局部组件的使用:
如果实例化对象Vue对象中既有el,又有 template,并且 template 中定义了模板的内容,那么 template 模板的优先级大于el 。
示例代码:
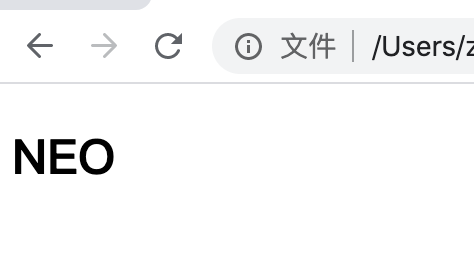
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <!-- 虽然 id="app" 的 div 没有渲染,但是这个标签必须得有,因为 el:"#app" 对它进行了绑定 --> <div id="app"> </div> </body> <script src="./vue.js"></script> <script> // 如果实例化对象Vue对象中既有el,又有 template,并且 template 中定义了模板的内容,那么 template 模板的优先级大于el new Vue({ el: "#app", data(){ return { msg: "NEO" } }, template:` <div> <h2>{{ msg }}</h2> </div> ` // 由于 template 的优先级高于 el, 所以浏览器上会优先渲染 template 中的内容 }) </script> </html>
浏览器效果示例:
组件三步走:
1、 声明子组件
2、 挂载子组件: 在 components 中挂载子组件
3、 使用子组件: 在 html标签中,或 其它子组件的 template 中使用子组件,并且 在template中定义html标签时,一定要用一对闭合标签包裹起来。
示例代码:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <!-- 虽然 id="app" 的 div 没有渲染,但是这个标签必须得有,因为 el:"#app" 对它进行了绑定 --> <div id="app"> </div> </body> <script src="./vue.js"></script> <script> // App 组件: header组件、 aside组件、 content组件 // 1. 声明子组件: Vue中组件的名字首字母要大写(跟标签做区分) let App = { // 声明App组件,其对应的是一个对象,该对象跟 Vue 实例化的时候一样,唯一不同的是没有 el data(){ // 在这个 data 中绑定当前组件()的数据属性 return { myText: "neoneoneo" } }, // 渲染页面的时候, template 中的内容会替换到 <App /> --- 该组件(App)会渲染到页面 template:` <div id="aa"> <h2>{{ myText }}</h2> </div> `, } // 如果实例化对象Vue对象中既有el,又有 template,并且 template 中定义了模板的内容,那么 template 模板的优先级大于el new Vue({ el: "#app", data(){ return { msg: "NEO" } }, // 3. 使用子组件; <App /> 相当于一个自定义标签,你也可以把这个自定义标签定义为Div,为了和 <div> 标签区分,所以自定义的标签首字母要大写 template:` <div id="bb"> <App /> </div> `, // 由于 template 的优先级高于 el, 所以浏览器上会优先渲染 template 中的内容 // 2. 挂载子组件 components:{ App // 等价于 App: App; key 和 value 一样的时候,可以只写一个 key } }) </script> </html>
浏览器效果示例:

局部组件:Vue中没有 template 且 子组件挂载子组件
示例代码:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <!-- 使用子组件 --> <App /> </div> </body> <script src="./vue.js"></script> <script> let Vheader = { data(){ return { } }, // 所有template 中的html内容,都要用一对闭合标签包裹起来,如: <div></div> template:` <div> <h2>HELLO</h2> <h2>WORLD</h2> </div> ` } // 声明子组件 let App = { data(){ return { myText: "neoneoneo" } }, // template 用于定义模板的内容 // 把 Vheader 子组件在下面的template中使用 template:` <div id="aa"> <h2>{{ myText }}</h2> <Vheader /> </div> `, // 挂载子组件 components:{ Vheader } } new Vue({ // 没有 template el: "#app", data(){ return { msg: "NEO" } }, // 2. 挂载子组件 components:{ App // 等价于 App: App; key 和 value 一样的时候,可以只写一个 key } }) </script> </html>
浏览器效果示例:

全局组件:
Vue全局组件用 Vue.component 去声明
示例代码:
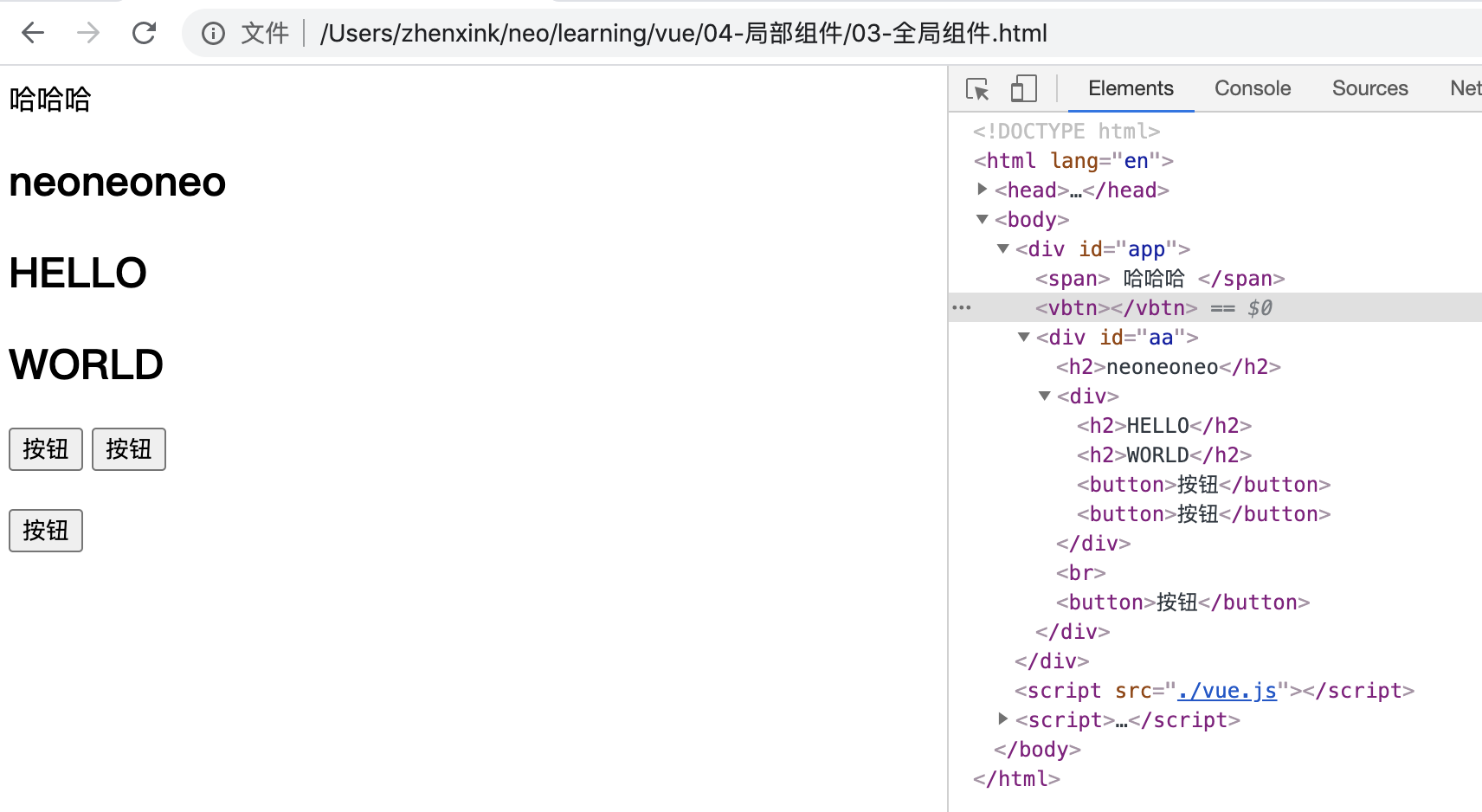
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <App></App> </div> </body> <script src="./vue.js"></script> <script> // 全局组件的注册: Vue.component(),第一个参数是组件的名字,第二个参数 options参数。全局组件可以在全局任意地方使用 Vue.component("VBtn",{ data(){ return { } }, template:`<button>按钮</button>`, }) let Vheader = { data(){ return { } }, // 全局组件使用的时候,,不需要再挂载 template:` <div> <h2>HELLO</h2> <h2>WORLD</h2> <VBtn></VBtn> <VBtn /> </div> ` } let App = { data(){ return { myText: "neoneoneo" } }, // 全局组件使用的时候,,不需要再挂载 template:` <div id="aa"> <h2>{{ myText }}</h2> <Vheader /> <br/> <VBtn /> </div> `, components:{ Vheader } } new Vue({ el: "#app", data(){ return {} }, components:{ App } }) </script> </html>
浏览器效果示例:
slot 组件:
<slot></slot> slot 是Vue 提供的内置组件,它能够分发内容
示例代码:
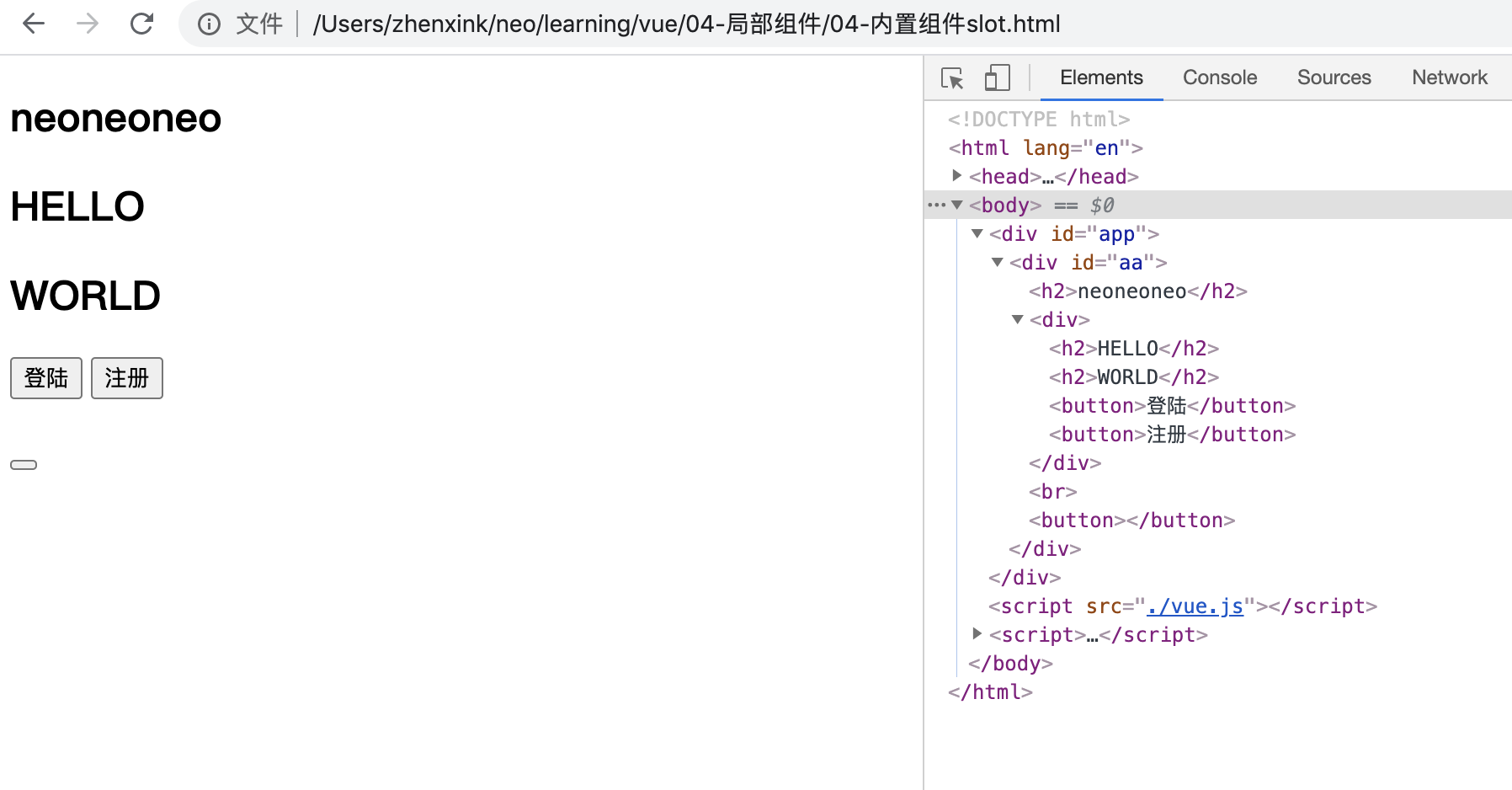
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <App></App> </div> </body> <script src="./vue.js"></script> <script> Vue.component("VBtn",{ data(){ return { } }, // slot 标签是 Vue 的内置组件,<VBtn></VBtn>中的内容能够被分发到 slot 处 template:` <button> <slot></slot> </button> `, }) let Vheader = { data(){ return { } }, // <VBtn></VBtn> 中的“登陆”、“注册”能够被分发到 slot 处 template:` <div> <h2>HELLO</h2> <h2>WORLD</h2> <VBtn>登陆</VBtn> <VBtn>注册</VBtn> </div> ` } let App = { data(){ return { myText: "neoneoneo" } }, template:` <div id="aa"> <h2>{{ myText }}</h2> <Vheader /> <br/> <VBtn /> </div> `, components:{ Vheader } } new Vue({ el: "#app", data(){ return {} }, components:{ App } }) </script> </html>
浏览器效果示例:
父子组件传值:
父组件向子组件传值:
1. 在子组件中使用 props 声明自定义属性,这些自定义属性就可以直接在子组件中任意使用;
2. 父组件中要定义这些属性(步骤1中 props 声明的属性)
示例代码:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> </div> </body> <script src="./vue.js"></script> <script> // 全局组件 VBtn 从 父组件 Vheader 中获取值 Vue.component("VBtn",{ data(){ return { } }, template:` <button> 按钮 {{ btid }} </button> `, props: ['btid'] }) let Vheader = { data() { return { } }, // props 挂载父组件的属性;props 对应的是一个数组; props 中声明的属性就相当于在 data 中绑定了 // mypro 这个属性要在父组件中定义传值 props: ['mypro', 'post'], // 在 template 中可以使用 mypro 这个自定义属性 template: ` <div> <h2>HELLO</h2> <h2>WORLD</h2> <h6>{{ mypro }}</h6> <p>{{ post.title }}</p> <VBtn :btid="post.id"></VBtn> </div> ` } // 声明子组件 let App = { data() { return { myText: "我是父组件App中的数据", child_pro: "要传给子组件的值", post: { id: 1, title: 'My Journey with Vue' } } }, // 父组件要把子组件自定义属性的值传过去,通过 v-bind template: ` <div id="aa"> <h2>{{ myText }}</h2> <Vheader :mypro='child_pro' v-bind:post="post"></Vheader> </div> `, components: { Vheader } } new Vue({ el: "#app", data() { return { msg: "NEO" } }, template: `<App />`, components: { App } }) </script> </html>
浏览器效果示例:

子组件往父组件传值:
触发父组件中自定义声明的事件,需要使用 Vue 提供的内置 $emit 方法
示例代码:
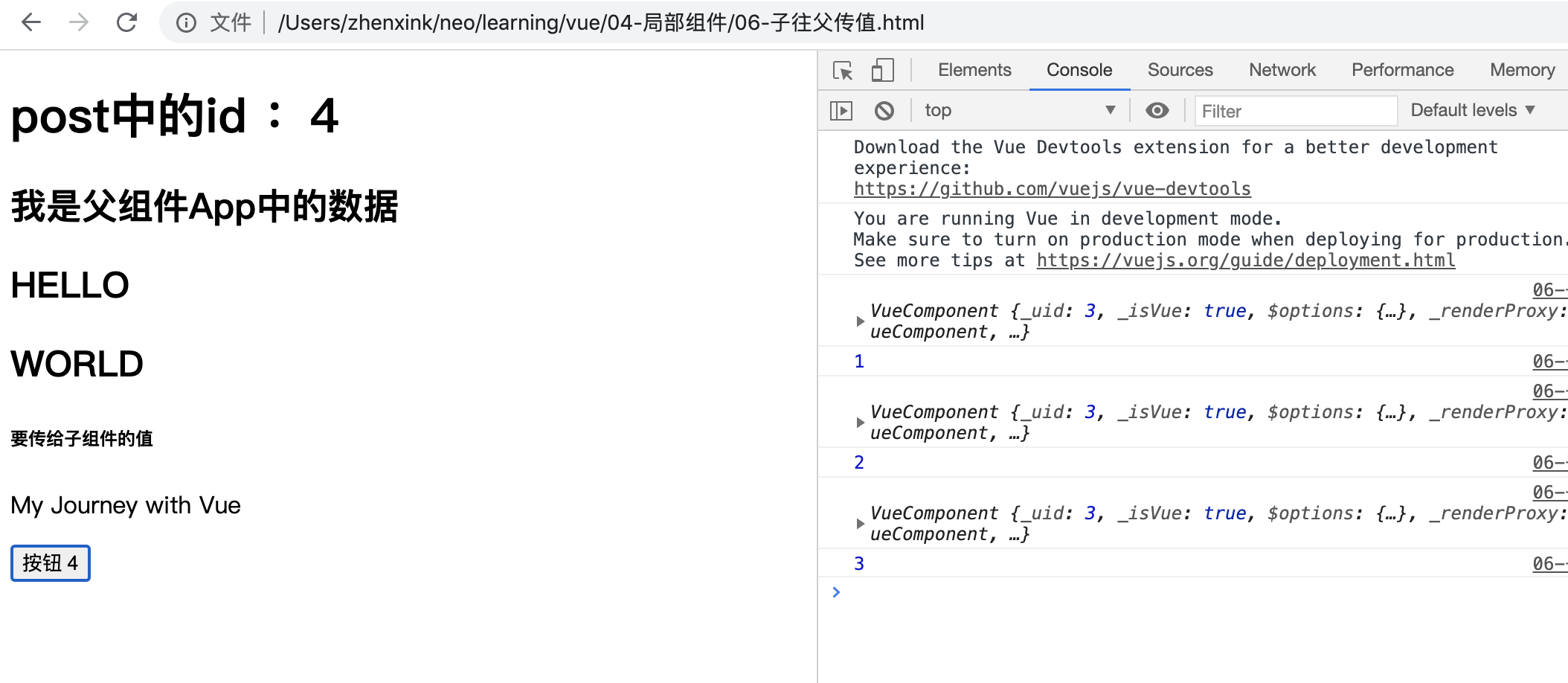
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> </div> </body> <script src="./vue.js"></script> <script> /* 想要实现的效果:点击 VBtn 中的按钮,修改App 中post对象的id值 */ Vue.component("VBtn",{ data(){ return { // 把 父组件传递过来的 btnid 赋值给 bid bid: this.btnid } }, // 给 button 添加一个点击事件 template:` <button @click="vbtnToHeader"> 按钮 {{ bid }} </button> `, // props 中声明的属性,即相当于绑定到了 data 中 props: ['btnid'], // 给button 中的点击事件添加对应的方法 methods: { vbtnToHeader(){ console.log(this) // 每个组件中的 this 都是指该组件对象,即一个 VueComponent 对象 this.bid++; console.log(this.btnid) // $emit 是 Vue 提供的内置方法,用于触发父组件中自定义声明的事件。 this.$emit("父组件中自定义声明的事件", "要传递的值") // vheaderClickHandler 是 VBtn 的父组件 Vheader 中对应的 自定义事件;后面的参数是传递到 vheaderClickHandler 对应的方法中 this.$emit('vheaderClickHandler', this.bid); } } }) let Vheader = { data() { return { } }, props: ['mypro', 'post'], // vheaderClickHandler 是自定义的事件(属性能自定义,事件也能自定义),该自定义事件绑定了一个方法 clickHandler template: ` <div> <h2>HELLO</h2> <h2>WORLD</h2> <h6>{{ mypro }}</h6> <p>{{ post.title }}</p> <VBtn :btnid="post.id" @vheaderClickHandler="clickHandler"></VBtn> </div> `, methods:{ clickHandler(val){ alert(val); // 这个 this 表示 Vheader 当前组件 VueComponent 对象 this.id = val; // 到这一步,就已经实现点击 VBtn 按钮修改按钮中id数据;但此时 post对象中id的值并没有改变;所以, 如果想要修改 post对象中id的值,就要接着往父组件emit // 继续往父组件 emit 来修改 post 中id的值 this.$emit('updatePost', val) } } } let App = { data() { return { myText: "我是父组件App中的数据", child_pro: "要传给子组件的值", post: { id: 1, title: 'My Journey with Vue' } } }, template: ` <div id="aa"> <h1>post中的id :{{ post.id }}</h1> <h2>{{ myText }}</h2> <Vheader :mypro='child_pro' v-bind:post="post" @updatePost="updatePostHandler"></Vheader> </div> `, components: { Vheader }, methods:{ updatePostHandler(val){ this.post.id = val; } } } new Vue({ el: "#app", data() { return { msg: "NEO" } }, template: `<App />`, components: { App } }) </script> </html>
浏览器效果示例:
平行组件传值:
假如 A 组件要向 B组件传值,即 A ==> B,那么接收方B要用 $on 声明事件, 发送方要用 $emit 触发事件。
$on('事件的名字', function(val){}) // val 是要传过来的数据
$emit('A组件中声明的事件名', val) // val 是要传递过去的数据
// $on 和 $emit 这两个方法必须绑定在同一个实例化对象中(bus 对象)
平行组件的这种传值方式,不仅能用于平行组件之间传值,同样也能用于父传子、子传父。
示例代码:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <!-- 使用 App 组件 --> <App /> </div> </body> <script src="./vue.js"></script> <script> // $emit 和 $on 要绑定在同一个实例化对象中;该示例中我们绑定到一个全局变量 Vue 实例 let bus = new Vue(); // 这是一个新的 Vue 对象,和下面的Vue 对象不是同一个内存地址 // Test01 和 Test02 是平行的关系;现在想要实现的效果是点击按钮,就把 Test01 中的数据传递级给 Test02 Vue.component('Test02', { data(){ return { passedData:'' } }, template:` <h2>{{ passedData }}</h2> `, created(){ // 注意:要把 $on 绑定到 bus 上,而不能绑定到 this上; bus.$on('passDataEvent', (val) => { this.passedData = val; console.log(this); // VueComponent /* 注意:$on的第二个参数回调函数,不能用 function(){},要用箭头函数。如果用 function(){},那么函数中的 this 指的是当前对象,即 bus (Vue 对象); 用 箭头函数,this 的指向会发生改变,改为 声明了该对象的上下文,即 Test02 组件。 判断 this 指的是谁,只需要看是谁调用的该函数即可 */ }) } }) Vue.component('Test01', { data(){ return { msg:"我是 Test01 中的数据,我要去Test02" } }, template:` <button @click="passDataHandler">传递</button> `, methods:{ passDataHandler(){ // $emit 绑定到 bus 上;注意:不能绑定到 this 上 bus.$emit('passDataEvent', this.msg); // 第一个参数是 $on 中声明的事件名,第二个参数是要传递的数据 } } }) let Vheader = { data(){ return { } }, template:` <div class="vheader"> <Test01 /> <Test02 /> </div> `, } let App = { data(){ return { } }, template:` <div class="apps"> <Vheader /> </div> `, // 挂载 components:{ Vheader } } new Vue({ el: "#app", data(){ return { } }, // 挂载 App组件 components:{ App } }) </script> </html>
浏览器效果示例:
点击按钮前:
点击按钮后:
