测试Channelhandler
EmbeddedChannel提供了下面一些方法:
- writeInbound(Object...),写一个消息到入站通道
- writeOutbound(Object...),写消息到出站通道
- readInbound(),从EmbeddedChannel读取入站消息,可能返回null
- readOutbound(),从EmbeddedChannel读取出站消息,可能返回null
- finish(),标示EmbeddedChannel已结束,任何写数据都会失败


@Test public void test1() { ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.buffer(); for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) { buf.writeByte(i); } ByteBuf input = buf.duplicate(); EmbeddedChannel channel = new EmbeddedChannel( new FixedLengthFrameDecoder(3)); // write bytes Assert.assertTrue(channel.writeInbound(input)); Assert.assertTrue(channel.finish()); // read message Assert.assertEquals(buf.readBytes(3), channel.readInbound()); Assert.assertEquals(buf.readBytes(3), channel.readInbound()); Assert.assertEquals(buf.readBytes(3), channel.readInbound()); Assert.assertNull(channel.readInbound()); }
实现
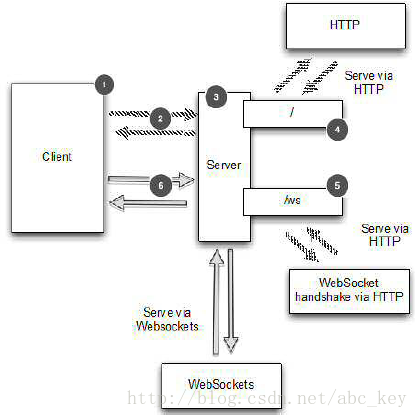
WebSocket使用HTTP升级机制从一个普通的HTTP连接WebSocket,因为这个应用程序使用WebSocket总是开始于HTTP(s),然后再升级。什么时候升级取决于应用程序本身。直接执行升级作为第一个操作一般是使用特定的url请求。
在这里,如果url的结尾以/ws结束,我们将只会升级到WebSocket,否则服务器将发送一个网页给客户端。升级后的连接将通过WebSocket传输所有数据。逻辑图如下: