //返回队列头部的元素,如果队列为空,则抛出一个NoSuchElementException异常
- E element();
- }
可以发现这些方法都是两两成对的。
Queue还有一个子接口BlockingQueue,主要定义了一些在并发环境下,方法应该具有特性。
- public interface BlockingQueue<E> extends Queue<E> {
- ...
- //添加一个元素,如果队列满,则阻塞
- void put(E e) throws InterruptedException;
- //移除并返回队列头部的元素,如果队列为空,则阻塞
- E take() throws InterruptedException;
- ...
- }
Java中还提供了一个java.util.Deque双端队列(deque,全名double-ended queue),就是队列中的元素可以从两端弹出,其限定插入和删除操作在表的两端进行。
这个我们就不细说了,因为在实际开发中,Deque远远没有Queue实用。
前面我们讲解的Queue是基于数组实现了,实际上,Queue也可以基于链表(LinkedList)实现,例如添加元素的时候总是调用addFisrt方法,移除元素的时候总是调用removeLast方法,则实现了FIFO的功能,因此链表是可以实现Queue的功能的,这也是我们在前面说链表是除了数组外另一种最广泛应用的基础数据结构的原因。
事实上,java中的LinkedList就实现了Deque接口。
- public class LinkedList<E>
- extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
- implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
因此LinkedList具有Deque和Queue的所有功能。