题目背景
在双人对决的竞技性比赛,如乒乓球、羽毛球、国际象棋中,最常见的赛制是淘汰赛和循环赛。前者的特点是比赛场数少,每场都紧张刺激,但偶然性较高。后者的特点是较为公平,偶然性较低,但比赛过程往往十分冗长。
本题中介绍的瑞士轮赛制,因最早使用于1895年在瑞士举办的国际象棋比赛而得名。它可以看作是淘汰赛与循环赛的折衷,既保证了比赛的稳定性,又能使赛程不至于过长。
题目描述
2*N 名编号为 1~2N 的选手共进行R 轮比赛。每轮比赛开始前,以及所有比赛结束后,都会按照总分从高到低对选手进行一次排名。选手的总分为第一轮开始前的初始分数加上已参加过的所有比赛的得分和。总分相同的,约定编号较小的选手排名靠前。
每轮比赛的对阵安排与该轮比赛开始前的排名有关:第1 名和第2 名、第 3 名和第 4名、……、第2K – 1 名和第 2K名、…… 、第2N – 1 名和第2N名,各进行一场比赛。每场比赛胜者得1 分,负者得 0 分。也就是说除了首轮以外,其它轮比赛的安排均不能事先确定,而是要取决于选手在之前比赛中的表现。
现给定每个选手的初始分数及其实力值,试计算在R 轮比赛过后,排名第 Q 的选手编号是多少。我们假设选手的实力值两两不同,且每场比赛中实力值较高的总能获胜。
输入输出格式
输入格式:
输入文件名为swiss.in 。
输入的第一行是三个正整数N、R 、Q,每两个数之间用一个空格隔开,表示有 2*N 名选手、R 轮比赛,以及我们关心的名次 Q。
第二行是2*N 个非负整数s1, s2, …, s2N,每两个数之间用一个空格隔开,其中 si 表示编号为i 的选手的初始分数。 第三行是2*N 个正整数w1 , w2 , …, w2N,每两个数之间用一个空格隔开,其中 wi 表示编号为i 的选手的实力值。
输出格式:
输出文件名为swiss.out。
输出只有一行,包含一个整数,即R 轮比赛结束后,排名第 Q 的选手的编号。
输入输出样例
2 4 2 7 6 6 7 10 5 20 15
1
说明
【样例解释】
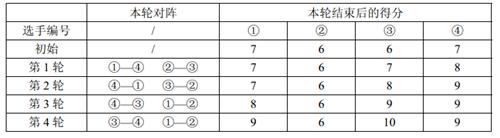
【数据范围】
对于30% 的数据,1 ≤ N ≤ 100;
对于50% 的数据,1 ≤ N ≤ 10,000 ;
对于100%的数据,1 ≤ N ≤ 100,000,1 ≤ R ≤ 50,1 ≤ Q ≤ 2N,0 ≤ s1, s2, …, s2N≤10^8,1 ≤w1, w2 , …, w2N≤ 10^8。
noip2011普及组第3题。
#include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> #define ct register int #define cr register char #define g() getchar() #define N 200005 #define fr(a,b,c,d) for(int a=b;a<=c;a+=d) int in(){ct f=1,x=0;cr c=g(); for(;c<'0'||c>'9';c=g())f=(c=='-')?-1:1; for(;'0'<=c&&c<='9';c=g())x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+(c^48);return x*f;} struct p{int ma,num,ab;}a[N],w[N],l[N]; bool cmp(p xx,p yy){if(xx.ma!=yy.ma)return xx.ma>yy.ma;return xx.num<yy.num;} using namespace std; int main(){ ct n=in(),r=in(),q=in(); fr(i,1,2*n,1)a[i].ma=in(),a[i].num=i;fr(i,1,2*n,1)a[i].ab=in(); sort(a+1,a+1+2*n,cmp); fr(i,1,r,1){ct ww=0,ll=0; fr(j,1,2*n,2) (a[j].ab>a[j+1].ab)?(w[++ww]=a[j],l[++ll]=a[j+1]):(w[++ww]=a[j+1],l[++ll]=a[j]),w[ww].ma++; //this is a ternary operator //it means if:a[i].ab>a[j+1].ab,do the option before ':',or do the option after ':' merge(w+1,w+1+ww,l+1,l+1+ll,a+1,cmp); }printf("%d",a[q].num); } //well this is a good program about the using of merge_sort //maybe someone would like to use sort,but the fact tells us it can be a overtime_solution //how can we make some optimization,well merge_sort is the best_ans //we just need to set two array:win or lose //because the winner_group's order can be ordered ,so can loser_group(we have made a sort before) //the merge_sort's definition is :mix two ordered array into one ordered array //in this case,merge_sort can successfully satisfy the requirement