虽然Logistic回归叫回归,但是其实它是一个二分类或者多分类问题
这里的话我们使用信用诈骗的数据进行分析
第一步:导入数据,Amount的数值较大,后续将进行(-1,1)的归一化
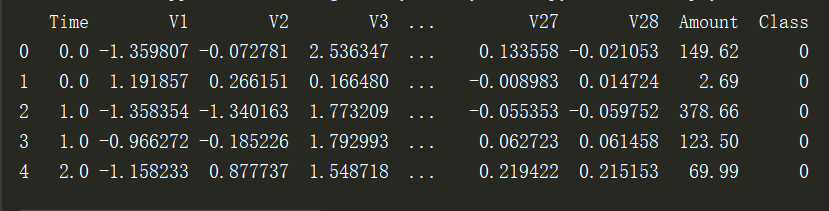
data = pd.read_csv('creditcard.csv') #读取数据 #查看前5行数据 print(data.head())
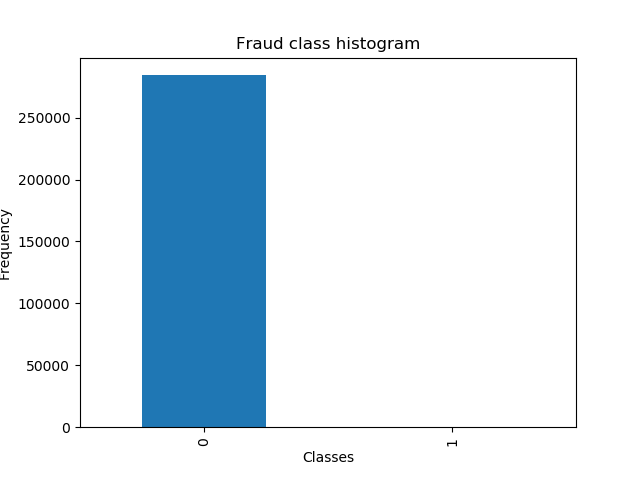
第二步: 对正常和欺诈的数目进行查看,正常样本的数目远大于欺诈样本,这个时候可以使用下采样或者过采样
# 画图查看 count_data = pd.value_counts(data['Class'], sort=True).sort_index() #统计样本数 count_data.plot(kind='bar') #画条形图 plt.title("Fraud class histogram") #标题 plt.xlabel('Classes') plt.ylabel('Frequency') plt.show()
第三步:将amount进行归一化形成amountNorm,并且去除time和amount项
#把amount数据标准化到-1, 1 from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler #reshape 需要转换到的数值范围 data['NormAmount'] = StandardScaler().fit_transform(data['Amount'].values.reshape(-1, 1),) data = data.drop(['Time', 'Amount'], axis=1) # 去除两列 #进行分组 X = data.ix[:, data.columns != 'Class'] y = data.ix[:, data.columns == 'Class']
第四步,使用随机挑选来生成下采样数据
number_record_fraud = len(data[data.Class==1]) #找出其索引,组成数组 fraud_indices = np.array(data[data.Class == 1].index) norm_indices = data[data.Class == 0 ].index #从Class=0中任意挑选500个组成正常的类别 random_norm_indices = np.random.choice(norm_indices, 500, replace=False) random_norm_indices = np.array(random_norm_indices) #把正常的类别和欺诈类别进行组合 under_sample_indices = np.concatenate([fraud_indices, random_norm_indices]) #根据重组索引重新取值 under_sample_datas = data.iloc[under_sample_indices,:] #选择出属性和结果 X_undersample = under_sample_datas.ix[:, under_sample_datas.columns != 'Class']
第5步,交叉验证选择权重,这里采用的加权方法为|L* w|
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression from sklearn.cross_validation import KFold, cross_val_score from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix,recall_score,classification_report def printing_Kfold_socres(x_train_data, y_train_data): fold = KFold(len(y_train_data), 5, shuffle=False) c_param_range = [0.01, 0.1, 1, 10, 100] #创建一个空的列表用来存储Mean recall score的值 results_table = pd.DataFrame(index=range(len(c_param_range), 2), columns=['C_parameter', 'Mean recall score']) results_table['C_parameter'] = c_param_range j = 0 for c_param in c_param_range: print('-----------------------') print('C paramter:', c_param) print('-----------------------') print('') recall_accs = [] for iteration, indices in enumerate(fold, start=1): lr = LogisticRegression(C = c_param, penalty='l1') #放入参数,权重模式为l1 print('indices', indices) #建立模型并训练 lr.fit(x_train_data.iloc[indices[0], :], y_train_data.iloc[indices[0], :].values.ravel()) y_pred_undersample = lr.predict(x_train_data.iloc[indices[1], :].values) print(y_pred_undersample) #计算回归得分 recall_acc = recall_score(y_train_data.iloc[indices[1],:].values, y_pred_undersample) recall_accs.append(recall_acc) print('Iteration', iteration, ': recall score=', recall_acc) #求得平均的值 results_table.ix[j, 'Mean recall score'] = np.mean(recall_accs) j += 1 print('') print('Mean recall score', np.mean(recall_accs)) print('') # 数据类型进行转换 results_table['Mean recall score'] = results_table['Mean recall score'].astype('float64') # 求得Mean recall score 对应的最大的C_parameter值 best_c = results_table.loc[results_table['Mean recall score'].idxmax()]['C_parameter'] print('*********************************************************************************') print('Best model to choose from cross validation is with C parameter = ', best_c) print('*********************************************************************************') return best_c
#执行程序
best_c = printing_Kfold_socres(X_train_undersample, y_train_undersample)